Abstract
A consumptive coagulopathy describes a situation where there is a loss of hemostatic factors, which leads to an increased risk of bleeding. Some recent studies have used the term interchangeably with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), but we have reverted to the older definition, which covers a broader range of issues where there is loss of hemostatic factors due to multiple causes, which includes systemic activation of coagulation as seen in DIC. Therefore, the term consumptive coagulopathy covers conditions from the hemostatic effects of major hemorrhage to the use of extracorporeal circuits to true DIC. We review the current understanding of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of common consumptive coagulopathy in critical care patients, focusing on recent advances and controversies. Particular emphasis is given to DIC because it is a common and often life-threatening condition in critical care patients and is characterized by the simultaneous occurrence of widespread microvascular thrombosis and bleeding. Second, we focus on the effect of modern medical technology, such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, on hemostasis.
Learning Objectives
To describe the causes and multiple mechanisms contributing to developing consumptive coagulopathy in critical care patients
To describe the management of consumptive coagulopathies in critically ill patients and consider the potential role of emerging therapies
Introduction
A coagulopathy is a derangement of hemostasis that can result in excessive bleeding and/or thrombosis. A consumptive coagulopathy describes a situation with a loss of hemostatic factors so that a patient is at increased risk of bleeding.1 Recently, this term has become synonymous with the term disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). We disagree with this development and have returned to the old definition where a consumptive coagulopathy covers the loss of hemostatic factors due to any cause, not just the uncontrolled activation of coagulation factors seen in DIC. Therefore, it includes patients who have had significant bleeding and/or those using an extracorporeal circuit.
Making a diagnosis of consumptive coagulopathy is a clinicopathologic diagnosis; it requires a clinical evaluation of the patient. We will explore the pathogenesis and management of the common consumptive coagulopathies in critical care through a clinical case. The laboratory changes of common coagulopathies seen in critical care are summarized in Table 1, and the causes of thrombocytopenia are in Table 2.
Laboratory findings in the coagulopathies of critical care
| Condition . | PT . | aPPT . | Fibrinogen levels . | D-dimer . | Bleeding time . | Platelet count . | Film comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver failure, early | Prolonged | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | |
| Liver failure, end stage | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Increased | Prolonged | Decreased | |
| Uremia | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Prolonged | Unaffected | |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Increased | Prolonged | Decreased | Fragmented red cells |
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Prolonged | Very low | Fragmented red cells |
| Hyperfibrinolysis | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Very high | Possibly prolonged | Unaffected |
| Condition . | PT . | aPPT . | Fibrinogen levels . | D-dimer . | Bleeding time . | Platelet count . | Film comments . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver failure, early | Prolonged | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | |
| Liver failure, end stage | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Increased | Prolonged | Decreased | |
| Uremia | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Prolonged | Unaffected | |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Increased | Prolonged | Decreased | Fragmented red cells |
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Unaffected | Prolonged | Very low | Fragmented red cells |
| Hyperfibrinolysis | Prolonged | Prolonged | Low | Very high | Possibly prolonged | Unaffected |
The differential diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in critical care
| First rule out pseudothrombocytopenia . |
|---|
| • Clotted blood sample • EDTA-dependent antibodies (collect CBC in anticoagulant such as citrate) • Review medications especially ○ Heparins, including heparin-associated thrombocytopenia ○ IIb/IIIa inhibitors (abciximab, eptifibatide, tirofiban) ○ Adenosine diphosphate receptor antagonists (clopidogrel) ○ Acute alcohol toxicity |
| Rule out hematinic deficiency, particularly acute vitamin B12 deficiency which has recently been associated with nitrous oxide abuse . |
| Investigation for the consumption of platelets: . |
| • Sepsis • Major blood loss • Mechanical fragmentation ○ Post–cardiopulmonary bypass ○ Intra-aortic balloon pump ○ Renal dialysis ○ ECMO • Immune mediated ○ Immune thrombocytopenic purpura ○ Antiphospholipid syndrome ○ Posttransfusion purpura • With a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ○ Disseminated intravascular coagulation ○ Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura ○ Hemolytic uremic syndrome • Hypersplenism • Other ○ Myelodysplastic syndrome ○ Malignancy ○ Hereditary thrombocytopenia |
| First rule out pseudothrombocytopenia . |
|---|
| • Clotted blood sample • EDTA-dependent antibodies (collect CBC in anticoagulant such as citrate) • Review medications especially ○ Heparins, including heparin-associated thrombocytopenia ○ IIb/IIIa inhibitors (abciximab, eptifibatide, tirofiban) ○ Adenosine diphosphate receptor antagonists (clopidogrel) ○ Acute alcohol toxicity |
| Rule out hematinic deficiency, particularly acute vitamin B12 deficiency which has recently been associated with nitrous oxide abuse . |
| Investigation for the consumption of platelets: . |
| • Sepsis • Major blood loss • Mechanical fragmentation ○ Post–cardiopulmonary bypass ○ Intra-aortic balloon pump ○ Renal dialysis ○ ECMO • Immune mediated ○ Immune thrombocytopenic purpura ○ Antiphospholipid syndrome ○ Posttransfusion purpura • With a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ○ Disseminated intravascular coagulation ○ Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura ○ Hemolytic uremic syndrome • Hypersplenism • Other ○ Myelodysplastic syndrome ○ Malignancy ○ Hereditary thrombocytopenia |
CBC, complete blood count.
CLINICAL CASE
A 28-year-old man presented to our hospital after a short history of flu-like symptoms and increasing shortness of breath. His electrocardiogram showed atrial tachycardia with a heart rate of 150 bpm. The chest radiograph showed widespread bilateral pulmonary infiltrates. He was hypoxemic (P/F ratio <140/normal >400, <300 indicates acute respiratory failure; the P/F ratio is the ratio of the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) divided by the fraction of inspired oxygen), shocked with a high lactate (8.9 mmol/L/normal <1.5 mmol), oliguric with acute kidney injury, and thrombocytopenic (platelets, 83 × 109/L). The aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was raised at 2600 IU with an activated partial thromboplastin time (aPPT) of 46 seconds. A transthoracic echocardiogram showed reduced biventricular function. A respiratory virus panel was positive for influenza B; latterly, he was confirmed to have coinfection with a toxin-producing group A streptococcus. He was treated with oseltamivir and benzylpenicillin. He was placed on venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for severe respiratory failure. A pan-body computed tomography scan immediately postcannulation confirmed almost complete consolidation/opacification of both lungs, satisfactory cannula placement, and a subsegmental pulmonary embolism in the left lower lobe of the lung. He was placed on high-dose renal replacement therapy (35 mL/kg/h). Three hours after cannulation, there was ongoing, continuous ooze of blood at the cannulation sites, and repeat bloods showed the platelet count had fallen to 28 × 109/L, prothrombin time (PT) ratio of 1.8, aPTT of 65 seconds, fibrinogen of 1.6 g/L, and anti-Xa of 0.6 (target range, 0.3-0.5 IU/mL). He was not bleeding but was given a pool of platelets to increment his platelet count to >50 × 109/L according to our local protocol for venovenous ECMO, and his unfractionated heparin infusion was held until the anti-Xa level was <0.5 IU/mL.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Patients with DIC may present with bleeding, thrombosis, or a combination of both.2 Our patient had DIC secondary to overwhelming sepsis and presented with multiple-organ failure. The diagnosis of DIC is based on clinical suspicion, laboratory findings, and the exclusion of other causes of coagulopathy. The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis scoring system includes platelet count, fibrinogen level, PT, and D-dimer levels.3 A score of 5 or higher is consistent with overt DIC. DIC is characterized by widespread coagulation system activation, resulting in intravascular thrombosis in small vessels and critical organ dysfunction. Hemorrhage occurs due to the loss of hemostatic factors.3,4 DIC is a complication of many medical conditions, including sepsis, trauma, malignancy, and obstetric complications, but sepsis is the most usual cause within critical care, present in around 30% of cases of severe sepsis. All classes of infectious organisms can cause DIC.
Severe infection induces a complex interplay between the innate immune system, inflammation, endothelial activation, and coagulation.3 Coagulation is primarily driven by proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor–α and interleukin 1, promoting tissue factor expression on monocytes. Endothelial activation results in increased permeability and a switch from an anticoagulant to a prothrombotic phenotype.2,5 Procoagulant microparticles are released, leading to further coagulation activation.4 Increased levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibits tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and thus contributes to the accumulation of microvascular thrombosis.4
The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in DIC
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are a complex web of DNA, nucleosomes, histones, and neutrophil-derived granular proteins ejected from activated neutrophils.2,5-7 They ensnare and neutralize pathogens, preventing their dissemination away from the origin of the infection.8 During sepsis, the overproduction of NETs and/or the inability to clear them can instigate a vicious cycle of coagulation and inflammation.7 NETs stimulate coagulation by binding to prothrombin fragment 1 (F1) and fragment 2 (F2) specifically to facilitate FXa cleavage of prothrombin to release active thrombin, unlike FVa, which requires phospholipid surfaces to anchor the classical prothrombinase complex (DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019002973). NETs also stimulate platelets and inactivate tissue factor pathway inhibitor.2,5 Simultaneously, histones and other NET-associated proteins inflict direct cytotoxic damage on endothelial cells.9 This endothelial damage fuels the inflammatory response, exacerbating the coagulopathy. Thrombin can also induce NETosis, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and coagulation,10 leading to the rapid progression of DIC. Our new understanding of NETs makes them a future therapeutic target. Potential options include the following:
DNase therapy: DNase is capable of degrading DNA and could potentially dismantle NETs.
Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase inhibitors: Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase are critical NET components that can propagate inflammation and thrombosis.
PAD4 inhibitors: PAD4 mediates histone citrullination, which is crucial for NET formation. PAD4 inhibitors decrease NET-associated thrombosis in murine models.11
Non-anticoagulant heparin: Non-anticoagulant forms of heparin bind to histones and can reduce histone-mediated cytotoxicity without increasing the risk of bleeding in a murine model of sepsis.12
However, caution is required given the vital role of NETs in innate immunity, and great care will be required in designing trials to prevent harm.
Management of disseminated intravascular coagulation
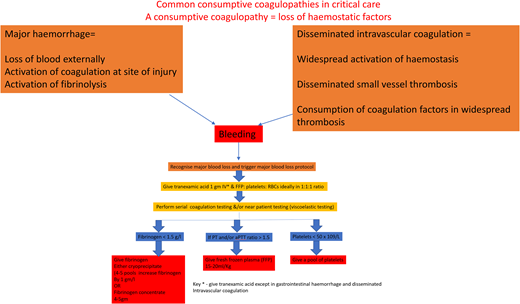
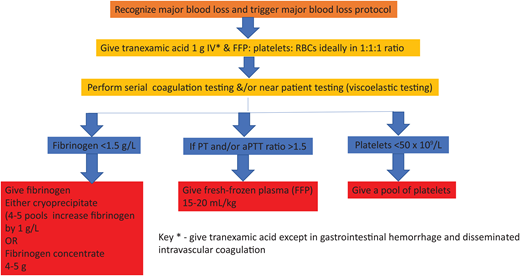
The cornerstone of managing DIC is the early and aggressive treatment of the underlying condition, such as administering antibiotics for sepsis, as in our case outlined above.3,4,13 Supportive measures, including fluid resuscitation, blood product transfusion, and organ support, play a crucial role. Algorithm-led transfusion of platelets, fresh-frozen plasma (FFP), and cryoprecipitate are indicated in patients with significant bleeding or at high risk for bleeding due to invasive procedures (see the suggested algorithm in Figure 1, but note not to use tranexamic acid; fibrinolysis is required to break down established thrombi during recovery). However, the optimal thresholds for transfusion and the use of prophylactic transfusion in nonbleeding patients remain controversial due to the lack of clinical trials.4
Suggested simple algorithm for the hemostatic management of major bleeding.
Suggested simple algorithm for the hemostatic management of major bleeding.
Trials of pharmacologic doses of the physiologic anticoagulants antithrombin, protein C, and activated protein C in sepsis have not been shown to improve clinical outcomes and caused bleeding.14,11 There have been years of ongoing interest in using low doses of heparin to “switch off” the prothrombotic drive from tissue factor. There is, however, minimal evidence supporting the routine use of heparin in acute DIC, and further research is needed. We would consider, however, using thromboprophylactic dose heparins in selected patients with thrombotic phenotypes of DIC, particularly in sepsis or malignancy.15
Recovery from the widespread microvascular thrombosis that is characteristic of DIC is dependent on breakdown by endogenous fibrinolysis. We recommend that antifibrinolytic drugs are not used in DIC because they will inhibit endogenous fibrinolysis and therefore recovery.
The prognosis of DIC is mainly dependent on the cause, the severity of the coagulopathy, and the presence of associated organ dysfunction,4 and the mortality rates in patients with DIC are high, ranging from 20% to 50%.15 Factors associated with poor outcomes in DIC include advanced age, high Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scores, and the presence of multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)
Twelve hours after cannulation, the patient's oxygenation had improved, but there was no improvement in the lactate, and he remained profoundly shocked on high doses of vasopressors. Coagulation testing showed a PT ratio of 1.4, aPTT of 52 seconds, fibrinogen of 2.0 g/L, and platelets of 58 × 109/L. An echocardiogram showed that the left ventricular function had deteriorated even further. Therefore, the patient was placed on peripheral venoarterial venous ECMO. Within an hour, however, the left ventricular function had deteriorated to such an extent that the aortic valve was no longer opening. A cardiac Impella was inserted to vent the left ventricle. There was a progressive improvement in organ perfusion, and after that, the inotropes and vasopressors were weaned. The management of the Impella was complicated by significant bleeding from the insertion site in the left groin. His hemoglobin fell to 62 g/L, platelets were 22 × 109/L, PT ratio was 2.1, aPPT ratio was 1.9, and fibrinogen was 0.8 g/L. He was resuscitated with intravenous fluids and transfusion with packed red cells, a pool of platelets, 2 pools of cryoprecipitate, and FFP at an approximate dose of 20 mL/kg. Repeated coagulation testing showed prolonged aPTT and PT ratios >1.5 and fibrinogen <1.5 g/L, so further FFP and cryoprecipitate were given.
Our patient had established DIC secondary to sepsis exacerbated by severe cardiac failure and renal and hepatic dysfunction.
The contribution of liver failure to coagulopathy
Liver failure results in reduced synthesis of coagulation factors and physiologic anticoagulants,1 but there is a balanced reduction so that while the PT and aPTT may be prolonged, the levels of coagulation factors will be the same as the physiologic anticoagulants: indeed, thrombin generation is preserved.16 Thrombocytopenia occurs due to splenic sequestration and reduced thrombopoietin production. Last, the failure to clear t-PA results in higher plasma levels, increasing the fibrinolytic potential. Liver failure and DIC produce similar laboratory coagulation changes (see Table 1), emphasizing that any patient with these changing needs clinical review. A history of cirrhosis, excess alcohol consumption, and/or ascites points more toward liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is “relatively” stable in liver disease, and D-dimers are only modestly elevated compared to DIC.17
We recommend that critically ill patients receive vitamin K to aid liver synthesis of vitamin K–dependent coagulation factors; usually adequate amounts are present in intravenous and intragastric feeding. If a patient is not being fed, then vitamin K can be given intravenously.
Warkentin and Ning have recently developed an interesting hypothesis as to why some patients with DIC develop a symmetrical peripheral gangrene.18 They describe that these patients always have severe shock, DIC, and usually acute ischemia of the liver (shock liver), the latter being the cause of physiologic anticoagulant depletion. The time course of symmetrical peripheral gangrene is usually a few days after the start of shock, in keeping with critical depletion of protein C (plasma t1/2 8 hours) and antithrombin (plasma t1/2 of 20 hours). Other risk factors are chronic liver disease and possible transfusion of colloids such as intravenous IgG and albumin. As yet, there are no detailed studies of protein C and antithrombin in this patient group. Warkentin and Ning suggest that treatment would be to replete physiologic anticoagulants by giving plasma or using plasma exchange.18
The contribution of renal failure to coagulopathy
Up to 30% of patients in critical care have acute renal failure,19,20 and this brings an increased risk of bleeding, thrombosis, and mortality.21 The “hemostatic” lesion is multifactorial and encompasses platelet dysfunction, increased levels of coagulation factors, and impaired fibrinolysis due to increased levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and anemia. Uremic toxins impair platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation. Reduced clearance of von Willebrand factor, factor VIII, and fibrinogen and simultaneously reduced synthesis of the physiologic anticoagulants protein C, protein S, and antithrombin are present. Anemia is associated with loss of axial flow, so there is diminished platelet– vessel wall interaction and, thus, a prolonged bleeding time. Recently, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) has been shown to be an independent predictor of hypercoagulability and platelet dysfunction.22
The hemostatic effects of extracorporeal circuits
Extracorporeal circuits are vital for short-term use in cardiac surgery and hemodialysis or for prolonged life-sustaining periods when ECMO is used. The surfaces of the circuit activate coagulation, and there is a particular fall of levels of plasma fibrinogen, which rapidly binds to and coats the surfaces. Additionally, the mechanical forces from the ECMO pump and the inflexible shape of the circuit result in areas of high sheer stress, which induce the fragmentation of red cells, platelets, and large molecules such as high-molecular-weight von Willebrand's multimers.23 The latter leads to an acquired von Willebrand syndrome. Management of anticoagulation with extracorporeal circuits is covered in Table 3.
Management of anticoagulation and bleeding with extracorporeal circuits
| Prior to commencing anticoagulation in ECMO measure . | Range . | Result . |
|---|---|---|
| • Hemoglobin | <70 g/L | Y/N |
| • Platelet count | >50 × 109/L | Y/N |
| • PT/INR | PT/INR <2.0 | Y/N |
| • aPTTr | aPTTr <2.0 | Y/N |
| • Anti-Xa level | Anti-Xa level <0.7 | Y/N |
| • Fibrinogen | >1 g/L | Y/N |
| • Triglycerides | <400 mg/dL | Y/N |
| • Bilirubin | <6 mg/dL | Y/N |
| • Active bleeding | Y/N | |
| • No CVA within last 4 weeks | Y/N | |
| Only commence anticoagulation if all the above answers are Y . | ||
| • If platelets <50 × 109/L, transfuse 1 pool of platelets and recheck • If INR >2 or aPTTr >2, transfuse 15 mL/kg FFP • If fibrinogen <1 g/L, transfuse 15 mL/kg | ||
| Starting dose of UFH 18 IU/kg/h using adjusted body weight . | ||
| • If total body weight is less than adjusted body weight, use the patient's ACTUAL weight • Dose is capped at 100 kg | ||
| Once 2 consecutive anti-Xa levels are within the therapeutic range, without a pause/interruption to the infusion or a dose adjustment being required, anti-Xa monitoring can be reduced to once daily. | ||
| Target anti-Xa 0.3 to 0.5 . | ||
| Daily bloods . | Range . | . |
| • Hemoglobin | <70 g/L | • Maintain hemoglobin >70 |
| • Platelet count | >50 × 109/L | • Maintain platelets >50 |
| • INR | INR <2.0 | |
| • aPTTr | aPTTr <2.0 | |
| • Anti-Xa level | Anti-Xa level <0.7 | • If >0.7, hold UFH infusion |
| • Fibrinogen | >1 g/L | • Maintain >1 g/L |
| • Triglycerides | <400 mg/dL | • Review sedation |
| • Bilirubin | <6 mg/dL | • Hemolysis screen |
| If anti-Xa in range and aPTTr <2, no change to anticoagulation | ||
| If anti-Xa in range and aPTTr >2, investigate for DIC, ensure fibrinogen >1 | ||
| Prior to commencing anticoagulation in ECMO measure . | Range . | Result . |
|---|---|---|
| • Hemoglobin | <70 g/L | Y/N |
| • Platelet count | >50 × 109/L | Y/N |
| • PT/INR | PT/INR <2.0 | Y/N |
| • aPTTr | aPTTr <2.0 | Y/N |
| • Anti-Xa level | Anti-Xa level <0.7 | Y/N |
| • Fibrinogen | >1 g/L | Y/N |
| • Triglycerides | <400 mg/dL | Y/N |
| • Bilirubin | <6 mg/dL | Y/N |
| • Active bleeding | Y/N | |
| • No CVA within last 4 weeks | Y/N | |
| Only commence anticoagulation if all the above answers are Y . | ||
| • If platelets <50 × 109/L, transfuse 1 pool of platelets and recheck • If INR >2 or aPTTr >2, transfuse 15 mL/kg FFP • If fibrinogen <1 g/L, transfuse 15 mL/kg | ||
| Starting dose of UFH 18 IU/kg/h using adjusted body weight . | ||
| • If total body weight is less than adjusted body weight, use the patient's ACTUAL weight • Dose is capped at 100 kg | ||
| Once 2 consecutive anti-Xa levels are within the therapeutic range, without a pause/interruption to the infusion or a dose adjustment being required, anti-Xa monitoring can be reduced to once daily. | ||
| Target anti-Xa 0.3 to 0.5 . | ||
| Daily bloods . | Range . | . |
| • Hemoglobin | <70 g/L | • Maintain hemoglobin >70 |
| • Platelet count | >50 × 109/L | • Maintain platelets >50 |
| • INR | INR <2.0 | |
| • aPTTr | aPTTr <2.0 | |
| • Anti-Xa level | Anti-Xa level <0.7 | • If >0.7, hold UFH infusion |
| • Fibrinogen | >1 g/L | • Maintain >1 g/L |
| • Triglycerides | <400 mg/dL | • Review sedation |
| • Bilirubin | <6 mg/dL | • Hemolysis screen |
| If anti-Xa in range and aPTTr <2, no change to anticoagulation | ||
| If anti-Xa in range and aPTTr >2, investigate for DIC, ensure fibrinogen >1 | ||
aPTTr, activated partial thromboplastin time ratio; CVA, cerebral vascular accident; INR, international normalised ratio; UFH, unfractionated heparin.
CLINICAL CASE (continued)4
The patient remained critically ill, but his peripheral perfusion and coagulation improved (PT ratio 1.2, aPTT 50 seconds, fibrinogen 2.5 f/L, platelets 51 × 109/L) after removing the Impella. He was weaned from ventilation, and the arterial cannula was removed. He was fully liberated from ECMO on day 9 of admission. The patient's course is summarized in Table 4.
Summary of the clinical case
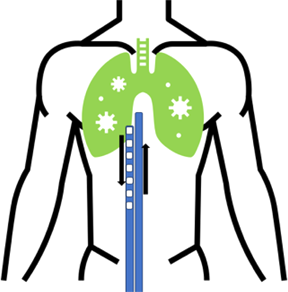 | The first figure shows extensive consolidation of the lung field secondary to coinfection with influenza and group A streptococcus. The patient was placed on bifemoral venovenous ECMO. The return cannula is placed just at the atrial caval junction. The access cannula for drawing in blood sits approximately 5 to 10 cm below the return cannula to prevent the recirculation of freshly oxygenated blood. |
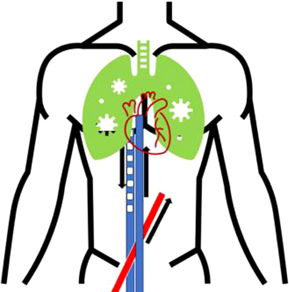 | The second figure shows extensive lung consolidation with evolving cardiogenic shock and biventricular failure. An additional 15 Fr arterial return pipe was placed in the right femoral artery. This improved arterial perfusion but increased the afterload and pressure on the failing left ventricle. |
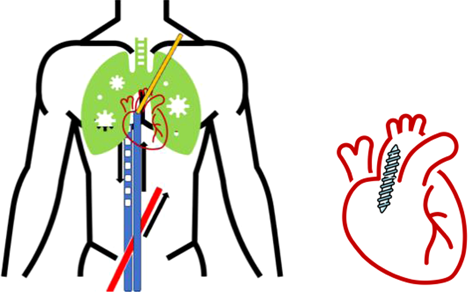 | The third figure illustrates the placement of a cardiac Impella* across the aortic valve. The patient's heart was so weak that it could no longer eject against the increased pressure generated by the ECMO arterial return. This is a potentially devastating complication as it leads to blood stasis and can result in thrombi in all 4 cardiac chambers and severe LV dilation and pulmonary edema. The Impella is, in essence, an Archimedes screw, which adds 2.5 L to the cardiac output and promotes forward flow, reducing the risk of stasis. |
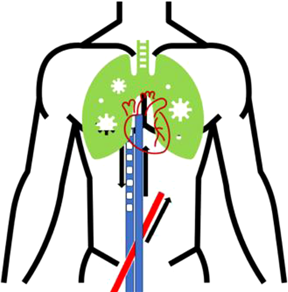 | The fourth figure shows the patient slowly improving. The placement of the Impella was complicated by both hemorrhage and hemolysis. Once the left ventricle had sufficiently recovered, it was removed. |
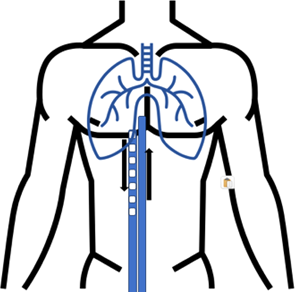 | The fifth figure illustrates the progressive improvement in pneumonia and the patient's return from venoarterial venous to venovenous ECMO for just respiratory support. |
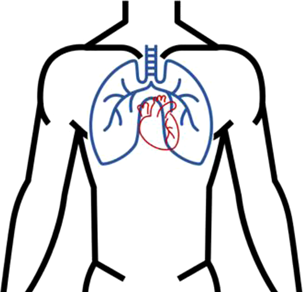 | The patient was finally decannulated from ECMO on the ninth day of their ITU. They were liberated from mechanical ventilation on day 12 and fully recovered. |
 | The first figure shows extensive consolidation of the lung field secondary to coinfection with influenza and group A streptococcus. The patient was placed on bifemoral venovenous ECMO. The return cannula is placed just at the atrial caval junction. The access cannula for drawing in blood sits approximately 5 to 10 cm below the return cannula to prevent the recirculation of freshly oxygenated blood. |
 | The second figure shows extensive lung consolidation with evolving cardiogenic shock and biventricular failure. An additional 15 Fr arterial return pipe was placed in the right femoral artery. This improved arterial perfusion but increased the afterload and pressure on the failing left ventricle. |
 | The third figure illustrates the placement of a cardiac Impella* across the aortic valve. The patient's heart was so weak that it could no longer eject against the increased pressure generated by the ECMO arterial return. This is a potentially devastating complication as it leads to blood stasis and can result in thrombi in all 4 cardiac chambers and severe LV dilation and pulmonary edema. The Impella is, in essence, an Archimedes screw, which adds 2.5 L to the cardiac output and promotes forward flow, reducing the risk of stasis. |
 | The fourth figure shows the patient slowly improving. The placement of the Impella was complicated by both hemorrhage and hemolysis. Once the left ventricle had sufficiently recovered, it was removed. |
 | The fifth figure illustrates the progressive improvement in pneumonia and the patient's return from venoarterial venous to venovenous ECMO for just respiratory support. |
 | The patient was finally decannulated from ECMO on the ninth day of their ITU. They were liberated from mechanical ventilation on day 12 and fully recovered. |
The image of the Impella was taken and modified from flaticon. www.flaticon.com/free-icons/bolt” title = “bolt icons.” Bolt icons created by Freepik–Flaticon. ITU, Intensive Therapy Unit; LV, left ventricle.
The Impella CP device
A vital aspect of this patient's course was the rapid deterioration in left ventricular function. The associated blood stasis can result in thrombosiss in all 4 cardiac chambers and is almost impossible to treat. The Impella device (ABiomed) is a percutaneous left ventricular assist device. It provides temporary support to assist the pumping function of the heart in patients with severe heart failure or undergoing high-risk angiography procedures. It directly pumps blood from the left ventricle to the aorta, bypassing the weakened or failing heart. Impella devices are minimally invasive and are inserted through a catheter-based approach. The catheter is typically introduced into the femoral artery in the groin and advanced up to the left ventricle under x-ray guidance. Once properly positioned, the Impella device unfolds and deploys its microaxial pump within the left ventricle. It draws blood from the left ventricle through an inlet area and expels it into the ascending aorta through an outlet area, assisting the heart's pumping function. Three types of Impella are available, providing between 2.5 and 5 L of cardiac support each minute. By direct comparison, on average, an intra-aortic balloon pump increases the cardiac output by approximately 0.5 to 1 L. While the Impella can be highly efficacious, its use can be complicated by significant blood loss,25 the pathogenesis being multifactorial. The Impella contains a purge system where heparin is “purged” through the motor housing to prevent it from ceasing. It is our practice to move to a bicarbonate purge if the Impella is associated with hemorrhage and to provide systemic anticoagulation with heparin as per our routine ECMO anticoagulation protocols. A meta-analysis demonstrated a higher in- hospital mortality in patients who developed bleeding complications following Impella placement when compared to those who did not.24 Meticulous attention to the device insertion and careful monitoring of hemostasis are essential. Our practice targets an anti-Xa level of 0.3 to 0.5 IU/mL.
The consumptive coagulopathy of hemorrhage
Our current understanding of the pathogenesis of bleeding comes mainly from research on traumatic coagulopathy.26 Previously, the management of hemorrhage was to restore oxygen- carrying capacity and volume with red cells and intravenous fluids and manage coagulopathy later. However, clinical trials in trauma have shown better outcomes in those treated with the early use of plasma and platelet products,26 and this principle has been applied to all types of bleeding.26 Global differences in the management of bleeding reflect the lack of a sound evidence base. Our suggested simple algorithm is in Figure 1. Hypofibrinogenemia is common in hemorrhage, for the fall in fibrinogen levels is greater than other coagulation factors due to loss in bleeding, consumption in clots, and fibrin(ogen)lysis. FFP lacks enough fibrinogen to achieve a fast rise in levels, so an additional source of fibrinogen is required.27
Multiple pragmatic trials have shown reduced mortality with tranexamic acid in traumatic and obstetric hemorrhage, as well as in preventing surgical bleeding.28,29 A meta-analysis of 216 trials (125 550 patients) showed no increased risk of thrombosis within 8 hours of use.29
There are few randomized controlled trials comparing the use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) instead of FFP in the management of major hemorrhages. While its use is safe and recommended in the reversal of vitamin K antagonists, the lack of evidence in major bleeding means it cannot be recommended at this current time. Indeed, a recent trial in trauma—the PROCOAG trial—showed no improvement in clinical outcome but significantly increased thrombotic rates.30
Conclusion
Consumptive coagulopathy is common in critically ill patients. Further research is required to improve understanding of hemostatic pathogenesis, refine diagnostic criteria, and develop evidence-based therapeutic interventions.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
Andrew Retter consults for Volition Diagnostics UK. He has received fees for presentations and reimbursement for travel to conferences. Volition Diagnostics was not involved with this article in any way.
Beverley J. Hunt: no competing financial interests to declare.
Off-label drug use
Andrew Retter: There is no specific off label drug use. DNase therapy, neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase inhibitors, and PAD4 inhibitors and non-anticoagulant therapy are suggested as potential future therapies.
Beverley J. Hunt: There is no specific off label drug use. DNase therapy, neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase inhibitors, and PAD4 inhibitors and non-anticoagulant therapy are suggested as potential future therapies.