Abstract
Iron-deficiency anemia occurs most commonly in young children due to a low-iron diet and adolescent girls due to menstrual blood loss. However, children with gastrointestinal conditions such as intestinal failure, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and/or other chronic conditions, including chronic kidney disease and heart failure, also commonly have iron deficiency. Many patients with classic iron-deficiency anemia will improve with oral iron therapy. However, in children who have an incomplete response to oral iron, intravenous iron therapy is increasingly being used. Benefits of intravenous iron therapy include a rapid repletion of iron stores in addition to resolution of anemia, less gastrointestinal side effects, and relief for patients and families struggling with long-term iron supplementation. Indications for first-line therapy with intravenous iron in children with chronic conditions have also increased. Four intravenous iron formulations have approved indications in pediatrics, and many are increasingly used off-label in children as well. Here we discuss the indications and appropriate timing of intravenous iron therapy in children with a wide range of underlying etiologies.
Learning Objectives
Identify the clinical indications for intravenous iron therapy in pediatric patients
Select appropriate intravenous iron therapies based on presentation and underlying conditions
Understand the clinical course and laboratory response in patients receiving intravenous iron
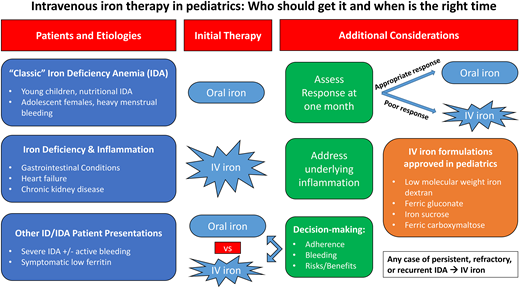
Overview of pediatric iron-deficiency anemia
Globally, iron deficiency remains a major cause of anemia in children. The incidence of pediatric iron deficiency is highest during 2 time periods: infancy and adolescence. In the United States, approximately 2% to 3% of infants and young children have iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) due to a low-iron diet, particularly in those without initiation of appropriate iron supplementation while breastfeeding and in toddlers with excessive cow's milk intake (>24 oz daily). Over 10% of adolescent females are iron deficient postmenarche, particularly in the setting of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB). Prevalence is lower (<1%) in healthy school-aged children and adolescent males. Across all ages, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or other gastrointestinal (GI) illnesses, cardiac disease, and/or other chronic conditions place children at high risk for iron deficiency and iron dysregulation due to chronic inflammation. Unique to pediatric patients are the increased iron requirements to support ongoing growth and development, which results in a higher daily iron requirement compared to adults. While prolonged iron deficiency will cause symptomatic microcytic anemia, iron-deficient children with a normal hemoglobin can exhibit similar symptoms. Risk factors and underlying conditions associated with IDA are listed in Table 1.
Indications for IV iron therapy in pediatrics by etiology
| IDA etiology and affected patient populations . | Indications for IV iron . |
|---|---|
| Nutritional IDA (low-iron diet) | |
| Infants Toddlers Children with restricted diets (vegan, vegetarian) Adolescents with eating disorders | Severe IDA causing hospital admission, hemodynamic compromise, or severe symptoms affecting daily functioning Failed oral iron therapy due to either inability to tolerate (poor taste or GI side effects) or poor adherence History of medication nonadherence or poor follow-up |
| Blood loss | |
| Menstrual (adolescent females with HMB) Gastrointestinal (IBD, other GI tract disease) Other (recurrent epistaxis in patients with bleeding disorders) | Brisk, ongoing, difficult to control bleeding Severe IDA causing hospital admission, hemodynamic compromise, or severe symptoms affecting daily functioning Inability to tolerate oral iron due to GI side effects (patients with IBD) Ongoing IDA secondary to medication nonadherence (adolescents) Recurrent IDA in a patient who previously required IV iron |
| Malabsorption | |
| History of GI surgery/tract alteration (intestinal failure or short gut syndrome) | Absence of duodenum for oral iron absorption |
| GI tract disease (celiac, Helicobacter pylori, atrophic gastritis) | Reduced soluble iron from stomach acid insufficiency |
| Chronic inflammation/disease states | |
| Chronic kidney disease Heart failure Rheumatologic/immunologic diseases | Renal replacement therapy on erythropoiesis-stimulating agents Heart failure with evidence of iron deficiency (to maximize cardiac function) Relative or absolute iron deficiency due to hepcidin activity in the setting of chronic inflammation and inability to correct iron deficiency with oral supplementation alone |
| IDA etiology and affected patient populations . | Indications for IV iron . |
|---|---|
| Nutritional IDA (low-iron diet) | |
| Infants Toddlers Children with restricted diets (vegan, vegetarian) Adolescents with eating disorders | Severe IDA causing hospital admission, hemodynamic compromise, or severe symptoms affecting daily functioning Failed oral iron therapy due to either inability to tolerate (poor taste or GI side effects) or poor adherence History of medication nonadherence or poor follow-up |
| Blood loss | |
| Menstrual (adolescent females with HMB) Gastrointestinal (IBD, other GI tract disease) Other (recurrent epistaxis in patients with bleeding disorders) | Brisk, ongoing, difficult to control bleeding Severe IDA causing hospital admission, hemodynamic compromise, or severe symptoms affecting daily functioning Inability to tolerate oral iron due to GI side effects (patients with IBD) Ongoing IDA secondary to medication nonadherence (adolescents) Recurrent IDA in a patient who previously required IV iron |
| Malabsorption | |
| History of GI surgery/tract alteration (intestinal failure or short gut syndrome) | Absence of duodenum for oral iron absorption |
| GI tract disease (celiac, Helicobacter pylori, atrophic gastritis) | Reduced soluble iron from stomach acid insufficiency |
| Chronic inflammation/disease states | |
| Chronic kidney disease Heart failure Rheumatologic/immunologic diseases | Renal replacement therapy on erythropoiesis-stimulating agents Heart failure with evidence of iron deficiency (to maximize cardiac function) Relative or absolute iron deficiency due to hepcidin activity in the setting of chronic inflammation and inability to correct iron deficiency with oral supplementation alone |
While many children and adolescents with IDA will respond appropriately to oral iron, a number will have an incomplete response or fail to complete a full oral iron course due to intolerance of side effects or nonadherence. Children with persistent or refractory IDA, as well as those with severe or recurrent IDA, are often referred to hematology for ongoing evaluation and management, including consideration of intravenous (IV) iron therapy. Here we review when to consider IV iron and available data on IV iron options in pediatrics.
CLINICAL CASE 1
A 15-year-old female is referred to hematology for evaluation of persistent anemia in the setting of HMB. Laboratory evaluation demonstrates hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dL and ferritin of 4 ng/mL. She was prescribed a ferrous sulfate 325-mg tablet (65 mg elemental iron) once daily for the past 6 months but admits difficulty taking it consistently due to abdominal cramps that develop following tablet ingestion. Menarche was at 11 years of age, and her current menstrual cycles last 7 days and require frequent pad changing during the first 3 days, often accompanied by bleeding onto her clothing and bedsheets at night. She complains of fatigue, which is limiting her participation in sports activities and causing intermittent headaches.
Intravenous iron for classic iron-deficiency anemia
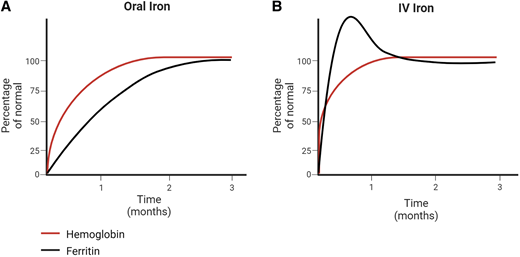
This patient represents a classic clinical scenario of IDA. Ongoing attempts to correct the iron deficiency with an alternative oral iron formulation or dosing regimen after 6 months of oral iron are unlikely to be successful. An appropriate response to oral iron is demonstrated by reticulocytosis within 5 to 7 days followed by an increment in hemoglobin within the first 1 to 2 weeks from initiation (Figure 1). In mild IDA, resolution of the anemia (ie, normalization of the hemoglobin) should occur within 1 month. Children with moderate to severe IDA should have an improvement in the hemoglobin by at least 2 g/dL within a month, although many patients will demonstrate a more robust response with a hemoglobin increment of up to 4 to 5 g/dL within that same time frame. All patients require ongoing iron therapy beyond normalization of the hemoglobin to ensure iron stores are replenished (normalization of serum ferritin). Therefore, in this patient, due to the persistence of anemia well beyond 1 month of therapy, IV iron as a second-line strategy for her persistent IDA should administered.1
Laboratory changes following oral vs intravenous iron therapy. Expected changes in hemoglobin and ferritin in (A) patients with an optimal response to oral iron therapy and (B) patients treated with intravenous iron therapy.
Laboratory changes following oral vs intravenous iron therapy. Expected changes in hemoglobin and ferritin in (A) patients with an optimal response to oral iron therapy and (B) patients treated with intravenous iron therapy.
In any child with moderate to severe IDA and suboptimal response after 1 month of oral iron, IV iron should be strongly considered. For most insurance carriers in the United States, this is also the minimum amount of time required to justify consideration of IV iron in children outside an emergent setting such as the emergency department, during an inpatient admission, or with active, uncontrolled blood loss. Children with mild IDA who cannot complete a course of oral iron or remain iron deficient after normalization of hemoglobin may also be considered for IV iron therapy to mitigate ongoing long-term effects associated with prolonged iron deficiency.
Intravenous iron formulations
Four of the 6 available IV iron formulations in the United States have a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved indication in pediatrics (Table 2). These include low-molecular-weight iron dextran (LMWD), iron sucrose (IS), ferric gluconate (FG), and ferric carboxymaltose (FCM).2-11
Intravenous iron formulations with FDA-approved indications in children
| Formulation . | Approved pediatric indication . | Approved dosing and administration notes* . |
|---|---|---|
| Iron dextran† | Children over 4 months of age | Dose (mL) = 0.0442 (Desired Hgb – Observed Hgb) × LBW + (0.26 × LBW) Requires test dose prior to full therapeutic dose |
| Iron sucrose | Iron maintenance in patients ≥2 years with dialysis-dependent or non-dialysis-dependent CKD receiving erythropoietin therapy | Dose = 0.5 mg/kg, not to exceed 100 mg per dose every 2 weeks (for hemodialysis-dependent patients) or 4 weeks (for non-dialysis-dependent patients on erythropoietin therapy) for 12 weeks |
| Ferric gluconate | Treatment of IDA in pediatric patients ≥6 years undergoing chronic hemodialysis receiving erythropoietin therapy | Dose = 0.12 mL/kg (1.5 mg/kg of elemental iron) administered intravenously over 1 hour during 8 sequential dialysis sessions (maximum 125 mg per dose) |
| Ferric carboxymaltose | Treatment of children aged >1 year with IDA who are intolerant of oral iron or who have unsatisfactory response to oral iron | Patients <50 kg: 15 mg/kg/dose for 2 doses Patients ≥50 kg: 750 mg/dose for 2 doses Separate doses by at least 7 days Alternative dose is 15 mg/kg (maximum 1000 mg) as single infusion Associated with hypophosphatemia |
| Formulation . | Approved pediatric indication . | Approved dosing and administration notes* . |
|---|---|---|
| Iron dextran† | Children over 4 months of age | Dose (mL) = 0.0442 (Desired Hgb – Observed Hgb) × LBW + (0.26 × LBW) Requires test dose prior to full therapeutic dose |
| Iron sucrose | Iron maintenance in patients ≥2 years with dialysis-dependent or non-dialysis-dependent CKD receiving erythropoietin therapy | Dose = 0.5 mg/kg, not to exceed 100 mg per dose every 2 weeks (for hemodialysis-dependent patients) or 4 weeks (for non-dialysis-dependent patients on erythropoietin therapy) for 12 weeks |
| Ferric gluconate | Treatment of IDA in pediatric patients ≥6 years undergoing chronic hemodialysis receiving erythropoietin therapy | Dose = 0.12 mL/kg (1.5 mg/kg of elemental iron) administered intravenously over 1 hour during 8 sequential dialysis sessions (maximum 125 mg per dose) |
| Ferric carboxymaltose | Treatment of children aged >1 year with IDA who are intolerant of oral iron or who have unsatisfactory response to oral iron | Patients <50 kg: 15 mg/kg/dose for 2 doses Patients ≥50 kg: 750 mg/dose for 2 doses Separate doses by at least 7 days Alternative dose is 15 mg/kg (maximum 1000 mg) as single infusion Associated with hypophosphatemia |
See product package insert for additional administration and dosing guidelines.
Large intravenous doses associated with delayed reactions: arthralgias, fever, nausea, and chills 24 to 48 hours after administration.
Hgb, hemoglobin; LBW, lean body weight.
LMWD, the oldest available form of IV iron, is approved for use in children as young as 4 months of age. Approved dosing in pediatrics is 100 mg per infusion. However, several case series in both adults and pediatrics have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of total dose infusions of up to 1000 mg. A case series of 31 pediatric patients with diverse underlying etiologies of IDA, including nutritional IDA and IDA due to HMB, demonstrated good efficacy, although hypersensitivity reactions did occur.3 Another larger series of 191 patients from 2021 demonstrated a hemoglobin increment of 2.1 g/dL and low rate of infusion reactions (4.7%).12 Utilization of premedications should be considered with this formulation, particularly in children with atopic conditions or a history of hypersensitivity.
FG and IS were both approved over 20 years ago for children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Dosing restrictions with FG result in limited utilization outside of children with CKD, for whom frequent infusions can be coupled with hemodialysis sessions.13 Although also approved for children with CKD, the utility of IS has been demonstrated in diverse groups of children, including those with a poor response to oral iron and HMB.6 IS allows for the administration of slightly increased doses compared to FG, although multiple infusions are required in adolescents to achieve the same total dose compared to newer formulations. A case series of 38 patients from 3 months to 18 years of age without CKD demonstrated that it was effective in raising the hemoglobin in all patient groups (median number of 3 infusions per patient). Of the 510 doses given, only 6 adverse events were recorded (5 mild; 1 serious event consisting of facial swelling and hypotension treated with epinephrine).6 Today, IS remains one of the most commonly used IV iron formulations in children.
The FDA approved FCM for the treatment of children 1 year and older with iron deficiency who do not tolerate or have an unsatisfactory response to oral iron.14 As one of the newer- generation IV iron formulations, large doses (15 mg/kg, maximum 750 mg [United States] or 1000 mg [Europe]) can be given in a single infusion over a shorter period of time compared to the older-generation formulations. Pediatric experience with FCM in patients with IDA refractory to oral therapy has demonstrated that patients with a hemoglobin less than 2 g/dL below the normal value for age have resolution of their IDA with 1 dose of FCM.10 This is an advantage of FCM over other IV iron formulations that require multiple doses to resolve IDA.2-4 Twenty-one patients with HMB within a larger cohort of children and adolescents with IDA refractory to oral iron therapy and treated with FCM demonstrated an improvement in median hemoglobin from 8.9 to 12.5, pre- and post-FCM infusion, respectively.10 Patients with moderate to severe anemia (hemoglobin is >2 g/dL below the lower limit for age) and those over 50 kg typically require 2 doses of FCM at least 7 days apart for a full treatment course.10
Two retrospective cohort studies in children refractory to oral iron treated with IV FCM reported no adverse effects experienced in 84% to 92% of patients. Pruritus and urticaria were the most common adverse events.9,10 In pediatric studies, hypophosphatemia occurred in 11.3% to 14% of patients within 4 weeks of FCM administration, although no symptomatic hypophosphatemia was reported.15,16 The typical nadir in phosphorus values occurs 2 weeks after infusion with subsequent improvement. It is recommended that patients with FCM have phosphorus levels monitored to ensure that no supplementation is required. In adults with underlying comorbidities receiving repeated treatment courses of FCM (median 17 infusions), osteomalacia causing fractures and pseudo-fractures has been reported. Switching IV iron formulations resolved the adverse skeletal symptoms in most patients.17 The long-term effect on bone health in children and adolescents receiving a short treatment course of FCM is unclear, although vitamin D deficiency should be identified and treated in those receiving it.
Two additional newer-generation formulations, ferumoxytol and ferric derisomaltose, are FDA approved for utilization in adults but do not have a pediatric indication at this time. One case series of 110 ferumoxytol infusions administered in 54 pediatric patients (median age 11.7 years) with underlying GI conditions and/or as part of a patient blood management program for surgical patients demonstrated an improvement from baseline hemoglobin of 9.2 to 11.5 g/dL and 11.8 g/dL at 1 week and 4 weeks postinfusion.18 Despite tolerance of previous doses, infusion reactions may occur with ferumoxytol upon repeat infusion.19 No pediatric data on ferric derisomaltose are yet available.
Infusion reactions can occur with IV iron therapy, although severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis are rare. Rather than an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction, most reactions to IV iron are likely complement-mediated pseudo-allergic responses triggered by the iron nanoparticles.20 Historically, a test dose has been required for LMWD before full-dose administration. Recent adult studies, however, have demonstrated that the test dose may be omitted for certain patients.21,22 Care should be taken to monitor patients during the initiation of an iron infusion for symptoms of hypersensitivity. Although not a vesicant, painless extravasation into the subcutaneous tissues with any formulation of IV iron can result in skin staining, and families should be counseled about this risk. The intensity and size of staining may be related to the concentration of the formulation (diluted administration with lighter stain) and volume distributed into the subcutaneous tissue. Over time, the iron may be absorbed, lessening the intensity of the stain, but there is no other known treatment, and laser therapy has not been demonstrated to be effective. Preventive measures such as IV placement away from joint spaces (including the antecubital fossa) may decrease the likelihood of extravasation, and patients who report pain around the IV site during an infusion should result in immediate cessation of the infusion to determine if a new IV must be placed.
Laboratory changes following intravenous iron
Hematologic response post-IV iron follows a similar timeline to patients closely adherent to oral iron, with a brisk reticulocytosis at 5 to 7 days followed by increase in hemoglobin. However, most patients receiving IV iron may see a greater improvement (compared to oral) since adherence to ongoing daily supplementation is unnecessary. In contrast to oral iron, wherein iron parameters normalize well after the anemia resolves, changes in iron values occur immediately with the administration of IV iron (Figure 1). Ferritin values may become markedly elevated within the weeks following iron infusions. As infused iron is used for red cell production and stored within other organs, levels trend down and plateau to a new, typically higher baseline value. In adults, observed persistence of very high serum ferritin levels 1 to 2 weeks after IV iron was not associated with any evident clinical consequence.1 One case series of pediatric patients with underlying GI conditions demonstrated a rise in ferritin from 51 to 192 ng/mL at 1 week with trend down to 89 ng/mL at 4 weeks postinfusion.18
Intravenous iron as first-line therapy for severe IDA
Increased efforts promoting patient blood management emphasize consideration of upfront IV iron for individuals who have severe IDA (hemoglobin <7 g/dL). The American Society of Hematology–American Society of Pediatric Hematology Oncology and American Association of Blood Banks Choosing Wisely Campaigns recommend avoiding red cell transfusion in hemodynamically stable individuals with IDA and no active bleeding.23,24 Two adult studies have demonstrated that implementation of an emergency department protocol for FCM infusion reduced red blood cell transfusions, hospital admissions, length of emergency department stay, and overall cost compared to preprotocol implementation.25,26
Although oral iron may be a reasonable option for children and adolescents with severe IDA in the absence of active bleeding, the ability to administer a total dose correction of the iron deficit in a single infusion reduces the disease burden to the patient and family. In patients with severe IDA and active bleeding, upfront administration of IV iron can mitigate prolonged anemia due to oral iron nonadherence, which is commonly seen in adolescence. Young children with severe IDA who have difficulty with oral medications should also be considered for upfront IV iron. Most oral iron formulations are not palatable, and in severe IDA, the risk of serious complications includes heart failure, stroke, and death.27 In all patients with IDA, identification and elimination of the underlying cause is essential. This most commonly includes hormonal supplementation to limit uterine blood loss and increasing dietary iron content (along with limiting milk intake) in young children.
CLINICAL CASE 2
A 12-year-old previously healthy male presents with moderate anemia and progressive weight loss. Initial laboratory stores demonstrate hemoglobin of 7.8 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume of 74, ferritin of 60, transferrin saturation of 10%, and C-reactive protein of 10. Stool occult is negative but subsequent endoscopic studies are consistent with Crohn disease. He is initiated on oral iron as well as immune-modulating therapy but has not yet achieved remission. Repeat laboratory values after 1 month demonstrate no significant change, with a hemoglobin of 7.6 g/dL.
Intravenous iron for children with anemia due to iron deficiency and inflammation
In contrast to classic cases of IDA in otherwise healthy children, those with active inflammation, like this case, benefit from first-line therapy with IV iron. Inflammation results in upregulation of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin, which both limits iron absorption from the duodenum and restricts the utilization of stored body iron. This iron-restricted state limits the effectiveness of oral iron. In contrast, IV iron bypasses the need for absorption and can partially overcome the restrictive effects of hepcidin on iron utilization, particularly at higher doses. Such benefits have been demonstrated in children and adolescents with IBD,28 epidermolysis bullosa,29 and heart failure.30-34 Treatment of the underlying cause of inflammation is key to fully addressing the anemia.
In addition to the limitations of oral iron therapy with ongoing inflammation, children with disorders that affect the GI tract may have reduced absorptive capacity due to either anatomic changes (history of intestinal failure or other bowel surgery) or IBD resulting in inflammation, reduced absorption, and GI blood loss.35 Patients with celiac disease in remission may continue to have inadequate oral iron absorption and may benefit from periodic IV iron.36 Children receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN) are also at risk for iron deficiency due to limitations in the amount of iron compatible within the TPN. In the United States, most TPN has no iron included. The North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Special Interest Group recommends IV iron for both children with intestinal failure and IDA and those with iron deficiency without anemia who cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to enteral supplementation.37
Intravenous iron for symptomatic low ferritin
Increasingly, children with symptomatic fatigue, restless legs syndrome, and other neurologic and sleep conditions with low ferritin in the absence of anemia are referred to hematology for consideration of IV iron. Data in these patient populations are limited, and variable target ferritin thresholds can further complicate management. A meta-analysis published in 2022 demonstrated that IV iron reduced fatigue scores in women with iron deficiency (defined as serum ferritin <100 ng/mL).38 Most studies of adult women with fatigue and low ferritin have demonstrated greatest improvement of fatigue scores post-IV iron in the setting of confirmed iron deficiency (<20 ng/mL) with variable response when ferritin values are between 20 and 50 ng/mL.39,40 One small prospective study in adolescent girls with fatigue demonstrated improved fatigue scores after a course of IS.41 The role of IV iron in endurance athletes is unclear at this time. Benefits have been demonstrated in athletes with confirmed iron deficiency,42 and in distance runners without iron deficiency, IV iron may improve perceived fatigue and mood.43 Yet, compared to oral iron supplementation, IV iron has not demonstrated superiority in improving oxygen transport capacity or erythropoietic response.44 Due to the lack of strong evidence yet potential benefit, a shared decision-making approach that reviews the risks and benefits of iron therapy (both oral and IV) with patients and families is recommended.
Summary
IV iron therapy can be considered in a wide variety of pediatric patients. Patients with classic IDA should receive a trial of oral iron, but a poor initial response (as early as 4 weeks) may prompt consideration of IV iron therapy. Patients with persistent, refractory, or recurrent IDA should be treated with IV iron. Children with concomitant inflammatory diseases should be treated with IV iron to overcome the restricting effects of hepcidin. All patients and families should be appropriately counseled on the indications, benefits, and risks of IV iron, and in the context of limited data, a shared decision-making approach is advised.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Clay T. Cohen: no competing financial interests to declare.
Jacquelyn M. Powers: discloses consultancy for Pharmacosmos, LLC.
Off-label drug use
Clay T. Cohen: Off-label use of IV iron in pediatrics is discussed.
Jacquelyn M. Powers: Off-label use of IV iron in pediatrics is discussed.