Abstract
Multiple myeloma (MM) is malignancy of isotype-switched, BM-localized plasma cells that frequently results in bone destruction, BM failure, and death. Important molecular subgroups are identified by three classes of recurrent immunoglobulin gene translocations and hyperdiploidy, both of which affect disease course. From a clinical standpoint, it is critical to identify MM patients carrying the t(4;14) translocation, which is present in 15% of myelomas and is associated with dysregulation of WHSC1/MMSET and often FGFR3. These patients should all receive bortezomib as part of their initial induction treatment because this has been shown to significantly prolong survival. In contrast, patients with translocations affecting the MAF family of transcription factors, del17p, or gene-expression profiling (GEP)–defined high-risk disease appear to have a worse prognosis that is not dramatically improved by any intervention. These patients should be enrolled in innovative clinical trials. The remaining patients with cyclin D translocations or hyperdiploidy do well with most therapies, and the goal should be to control disease while minimizing toxicity.
Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an increasingly treatable plasma cell malignancy, properly designated plasma cell myeloma by the World Health Organization. In 2010, it was estimated that 20 180 new MM cases would be diagnosed, with 10 650 patients succumbing to the disease.1 The median age of diagnosis of MM is 69 years, and it occurs more frequently in men than in women and in blacks more than whites. It is almost always preceded by a premalignant tumor called plasma cell monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS).2,3 Lymphoid IgM MGUS (15%) and plasma cell (PC) non-IgM MGUS (85%), including light-chain MGUS,4 are present in 4% of whites over the age of 50, and progress at a rate of approximately 1% per year to lymphoma and MM, respectively.5 Surprisingly, most of the genetic changes found in MM can sometimes be found in PC-MGUS.6
MM is a plasma cell tumor of post–germinal center B-cells
Antigen-driven, post-germinal center B cells that have undergone productive somatic hypermutation and immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IGH@) class switching can generate either memory B cells or plasmablasts, which typically migrate to the BM and terminally differentiate into long-lived PCs. PC-MGUS and MM are monoclonal tumors that share with plasmablasts and long-lived PCs a strong dependence on the BM microenvironment for survival and growth. In contrast to normal long-lived PCs, however, MM tumors retain the potential for a low rate of proliferation (1%-3% of cycling cells). Over time, PC neoplasm progression from MGUS to intramedullary MM to extramedullary MM is associated with increased proliferation and independence from the BM microenvironment.7
Primary IGH@ translocations: an early oncogenic event in 40% of MM tumors
There are 7 recurrent chromosomal partners and oncogenes that are involved in IGH@ translocations in MGUS and MM tumors. They comprise 3 translocation groups, with the chromosomal site, target oncogene(s), and prevalence in MM as indicated: (1) CYCLIN Ds: 11q13 (CCND1) 15%; 12p13 (CCND2) < 1%; 6p21 (CCND3) 2%; (2) MAFs: 16q23 (MAF) 5%; 20q12 (MAFB) 2%; 8q24.3 (MAFA) < 1%; and (3) MMSET/FGFR3 4p16 (WHSC1/MMSET, and usually FGFR3) 15%.
Typically, these balanced chromosomal translocations bring an oncogene under the control of the strong immunoglobulin intronic (Emu) and/or 3′ IgH alpha (3′E) enhancers. The fact that the break points usually occur within the switch regions and occasionally near VDJ sequences suggests that these translocations are mediated by errors in class-switch recombination or somatic hypermutation processes occurring as normal B cells pass through germinal centers. Unique among the recurrent translocations, the t(4;14) break point is always in a switch region, resulting in the concomitant dysregulation of 2 genes: WHSC1/MMSET becomes dysregulated by Emu on der (4) and the FGFR3 oncogene is dysregulated by the stronger 3′E on der.8
Different consequences for the three types of primary IGH@ translocations
It is presumed that the cyclin D translocations only cause dysregulated expression of a cyclin D gene. In contrast, the MAF translocations dysregulate a transcription factor that causes increased expression of CCND2 and a large number of other genes, some of which encode adhesion proteins that are postulated to enhance the ability of the tumor cell to interact with the BM microenvironment.9 The pathogenic consequences of the MMSET/FGFR3 translocation and the relative contribution of the putative oncogenes are still controversial. WHSC1/MMSET, a chromatin-remodeling factor, is expressed in all tumors with a t(4;14), whereas 25% of the t(4;14) MM tumors lack FGFR3 expression. The acquisition of FGFR3-activating mutations during MM progression, although rare, clearly indicates a role for FGFR3 in MM pathogenesis. The expression of an activated mutant FGFR3 is clearly oncogenic; however, it was recently demonstrated that wild-type FGFR3, as in most t(4;14) MM, can also contribute to oncogenesis in B cells.10 It remains to be determined whether FGFR3 is critical early in the pathogenesis of t(4;14) MM, but may become dispensable during tumor progression. In any case, FGFR3 represents an attractive therapeutic target warranting the clinical evaluation of the available tyrosine kinase inhibitors (AB1010 and TKI258) and mAbs (MFGR1877S), at least in patients expressing FGFR3.11,12 Based on preclinical data, the kinase inhibitors may be the most effective in the rare patients with activating mutations, whereas MFGR1877S also demonstrated preclinical activity against MM-expressing wild-type FGFR3, explained in part by its ability to not only inhibit FGFR3-dependent signaling, but also to elicit antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
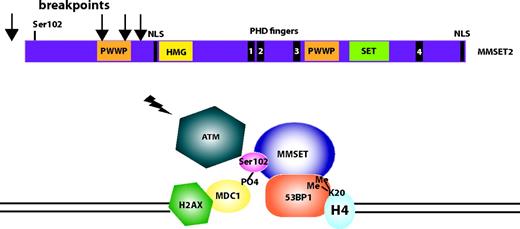
Conversely, WHSC1/MMSET is a histone methyltransferase with activity for H4K20,13 and when overexpressed results in a global increase in H3K36 and decrease in H3K27 methylation.14 Loss of MMSET expression alters adhesion, suppresses growth, and results in apoptosis, suggesting that it is a good therapeutic target.14 Recently, we identified a role for MMSET in DNA repair (Figure 1).15 After DNA damage, MMSET is phosphorylated on Ser102 by ATM and is recruited to sites of double-strand breaks, where it methylates H4K20, resulting in the recruitment of p53-binding protein (53BP1). 53BP1 is required for p53 accumulation, G2/M checkpoint arrest, and the intra-S-phase checkpoint in response to ionizing radiation. Approximately half of the translocation break points in t(4;14) MM result in a truncated MMSET that lacks Ser102 and cannot be recruited to double-strand breaks, resulting in a failure to recruit 53BP1 and a loss of the normal DNA damage-response pathway. It is not known whether this biologic difference results in a different clinical outcome for t(4;14) MM patients with a truncated versus a full-length MMSET.
MMSET is involved in DNA repair. An ideogram of MMSET highlights the important functional domains of the protein, with arrows indicating the initiation of translation of the truncated forms, lacking Ser102, that result from translocation break points between the coding exons. After DNA damage, MMSET is phosphorylated on Ser102 by ATM and is recruited to sites of double-strand breaks by MDC1, where it methylates H4K20. Dimethylation of H4K20 recruits p53-binding protein (53BP1), a key transducer of the DNA-damage checkpoint signal. 53BP1 is required for p53 accumulation, G2/M checkpoint arrest, and the intra-S-phase checkpoint in response to ionizing radiation.
MMSET is involved in DNA repair. An ideogram of MMSET highlights the important functional domains of the protein, with arrows indicating the initiation of translation of the truncated forms, lacking Ser102, that result from translocation break points between the coding exons. After DNA damage, MMSET is phosphorylated on Ser102 by ATM and is recruited to sites of double-strand breaks by MDC1, where it methylates H4K20. Dimethylation of H4K20 recruits p53-binding protein (53BP1), a key transducer of the DNA-damage checkpoint signal. 53BP1 is required for p53 accumulation, G2/M checkpoint arrest, and the intra-S-phase checkpoint in response to ionizing radiation.
Chromosome content associated with different oncogenic pathways
MM tumors can be grossly divided into hyperdiploid (HRD) and non-hyperdiploid (NHRD). Nearly half of MGUS and MM tumors are HRD, with 48-75 chromosomes and multiple trisomies involving chromosomes 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, and 21. Only 10% of these tumors have one of the primary IGH@ translocations listed above, whereas usually (∼ 70%) NHRD tumors (with a chromosomal content < 48 and/or > 75) have a primary IGH@ translocation.8 Tumors with a t(11;14) translocation may represent a distinct category of NHRD tumors because they often are diploid or pseudodiploid. Extramedullary MM tumors and human myeloma cell lines (HMCLs) nearly always have an NHRD phenotype, which is consistent with the hypothesis that HRD tumors are more stromal cell dependent than are NHRD tumors. Although it has been proposed that NHRD and HRD tumors represent different pathways of pathogenesis, we have virtually no information about the timing, mechanism, or molecular consequences of hyperdiploidy, except for the fact that HRD is found in MGUS. For tumors that are hyperdiploid but have one of the recurrent translocations—most often a t(4;14)—we do not know if hyperdiploidy occurred before or after the translocation. In contrast to the selective occurrence of recurrent IGH@ translocations in NHRD tumors, other genetic events such as 17p loss or TP53 mutations, RAS (NRAS or KRAS) mutations, secondary Ig translocations, and MYC translocations, often occur with a similar prevalence in HRD and NHRD tumors.
Universal Cyclin D dysregulation
Despite a low proliferation index in MGUS and most MM tumors, there is increased expression of one of the three CCNDs genes in virtually all MGUS and MM tumors.16 First, there is direct or indirect dysregulation of a CCND− gene by the CYCLIN D or MAF group primary translocations. Second, there is a moderately high level of CCND2 expression in the MMSET/FGFR3 tumors even though the mechanism is not understood. Third, although CCND1 is not expressed by normal B cells and PCs, nearly 40% of MGUS or MM tumors (virtually all are HRD) bi-allelically express CCND1 and sometimes CCND2. Fourth, most of the remaining tumors express increased CCND2 compared with normal PCs. Finally, the few tumors that do not express increased levels of CCNDs often have inactivated RB1, obviating the need for cyclin Ds to allow proliferation.
Molecular classification of MM
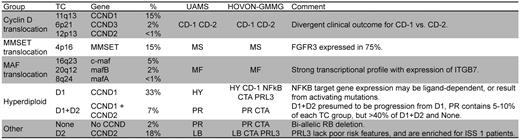
The patterns of spiked expression of genes deregulated by primary IGH@ translocations and the universal overexpression of CCNDs genes either by these translocations or other mechanisms led to the translocations and cyclin D (TC) classification, which includes 8 groups: those with primary translocations (designated 4p16, 11q13, 6p21, and MAF), those that overexpressed CCND1 and CCND2 either alone or in combination (D1, D1 + D2, and D2), and the rare cases that do not overexpress any CCND genes (“none”; Table 1).16 Greater than 95% of the D1 group are HRD. In addition, most of the patients with HRD MM and trisomy 11 fall within the D1 and D1 + D2 groups, whereas those without trisomy 11 fall within the D2 group, although a majority of the D2 group are NHRD. This classification system therefore focuses on the different kinds of mechanisms that dysregulate a CCND gene as an early and unifying event in pathogenesis.
An MM classification based on an unsupervised analysis of microarray gene-expression profiling (GEP) from the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences identified 7 tumor groups characterized by the co-expression of unique gene clusters.17 This classification was partially replicated in an independent unsupervised analysis of a combined HOVON-GMMG dataset that identified 10 tumor groups with considerable overlap with the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences groups.18 Interestingly, these clusters also identify subgroups corresponding to the different primary translocations and hyperdiploidy. However, they also highlight other important secondary events that can occur in each subtype of MM: proliferation, expression of NFκB target genes, cancer-testis antigens, and the phosphatase PTP4A3/PRL3 (PRL3). The CD-1 and CD-2 groups represent subgroups of patients with t(11;14) and t(6;14), with the former characterized by arginosuccinate synthetase 1 expression, and the latter by expression of B-cell antigens (CD20, VPREB, and CD79A). Interestingly, they identify patients with markedly different clinical outcomes. Of all of the molecular subgroups, CD-1 has the quickest onset and the highest frequency of complete remission (CR) (90%), whereas CD-2 has the slowest onset and the lowest frequency of CR (45%) when treated with Total Therapy 3. However, after the MF molecular subgroup, the CD-1 groups have the shortest CR duration (77% at 2 years), whereas the CD-2 have the longest (100% at 2 years).19
Additional events in MM progression
Activating RAS and BRAF mutations
The prevalence of activating NRAS or KRAS mutations is approximately 15% each in newly diagnosed MM tumors, whereas the prevalence of NRAS mutations is 7% in MGUS and KRAS mutations have not been identified, which is consistent with the hypothesis that KRAS mutations are one mark, if not a mediator, of the transition of MGUS to MM.20,21 The prevalence of RAS mutations is substantially higher in tumors that express CCND1 compared with tumors that express CCND2, with t(4;14) tumors having a particularly low prevalence of RAS mutations.22 MM cells depend on the continued expression of activated, but not wild-type, NRAS or KRAS, an effect independent of the ability of RAS to activate the AKT-signaling pathway.23 Recently, BRAF mutations were described in 4% of MM patients, suggesting a possible role for BRAF inhibitors in the treatment of this subset of patients.24
PI3K/AKT pathway
Mammalian target of rapamycin (MTOR) is a serine/threonine kinase that integrates signals from growth factors, nutrients, and stresses to regulate multiple processes, including mRNA translation, cell-cycle progression, autophagy, and cell survival. It resides in 2 multiprotein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. DEPTOR is an mTOR-interacting protein that inhibits mTORC1 activity but by inhibition of negative feedback effects maintains high levels of PI3K, AKT, and mTORC2.25,26 DEPTOR is overexpressed in TC 11q13, TC 6p21, and TC maf patients, who may be particularly sensitive to targeted inhibition of the related pathways. Inactivating mutations of PTEN and activating mutations of PIK3CA are uncommon.27
NFκB pathway has a critical role in normal PCs and in MGUS and MM tumors
Extrinsic ligands (APRIL and BAFF) produced by BM stromal cells provide critical survival signals to long-lived PCs by stimulating TACI, BCMA, and BAFF receptors to activate the NFκB pathway. Similar to PCs, most MGUS and MM tumors have a high signature expression of NFκB target genes (NFκB index, calculated by GEP), suggesting a continued role of extrinsic signaling in normal and malignant PC survival. Recently, NFκB–activating mutations in 6 positive regulators and inactivating mutations in 5 negative regulators of the NFκB pathway have been identified in approximately 20% of untreated MM tumors and in 45% of HMCLs, rendering the cells autonomous from ligand-mediated NFκB activation (Figure 2A).28,29 A whole-genome sequencing approach in 38 patients identified an additional 8 genes with mutations in the NFκB pathway, highlighting the importance of this pathway and the multiple methods that dysregulate it.24 Small molecules that inhibit extrinsic signaling (TACI.Fc) or intrinsic IKKβ are being developed as potential therapeutic agents (Figure 2B).28,30 Proteasome inhibitors have been reported to inhibit the NFκB pathway and patients with apparent TRAF3 inactivation (the most common mutation of the NFκB pathway) had a 90% response rate when randomized to bortezomib compared with a 10% response rate with dexamethasone, suggesting that cells addicted to constitutive activation of the NFκB pathway may be particularly sensitive to proteasome inhibition.29
A promiscuous array of mutations activate the classical and alternative NFκB pathways in MM. (A) Mutations of several genes (CD40, TACI, LTBR, CYLD, TRAF2, TRAF3, cIAP1, cIAP2, NIK, NFκB1, NFκB2, BTRC, CARD11, IKBIP, IKBKB, MAP3K1, RIPK4, TLR4, and TNFRSF1A) that result in activation of the NFκB pathways have recently been identified. (B) In PCs and early during neoplastic transformation, the cells are dependent on extrinsic ligands (BAFF and APRIL) to activate the NFκB pathway. With tumor progression, the cells acquire mutations that result in constitutive activation of the NFκB pathway and stromal independence or other mutations as yet unknown, which substitute for the requirement for NFκB activation. Different therapeutic interventions that may be effective at the distinct stages of tumor progression are shown at the bottom.
A promiscuous array of mutations activate the classical and alternative NFκB pathways in MM. (A) Mutations of several genes (CD40, TACI, LTBR, CYLD, TRAF2, TRAF3, cIAP1, cIAP2, NIK, NFκB1, NFκB2, BTRC, CARD11, IKBIP, IKBKB, MAP3K1, RIPK4, TLR4, and TNFRSF1A) that result in activation of the NFκB pathways have recently been identified. (B) In PCs and early during neoplastic transformation, the cells are dependent on extrinsic ligands (BAFF and APRIL) to activate the NFκB pathway. With tumor progression, the cells acquire mutations that result in constitutive activation of the NFκB pathway and stromal independence or other mutations as yet unknown, which substitute for the requirement for NFκB activation. Different therapeutic interventions that may be effective at the distinct stages of tumor progression are shown at the bottom.
Rearrangements of MYC
The translocations described above (MMSET/FGFR3, MAF, and CYCLIN D) appear to be primary events in the pathogenesis of MM, and are often found in MGUS. In contrast, translocations of a MYC gene (MYC ≫ MYCN > MYCL1) frequently appear to be secondary events that do not involve B-cell–specific recombination mechanisms, are often complex, and sometimes do not involve immunoglobulin loci. They are rare or absent in MGUS, but occur in 15% of newly diagnosed tumors, > 40% of advanced tumors, and nearly 90% of HMCLs. Increased expression of MYC in MGUS versus normal PCs and MM versus MGUS appears early in pathogenesis, presumably resulting from other mechanisms, with MYC-Ig translocations appearing to represent a very late progression event occurring at a time when MM tumors are becoming less stromal cell dependent and/or more proliferative.31 A recent transgenic mouse model in a strain that spontaneously develops a high rate of monoclonal gammopathy supports a functional role for MYC in the progression of MGUS to MM. In this strain, sporadic activation of MYC in germinal center B cells led to the universal development of MM by 1 year of age.32
Abnormalities of TP53 and chromosome 17p loss
Mutations of TP53 are relatively rare in newly diagnosed MM, occurring in approximately 5% of tumors. However, the frequency of mutations appears to increase with disease stage, and is approximately 30% in PC leukemia and in 65% of HMCLs.33 Deletion (mainly mono-allelic) of the TP53 locus, as detected by interphase FISH, occurs in approximately 7% of untreated MM tumors and in approximately 50% of PC leukemias and HMCLs. Sanger sequencing identified mutations of TP53 in only 37% of untreated patients with del17p.34 We hypothesize that the poor prognosis associated with del17p is related to its predisposition to eventual inactivation of TP53. For patients who initially present with del17p without a TP53 mutation, an analysis of the mutations status of the preterminal sample is required to determine whether mutations of TP53 have been selected for by therapy and disease progression. As in other tumors, up-regulation of MDM2 can antagonize p53 function in MM, and has recently been reported to be a consequence of decreased expression of the miRNAs miR-194, miR-192, and miR-215.35
Gain of chromosome 1q and loss of chromosome 1p
Gains of 1q and loss of 1p occur frequently together in MM and are associated with frequent del13 and with a poor prognosis.36 The mechanism appears to involve rearrangements of the pericentric heterochromatin, but the precise genes implicated are unclear at this time.37 It may be that it is a marker of a fatal genomic instability. Certainly, a gene-expression signature that is driven largely by up-regulated genes on 1q and down-regulated genes on 1p is a powerful predictor of outcome.38
Model of molecular pathogenesis of MM
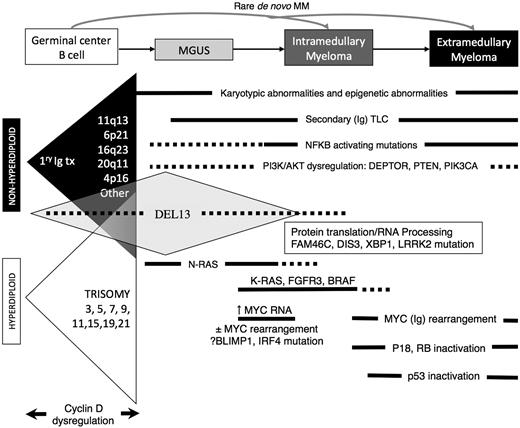
Based on the results summarized above, a model for the molecular pathogenesis of MM has been proposed (Figure 3). Chromosome content appears to identify two different, but perhaps overlapping, pathways of pathogenesis: NHRD tumors and HRD tumors. In approximately 40% of the tumors, a primary chromosome translocation results in the dysregulated expression of an oncogene and direct or indirect CCND dysregulation. Like the primary IGH@ translocations, trisomies of chromosomes 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 19, and 21, are already present at the earliest identified stage of tumorigenesis, and define subtypes of MM with distinctive clinical (eg, bone disease, heavy-chain subtypes, and prognosis), molecular (eg, types of CCND expressed and associated mutations), pathological (eg, morphology and CD expression), and cytogenetic (ploidy) features. A second “genetic hit” leading to subsequent transformation from MGUS to MM may be mediated by activation of MYC, mutation of KRAS, or del(13). The MYC pathway may be further dysregulated by late rearrangements, often involving an Ig locus. Activating mutations of the NFκB pathway and inactivating mutations of TP53 are associated with extramedullary spread of disease, and inactivation of CDKN2C (p18) and RB1 with increasingly proliferative disease.
Model for the multistep molecular pathogenesis of MM. Two largely nonoverlapping pathways (Ig translocations vs multiple trisomies) are primary events associated with dysregulated cyclin D expression. The most common secondary genetic events associated with tumor progression are shown, including early and late dysregulation of MYC and late-inactivating mutations of p53.
Model for the multistep molecular pathogenesis of MM. Two largely nonoverlapping pathways (Ig translocations vs multiple trisomies) are primary events associated with dysregulated cyclin D expression. The most common secondary genetic events associated with tumor progression are shown, including early and late dysregulation of MYC and late-inactivating mutations of p53.
Prognostic and therapeutic implications of molecular classifications
Of the various genetic events in MM, the one with by far the most important clinical significance is the t(4;14) chromosome translocation. It is a poor prognostic factor for patients treated with alkylating agents, immunomodulating drugs (IMiDs), and bortezomib.39,46–48 However, there is a clear survival advantage to the upfront use of bortezomib versus control in these patients,39,41,45,49 with a possibility that prolonged use totally overcomes the adverse prognosis.41,45 Despite numerous randomized clinical trials of IMiDs compared with control in the treatment of thousands of MM patients (thalidomide-dexamethasone vs dexamethasone, Total Therapy 2, melphalan prednisone thalidomide vs melphalan prednisone, cyclophosphamide thalidomide dexamethasone vs melphalan prednisone, bortezomib thalidomide dexamethasone vs bortezomib melphalan prednisone, lenalidomide dexamethasone vs dexamethasone, and lenalidomide maintenance) some of which showed improvements in overall survival (OS) for the cohort as a whole, we do not know which molecular subgroups received the maximum benefit from IMiDs versus those that received no benefit or those that may have been harmed. From all of these studies, there are a few reports of the effects of IMiDs versus control on the survival of a molecular subgroup (Table 2).
In TT2, the OS advantage of thalidomide versus placebo appeared to be confined to the 23% of patients with both GEP-defined low-risk disease and metaphase cytogenetic abnormalities.50 In contrast, in the MRC IX study, the 44% of patients with unfavorable cytogenetics, including t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), gain(1q21), del(1p32), and del(17p) randomized to thalidomide maintenance saw no prolongation of progression-free survival, and the OS was significantly shorter than those randomized to placebo.44 In the IFM 99-02 trial, the patients with del13 randomized to thalidomide maintenance saw no prolongation of event-free survival, but the OS was not reported.51 In the nonintensive pathway of MRC IX, cyclophosphamide thalidomide dexamethasone versus melphalan prednisone, a trend to improved OS with thalidomide induction was noted only in the group with favorable cytogenetics, but the OS for the group with unfavorable cytogenetics was not reported.43 In the Spanish study of bortezomib thalidomide dexamethasone versus bortezomib melphalan prednisone, the NHRD patients, including those with high-risk t(4;14), t(14;16), and t(14;20) translocations, randomized to thalidomide induction had significantly shorter 3-year OS (53% vs 72% P = .02).42 The HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial randomized patients to 1 of 2 pathways: vincristine-Adriamycin-dexamethasone induction followed by high-dose melphalan and thalidomide maintenance versus bortezomib-doxorubicin-dexamethasone induction followed by high-dose melphalan and bortezomib maintenance. They noted a significantly shorter 3-year OS (P < .01) for the patients randomized to the thalidomide arm with del13 (58% vs 79%), t(4;14) (40% vs 60%), and del17p (17% vs 61%).41 There are no data regarding the OS of different cytogenetic subgroups randomized to lenalidomide versus placebo. In the IFM 2005 study, both the del13 and del17p patients randomized to lenalidomide maintenance had a significant improvement in PFS, but only a very minimal effect was seen in the t(4;14).52 In summary, therefore, it appears that the maximum benefit of thalidomide is seen in the good-risk patients, whereas no benefit and sometimes worse outcomes are seen with its use in poor-risk patients. Further studies are urgently required to define the utility and safety of IMiDs in the various molecular subtypes of MM.
The MF molecular subgroups t(14;16) and t(14;20) have each individually been associated with a poor prognosis,19,53 although this was not seen for t(14;16) in one study.54 In addition, del17p is universally associated with poor prognosis.36,39 Finally, patients defined as high-risk by a GEP index of proliferation55 or other GEP-defined risk scores38,56 (which all appear to discriminate prognosis equally in an independent dataset55 ) do poorly. Unlike t(4;14) patients, for these latter subgroups, neither bortezomib nor any other intervention has been shown to offer a survival advantage, although the data are unfortunately very limited. These patients should be considered for clinical trials exploring innovative approaches.
Conclusions
Based on all of these considerations, the hematologists at the Mayo Clinic have proposed a risk-adapted strategy for the treatment of patients who cannot be enrolled in clinical trials (Figure 4).57 Guidelines for initial risk stratification of patients have also been reported recently (Table 3).58 Standard-risk patients can be treated with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone, postponing the toxicity and inconvenience associated with bortezomib. In contrast, t(4;14) patients receive bortezomib as part of induction and maintenance for at least 1 year. Finally, an innovative combination of lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone with a goal of CR is recommended for high-risk patients.
mSMART recommendations for a risk-adapted approach to therapy. Clinical trials are preferred for all patients, especially those with high-risk disease. *Note that a subset of patients with standard or intermediate risk will be classified as high-risk by GEP. †LDH > ULN and beta-2 microglobulin > 5.5 indicate a worse prognosis. ‡Prognosis is worse when associated with high beta-2 microglobulin and anemia. §t(11;14) may be associated with plasma cell leukemia. |Bortezomib-containing regimens are preferred in renal failure or if rapid response is needed. ¶If age > 65 years or there have been > 4 cycles of lenalidomide, consider G-CSF plus Cytoxan or plerixafor. #Continuing lenalidomide is an option for patients responding to it with low toxicities; dexamethasone is usually discontinued after the first year. Abbreviations: Rd–lenalidomide and dexamethasone, CyBorD–cyclophosphamide bortezomib and dexamethasone, MPT–melphalan prednisone and thalidomide, VRd–bortezomib lenalidomide and dexamethasone.
mSMART recommendations for a risk-adapted approach to therapy. Clinical trials are preferred for all patients, especially those with high-risk disease. *Note that a subset of patients with standard or intermediate risk will be classified as high-risk by GEP. †LDH > ULN and beta-2 microglobulin > 5.5 indicate a worse prognosis. ‡Prognosis is worse when associated with high beta-2 microglobulin and anemia. §t(11;14) may be associated with plasma cell leukemia. |Bortezomib-containing regimens are preferred in renal failure or if rapid response is needed. ¶If age > 65 years or there have been > 4 cycles of lenalidomide, consider G-CSF plus Cytoxan or plerixafor. #Continuing lenalidomide is an option for patients responding to it with low toxicities; dexamethasone is usually discontinued after the first year. Abbreviations: Rd–lenalidomide and dexamethasone, CyBorD–cyclophosphamide bortezomib and dexamethasone, MPT–melphalan prednisone and thalidomide, VRd–bortezomib lenalidomide and dexamethasone.
Disclosures
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.C. declares no competing financial interests. P.L.B. has received research funding from Genentech and has consulted for Novartis and Celgene. Off-label drug use: lenalidomide, thalidomide, and bortezomib used as maintenance therapy for MM.
Correspondence
P. Leif Bergsagel, Department of Hematology, Mayo Clinic, 13400 East Shea Blvd, Scottsdale, AZ 85259; Phone: (480) 301-8335; Fax: (480) 301-8387; e-mail: bergsagel.leif@mayo.edu.