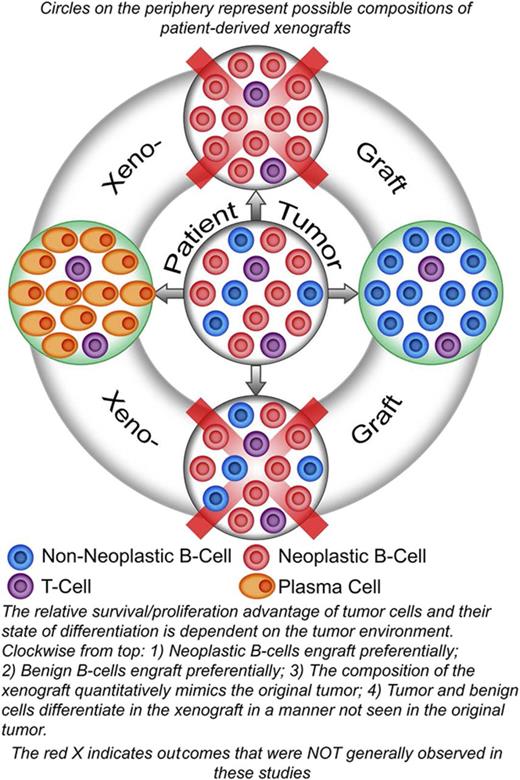
Key Points
The relative survival/proliferation advantage of lymphoma B cells compared with nonneoplastic B cells is dependent on environmental factors.
The tumor environment can dictate the differentiation of neoplastic B cells.
Abstract
To discern features of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) that are autonomous from those that are shaped by the tumor environment (TE), we used patient-derived xenografts (PDX) to probe the effects on neoplastic cells of manipulating the TE. Properties of neoplastic cells that are often considered to be autonomous include their relative independence from stromal support, their relative survival and/or proliferation advantages compared with nonneoplastic cells, and their state of differentiation. Prior approaches to creation of PDX models likely select for neoplasms, which are the most capable of engraftment, potentially masking the effects of the TE. To overcome this bias, we developed a robust protocol that rapidly produced xenografts with more than 85% of unselected, cryo-preserved, B-cell NHL specimens, including low-grade tumors such as follicular and marginal zone lymphoma. To discern features that are shaped by the TE, we extensively studied 4 low-grade lymphoma specimens. B-cell engraftment required components of the native TE; specifically, CD4+ cells. The relative survival of neoplastic compared with nonneoplastic B cells was not autonomous in 2 specimens; specifically, neoplastic B cells from 2 specimens showed a greater dependence on the TE than normal B cells for engraftment. Furthermore, the differentiation of neoplastic B cells was dependent on the TE; mature B-cell neoplasms converted to plasmacytoma-like lesions in the grafts. These results highlight the central and patient-specific roles of the TE in maintaining the relative survival of neoplastic cells compared with normal cells and in controlling the differentiation of neoplastic cells.
Introduction
The clinical behavior of mature B-cell lymphomas reflects the properties of both the tumor environment (TE) and neoplastic cells.1,2 For example, observational studies of human specimens have shown relationships between features of the nonneoplastic immune cells and prognosis.3,4 To dissect the effects of the TE from those intrinsic to neoplastic cells, we used a xenograft system for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL), focusing on follicular lymphoma (FL) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) because the TE is particularly well studied and clearly relevant in these diseases.1 We reasoned that if the TE was largely self-organizing and the properties of the neoplastic cells were largely cell-autonomous, then the xenograft would retain many of the native properties seen in the patient. On the contrary, if the TE is dependent on the systemic environment of the host to maintain its tumor-associated functions and the properties of the neoplastic cells are responsive to environmental cues, then properties of the neoplastic cells might be distinctive in the xenograft setting. Therefore, a xenograft model could allow us to test a basic question in tumor biology: How dependent are the properties of neoplastic cells on environmental cues?
A robust system for xenografting NHL specimens is critical to our studies. Although genetic models of low-grade NHL exist, these cannot reproduce the interpatient variation in the TE that originally allowed Dave and colleagues to demonstrate the pivotal role of the TE in prognosis of FL.3 Therefore, we sought an approach to xenografting NHL specimens such that patient-specific components of the TE could be systematically studied. Host NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice lack B, T, and NK cells and have proven robust for creating xenografts of leukemia and lymphoma.5 Here we use the omental tumor xenograft (OTX) model, which supports rapid and preferential engraftment of both tumor cells and tumor-associated nonmalignant cells (the TE) into an anatomically well-defined site, the greater omentum, allowing for quantitative measurements of the grafts. Using nondisrupted pieces of human non-small cell lung, breast, and ovarian carcinomas, we have previously demonstrated long-term engraftment in the murine omentum of tumor-derived memory T cells, B cells, plasma cells, dendritic cells, and monocytes.6,7 An adipose-rich, highly vascularized structure, the omentum is a key organ for lymphocyte trafficking to and from the peritoneal cavity, potentially accounting for the preferential engraftment of human immune cells at this site.8 Here, we apply the OTX system to single-cell suspensions of NHL specimens, allowing separate implantation of the neoplastic cells and the tumor-associated nonneoplastic components. The data reveal distinctive growth and differentiation potentials of individual patients’ lymphomas, allowing the recognition of aspects of these neoplasms that are modulated by their environment.
Methods
Tumor collection and banking was performed as previously described and approved by the various institutional research subjects’ review boards,9 in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Histology and immunohistochemical staining used standard techniques. A magnetic bead system (LS columns MidiMacs; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) was used to positively select CD4 (BW135/80 Fab) and CD8 (M-T466) cells and to negatively select B cells (using a cocktail of biotin-conjugated antibodies against CD2, CD3, CD4, CD14, CD15, CD16, CD56, CD61, CD235a, FcεRI, CD34, and Anti-Biotin MicroBeads [“B-CLL” kit]; Miltenyi Biotec Inc., Auburn, CA). Viability was performed by 7-aminoactinomycin D exclusion. For qualitative studies, DNA was extracted from sections of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue (range, 4-25 microns, depending on the size of the graft) or ∼5 × 106 cryopreserved cells (tumor inputs). For quantitative studies, DNA was extracted from the fresh mesenteric organs obtained at necropsy.
OTX model: 5 × 106 to 10 × 106 viable cells (suspended in 500 μL RPMI-1640) were injected into the peritoneum (intraperitoneally; i.p.) of young adult male and female NSG mice. In preliminary experiments, engraftment was assessed at several intervals (range, 2-60 days); 14 days was selected as the standard time for assessment of engraftment. Engraftment was assessed by harvesting the intra-abdominal organs; the omentum (often with associated variable amounts of pancreas, spleen, bowel, and liver) and the spleen were separately prepared for histology or other quantitative studies. Histologic blocks containing omentum were serially sectioned to exhaustion (median, 240 sections/block); selected sections were hematoxylin and eosin stained or used for immunohistochemistry.
Clonality testing
Various molecular approaches were used to confirm that each xenograft contained the neoplastic B cells specific to the tumor that had been implanted (Table 1). Clonality assays based on the IGHV and IGKV used commercially available systems (IdentiClone Assay; InVivoScribe Technologies, Inc., San Diego, CA). The clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) sequence was determined using IGVH family primers, pooled into 3 sets, coupled with a single downstream primer beyond the IGHJ genes (see supplemental Methods). IG sequences were analyzed using the International ImMunoGeneTics information system (http://www.imgt.org/). The t(14;18) translocation junction was identified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), as previously described.10
Quantitative IGHV sequencing
Amplicon-based libraries were produced using Q5 polymerase (NEB, Ipswich, MA) and 8N bar-coded primers containing the Illumina S16 overhang adapter sequences followed by germline specific sequences (supplemental Methods). Family-specific IGH primers were designed for the IGHV FR2 and IGHJ FR4 regions. The multiplex IGH PCRs used 3 different primer pools, each with ∼150 μg DNA per reaction. Two rounds of PCR generated amplicons with bar codes on each end; bar-coded primers were removed (ExoI digestion, 20 U/50 μL; 37°C; 1 hour; NEB) followed by heat inactivation (20 min; 80°C). Bar-coded products were amplified (primers to the Illumina adapters; 5 cycles) and size selected (SPRIselect beads; Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA), keeping fragments 200-1000 nt. Indexed products larger than 250 nt were selected from a final amplification (15 cycles; Illumina adapter sequences; SPRIselect). See supplemental Table 3 for thermocycler settings. Sequencing was performed by the University of Rochester Genomic Research Center (Illumina MiSeq, V3 chemistry, 300 nt paired-end reads).
Sequence analysis
Illumina 2 × 301 paired-end read data were processed to remove adapter sequences and low-quality bases and merged into single end-to-end reads using AdapterRemoval v2.11 Read data with identical bar codes were processed to generate a consensus read, followed by bar-code removal. Read ends were compared with primer sequences to assign reads to a primer pair, provided there was a primer sequence match greater than 22/25 nt. Reads generated with identical primer pairs were clustered and counted, using Needleman-Wunsch scores12 as a similarity metric to produce a smaller collection of clonal sequences. The presumed IGH sequences were batch processed, using IMGT High-VQUEST (https://www.imgt.org/HighV-QUEST/login.action) to determine whether the sequence represents a productive rearrangement and to obtain its CDR3 amino acid sequence. These amino acid sequences were then clustered and counted, based on Needleman-Wunsch scores, to identify clonally related sequences and determine their frequencies in the sample.
Results
The OTX model is versatile and robust
Studies of more than 1000 mice using cell suspensions from more than 50 different primary lymphomas, both fresh and in viably frozen formats, suggested the OTX approach using frozen cells was effective. To objectively assess the efficacy of the OTX model for tumor engraftment in an unbiased manner, we selected 20 NHL specimens from a pool of more than 1000 viably frozen, single-cell suspensions of nonchronic lymphocytic leukemia NHL tumors (Table 1). These cases were selected as the 20 B-cell NHL specimens in our tumor bank with the largest number of aliquots; no other selection criteria were used. The 20 cryopreserved B-cell lymphoma suspensions were each injected i.p. into 3 mice for the survey study, and omental-associated organs of each mouse were subjected to exhaustive histologic review (see “Methods”). 17 specimens showed histologic evidence of engraftment in the omentum at 14 days in all 3 of the mice used for each specimen. Three of the 20 samples (tumor O, P, and K with viabilities of 5%-10% of the thawed cell suspension) failed to engraft in any mice; no other parameter affecting engraftment, including the number of aliquots available, was identified. Engraftment was defined as morphology- and immunohistochemical-based detection of human lymphocytes (note that the NSG strain has no endogenous lymphocytes, a feature that greatly simplifies scoring of engraftment).
Molecular characterization of clonality in the survey experiments
For the 17 specimens that engrafted, at least 1 clone-specific molecular feature of the original tumor was identified in the corresponding graft (Table 1). Identity of clone-specific IGHV or IGKV was established through PCR-based clonality assays. Additional approaches to corroborate clonal identity of the graft with the original tumor included identification of the BCL2:IGH translocation breakpoint and the presence of BCL1 overexpression (as an indicator of the BCL1:IGH translocation in a single case of mantle cell lymphoma).
General features of grafts
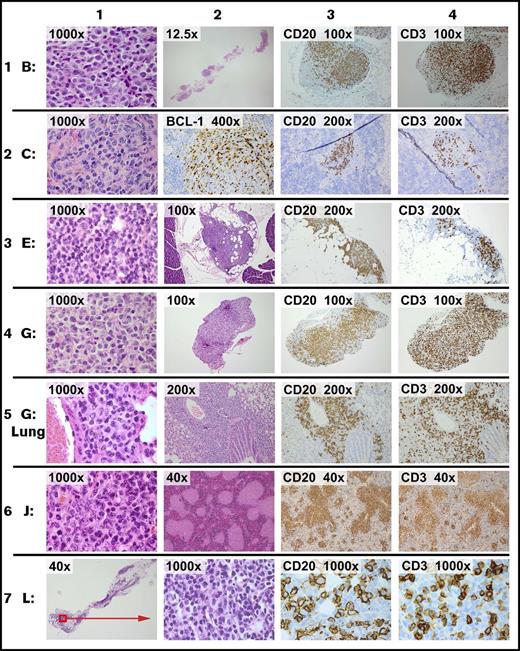
Although the time course and characteristics of the grafts depended substantially on the specific source specimen, there were several generalizable features. Of the 19 specimens that were viable at thaw, 17 engrafted in all 3 mice tested for each specimen. The omental xenografts were microscopic or just visible at 2 weeks and retained cytologic features of the original neoplasm (Figure 1). All 17 xenografts contained both B and T cells in variable proportions (Figure 1, columns 3 and 4). In every case, specimens that implanted in the omentum also involved the splenic white pulp at 14 days (eg, see Figure 1, specimen C, columns 2, 3, and 4). In some tumors (eg, Figure 1, specimen G Lung, column 3), B cells were abundant at other distant sites by 1 month. Engraftment did not appear to reflect Epstein-Barr virus-mediated immortalization: 16/17 xenografts were negative for the 2 early Epstein-Barr virus transcripts, EBER 1 and EBER 2. All xenografts of tumor F were floridly positive for Epstein-Barr virus; only rare positive cells were present in the original tumor specimen (data not shown).
Representative images of xenografts. On day 1, 5 × 106 viable cells of each tumor were injected i.p. Necropsy was performed on day 14 (except row 5, which was performed at 1 month). Representative images from 6 of 20 tumors are shown. Staining was by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) unless otherwise stated. Row 1: tumor B is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: xenograft (full extent of omental implant). Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 2: tumor C is a mantle cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: splenic section showing xenograft stained for BCL1 in a white pulp distribution. Column 3: CD20 in spleen. Column 4: CD3 in spleen. Row 3: tumor E is a follicular lymphoma, grade one. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: xenograft (representative cross-section of the omental implant with adjacent pancreas). Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 4: tumor G is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: representative cross-section of the omental implant. Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 5: tumor G is same tumor as prior row, showing involvement of the lung at 1 month. Columns 1 and 2: xenograft surrounding airway. Column 3: CD20 in lung. Column 4: CD3 in lung. Row 6: tumor J is a follicular lymphoma, grade 2. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: white pulp pattern of splenic involvement. Column 3: CD20 in spleen. Column 4: CD3 in spleen. Row 7: tumor L is a follicular lymphoma, grade one. Column 1: xenograft in the omentum (representative cross-section of full omental tissue). Column 2: xenograft in omentum. Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum.
Representative images of xenografts. On day 1, 5 × 106 viable cells of each tumor were injected i.p. Necropsy was performed on day 14 (except row 5, which was performed at 1 month). Representative images from 6 of 20 tumors are shown. Staining was by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) unless otherwise stated. Row 1: tumor B is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: xenograft (full extent of omental implant). Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 2: tumor C is a mantle cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: splenic section showing xenograft stained for BCL1 in a white pulp distribution. Column 3: CD20 in spleen. Column 4: CD3 in spleen. Row 3: tumor E is a follicular lymphoma, grade one. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: xenograft (representative cross-section of the omental implant with adjacent pancreas). Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 4: tumor G is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: representative cross-section of the omental implant. Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum. Row 5: tumor G is same tumor as prior row, showing involvement of the lung at 1 month. Columns 1 and 2: xenograft surrounding airway. Column 3: CD20 in lung. Column 4: CD3 in lung. Row 6: tumor J is a follicular lymphoma, grade 2. Column 1: xenograft in omentum. Column 2: white pulp pattern of splenic involvement. Column 3: CD20 in spleen. Column 4: CD3 in spleen. Row 7: tumor L is a follicular lymphoma, grade one. Column 1: xenograft in the omentum (representative cross-section of full omental tissue). Column 2: xenograft in omentum. Column 3: CD20 in omentum. Column 4: CD3 in omentum.
Extensive immunohistochemical studies showed no definitive evidence of human macrophages (as marked by CD68 or CD163) or dendritic cells (marked by CD21 or CD23) at any time in the xenografts, despite their relative abundance in many of the original specimens; it is unclear whether this reflects a failure of these cells to survive processing (eg, disaggregation, filtering, cryopreservation, or thaw) or a failure of these cell types to engraft at the sites examined. In all engrafted specimens, the ratio of T cells to B cells was higher in the xenograft compared with original tumor (data not shown). The preponderance of T cells were CD4, rather than CD8, with only sparse CD56-, CD57-, FOXP1-, or PD1-positive cells detected in a subset of specimens (data not shown).
Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires the nonneoplastic components of the tumors
Engraftment was entirely dependent on nonneoplastic cells (Figure 2). Aliquots of tumors J (FL) and W (MZL) were depleted of non-B-hematopoietic cells, using a cocktail of antibodies (CD2, CD14, CD16, CD36, CD43, CD235a). Exhaustive sectioning of the omentums and thorough necropsy of the animals injected with samples consisting only of B cells showed no evidence of engraftment. In contrast, mock-depleted aliquots engrafted similarly to the nonmanipulated specimens. The ability to engraft was reconstituted by adding back the nonneoplastic components (Figure 2D).
Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires tumor-associated non-B cells. A representative experiment using tumor J (FL; 68% B cells in the thawed aliquot of tumor tissue) is shown. The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days postinjection; each panel is a representative section from 1 of 3 mice in each experimental group. Qualitatively similar results were obtained using tumor W (MZL; data not shown). The images show representative sections for each graft, which include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells made up 28% of the specimen, B cells and other cell types made up 72% of the specimen, and viability was higher than 80%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (cell number for injection, 7 × 106 with 94% viability was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. (C) The nonneoplastic T-cell fraction of the B-cell tumor can engraft despite removal of the B cells (cell number for injection, 3 × 106 [85% viable], was matched to the number of non-B cells injected in A). Note that although tumor volume is clearly decreased compared with the mock-depleted specimen (A), there are definitive foci of lymphoid tumor marked by the green arrows (immunohistochemical studies indicate that these foci are >90% T cells, with no evidence of B cells; data not shown). (D) The non-B-cell fraction rescues engraftment of the B-cell fraction. The fractions used in B and C were mixed in appropriate proportions to recapitulate the composition of the mock-depleted specimen (cell number for injection, 1 × 10 7 [91% viable] was matched to the number injected in A). The reconstitution suggests that the failure of B cells to engraft in B is a result of loss of a cellular component in the non-B-cell fraction as opposed to any other nonspecific effect of the bead-based manipulation. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); each treatment with each tumor was assessed with 3 mice; the entire set of studies using tumor J was conducted twice, and the studies of tumor W were conducted once, all with essentially indistinguishable results.)
Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires tumor-associated non-B cells. A representative experiment using tumor J (FL; 68% B cells in the thawed aliquot of tumor tissue) is shown. The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days postinjection; each panel is a representative section from 1 of 3 mice in each experimental group. Qualitatively similar results were obtained using tumor W (MZL; data not shown). The images show representative sections for each graft, which include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells made up 28% of the specimen, B cells and other cell types made up 72% of the specimen, and viability was higher than 80%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (cell number for injection, 7 × 106 with 94% viability was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. (C) The nonneoplastic T-cell fraction of the B-cell tumor can engraft despite removal of the B cells (cell number for injection, 3 × 106 [85% viable], was matched to the number of non-B cells injected in A). Note that although tumor volume is clearly decreased compared with the mock-depleted specimen (A), there are definitive foci of lymphoid tumor marked by the green arrows (immunohistochemical studies indicate that these foci are >90% T cells, with no evidence of B cells; data not shown). (D) The non-B-cell fraction rescues engraftment of the B-cell fraction. The fractions used in B and C were mixed in appropriate proportions to recapitulate the composition of the mock-depleted specimen (cell number for injection, 1 × 10 7 [91% viable] was matched to the number injected in A). The reconstitution suggests that the failure of B cells to engraft in B is a result of loss of a cellular component in the non-B-cell fraction as opposed to any other nonspecific effect of the bead-based manipulation. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); each treatment with each tumor was assessed with 3 mice; the entire set of studies using tumor J was conducted twice, and the studies of tumor W were conducted once, all with essentially indistinguishable results.)
CD4 but not CD8 T cells are required for engraftment of tumor B cells
To define the components of the TE required for engraftment, we performed various flow-based cell sorting studies to selectively deplete or augment the T follicular helper and T regulatory compartments. In extensive studies of specimens J and W, no discernable effect on engraftment was seen (data not shown). Because depletion of the defined subtypes of T cells did not discernably alter engraftment, we depleted either all CD4- or CD8-positive cells (Figure 3). Flow cytometry before i.p. injection indicated that all CD4-positive and CD8-positive cells in these specimens were CD3+. For 4 of 5 specimens studied, engraftment of tumor-derived B cells was entirely dependent on the presence of CD4-positive cells (Figure 3 shows representative data for tumor W). Specimen E showed marked attenuation of B-cell engraftment on CD4+ cell depletion (data not shown). Depletion of CD8-positive cells had no discernable effect on the engraftment of any of the 4 specimens tested (J, W, M, L).
Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires CD4+tumor-associated cells. A representative experiment using tumor W (MZL) is shown. Qualitatively similar results were also obtained using tumors M (MZL) and J (FL; data not shown). The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days; each panel is a representative section from one of 3 mice in each experimental group. The images show representative sections for each graft that include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows; examples of uninvolved omentum are marked with blue arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells make up 11% of the specimen with a CD4:CD8 ratio of 1.7, B cells make up 76% of the specimen, and viability was 91%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. The grafts of this tumor contains a mixture of B and T cells (Figure 5). (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (viability after depletion of B cells was 94%; cell number for injection, 7 × 106, was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). (C) CD8+ cells are not required for engraftment. CD8+ cells were depleted by a factor of at least 20-fold. For CD8+ cells (viability after depletion was 79%; cell number for injection was 1 × 107), there was no discernable effect on the tumor volume or B-cell composition (D) CD4+ cells are required for engraftment. The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. Viability at the time of implementation was 83%. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); the CD4 depletions were assessed with 3 mice each for tumors W, M, and J; the CD8 depletions were performed with 3 mice each on tumors W and M; the various treatments showed essentially indistinguishable results with the various source tumors.)
Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires CD4+tumor-associated cells. A representative experiment using tumor W (MZL) is shown. Qualitatively similar results were also obtained using tumors M (MZL) and J (FL; data not shown). The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days; each panel is a representative section from one of 3 mice in each experimental group. The images show representative sections for each graft that include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows; examples of uninvolved omentum are marked with blue arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells make up 11% of the specimen with a CD4:CD8 ratio of 1.7, B cells make up 76% of the specimen, and viability was 91%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. The grafts of this tumor contains a mixture of B and T cells (Figure 5). (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (viability after depletion of B cells was 94%; cell number for injection, 7 × 106, was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). (C) CD8+ cells are not required for engraftment. CD8+ cells were depleted by a factor of at least 20-fold. For CD8+ cells (viability after depletion was 79%; cell number for injection was 1 × 107), there was no discernable effect on the tumor volume or B-cell composition (D) CD4+ cells are required for engraftment. The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. Viability at the time of implementation was 83%. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); the CD4 depletions were assessed with 3 mice each for tumors W, M, and J; the CD8 depletions were performed with 3 mice each on tumors W and M; the various treatments showed essentially indistinguishable results with the various source tumors.)
Nonneoplastic B cells present within some tumor specimens engraft with a higher efficiency than neoplastic B cells
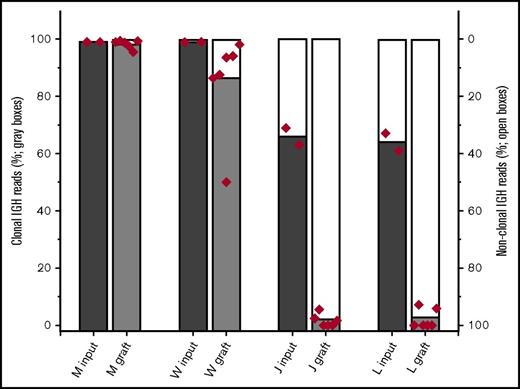
We hypothesized that the composition of the TE has been selected through the process of tumorigenesis to provide supportive cues to which neoplastic B cells (compared with nonneoplastic B cells) are especially sensitive. To test this hypothesis, we exploited the consistent presence of nonneoplastic B cells in the tumors. The nonneoplastic B cells presumably represent cells that transit the tumor but are not intrinsic to the neoplastic process. If the TE preferentially supports the neoplastic B cells, a time-dependent reduction in the relative number of nonneoplastic B cells is predicted. At the 2-week point, all grafts contained substantial numbers of CD20-positive B cells. Contrary to expectations, the fraction of nonneoplastic B cells increased for all specimens tested (Figure 4). For 2 MZL specimens (W and M; each with 1%-2% of B cells at thaw identified as nonclonal; data not shown), the fraction of B cells that were nonclonal showed a modest increase, but the clonal B cells remained greater than 90% of all B cells by 2 weeks. In contrast, xenografts established with 2 FL samples (J and L; each tumor with about 20% of B cells at thaw identified as nonclonal by flow cytometry) showed a substantial relative loss of neoplastic B cells by 2 weeks.
Neoplastic and nonneoplastic B cells within tumor specimens engraft with differing relative efficiencies. The fraction of B cells that are clonal is estimated from the fraction of IGHV sequencing reads that match the specimens’ previously determined sequence. To assess the relative engraftment of clonal and nonclonal B cells, the entire omentum (with fragments of associated organs) was harvested from mice implanted with tumors M, W, J, and L. 3 mice with each xenograft were harvested at 2 weeks. DNA was prepared from these fresh specimens. The fraction of IGHV sequence reads that were aligned to the established clonal IGHV sequence for that tumor was determined (sequencing studies were performed in duplicate for all specimens; each symbol represents the results for individual assays performed on the omentum and all associated organs from an individual mouse).
Neoplastic and nonneoplastic B cells within tumor specimens engraft with differing relative efficiencies. The fraction of B cells that are clonal is estimated from the fraction of IGHV sequencing reads that match the specimens’ previously determined sequence. To assess the relative engraftment of clonal and nonclonal B cells, the entire omentum (with fragments of associated organs) was harvested from mice implanted with tumors M, W, J, and L. 3 mice with each xenograft were harvested at 2 weeks. DNA was prepared from these fresh specimens. The fraction of IGHV sequence reads that were aligned to the established clonal IGHV sequence for that tumor was determined (sequencing studies were performed in duplicate for all specimens; each symbol represents the results for individual assays performed on the omentum and all associated organs from an individual mouse).
The tumor environment in the xenograft supports anomalous plasmacytic differentiation
In the course of these studies, we observed a consistent accumulation of plasma cells in all grafts, regardless of the original histology of the tumor. The plasma cell fraction (marked by CD138), initially undetectable by our methods, increased in the xenografts, and the mature B-cell (CD20 positive) fraction decreased. Although this overall accumulation of plasma cells was consistent across all specimens, the time course of accumulation and evidence of clonal restriction varied with the specific specimen. The evolution of the xenograft composition was studied in detail using tumors J (FL) and W (MZL) (Figures 5 and 6). The T-cell fraction and Ki67 index were increased at day 7 compared with that seen at day 1, and especially compared with the original tumor. In replicate experiments, tumor J (FL) showed an abrupt loss of CD20 expression and gain of CD138 expression between days 7 and 14, whereas tumor W (MZL) showed a similarly consistent increase in cells expressing CD138 between days 14 and 21. The plasma cells that emerged in the xenografts of 4 specimens were light chain restricted, suggesting the plasma cells were directly derived from the neoplastic B cells (Figure 7 contrasts the light chain restriction of specimens J and W). Definitive monoclonality (light chain restriction) of the plasma cells was seen in 2/4 MZLs (specimens M and W), 1/7 FLs (specimen E; data not shown), and the single mantle cell lymphoma (specimen C; data not shown). All other xenografts showed a mixture of κ- and λ-expressing plasma cells, and therefore could be entirely polyclonal or a mixture of clonally derived and polyclonal plasma cells (Table 1). Note that there is strong correlation between the presence of overtly clonal plasma cell proliferations and the lack of nonclonal B cells in the original diagnostic specimen (Wilcoxon rank-sum, P < .001); for example, the 4 specimens (W, M, C, E) with the least polyclonal B cells in the original diagnostic specimen are the 4 with overtly clonal plasma cells. These data suggest that in the environment of the xenograft, both neoplastic and nonneoplastic B cells undergo plasmacytic differentiation, indicating that the differentiation state of neoplastic B cells, similar to nonneoplastic B cells, is responsive to environmental cues, and is not solely determined by cell-autonomous, fixed genetic, or epigenetic factors.
Time course of specimen J (FL) xenograft development demonstrates abrupt plasma cell differentiation between 7 and 14 days. A total of 1 × 107 cells of specimen J were implanted in each of 6 mice; 2 mice were harvested at 2, 7, and 14 days (H&E stained). Ki67 staining was low at day 2, similar to the level in the original excised node (see insets on far right). Numbers of Ki67-positive cells increased by day 7, with a simultaneous increase in both T cells (CD2) and B cells (CD20). Between days 7 and 14, there was an abrupt loss of CD20 expression with appearance of CD138-positive forms. Note that CD138-positive forms were not present in the original biopsy (see inset). Tissue marked with asterisks are pancreas; original magnification of all images ×40.
Time course of specimen J (FL) xenograft development demonstrates abrupt plasma cell differentiation between 7 and 14 days. A total of 1 × 107 cells of specimen J were implanted in each of 6 mice; 2 mice were harvested at 2, 7, and 14 days (H&E stained). Ki67 staining was low at day 2, similar to the level in the original excised node (see insets on far right). Numbers of Ki67-positive cells increased by day 7, with a simultaneous increase in both T cells (CD2) and B cells (CD20). Between days 7 and 14, there was an abrupt loss of CD20 expression with appearance of CD138-positive forms. Note that CD138-positive forms were not present in the original biopsy (see inset). Tissue marked with asterisks are pancreas; original magnification of all images ×40.
Time course of specimen W (MZL) xenograft development demonstrates abrupt plasma cell differentiation between 1 and 2 weeks. A total of 1 × 107 cells of specimen W were implanted in each of 6 mice; 2 mice were harvested at 7, 14, and 30 days (H&E stained). By day 7, T cells (CD2+) were more abundant in the graft than in the original specimen, and B cells (CD20+) were relatively less abundant. Plasma cells (CD138+) appeared between days 14 and 30. In contrast to specimen J, the CD20+ cells of specimen W coexist with the CD138+ forms. Furthermore, there was a consistent peripheral distribution of the plasma cells (see day 30, CD138). By day 30, the Ki67 appears to be decrementing. Tissue marked with asterisks are pancreas; original magnification of all images ×40.
Time course of specimen W (MZL) xenograft development demonstrates abrupt plasma cell differentiation between 1 and 2 weeks. A total of 1 × 107 cells of specimen W were implanted in each of 6 mice; 2 mice were harvested at 7, 14, and 30 days (H&E stained). By day 7, T cells (CD2+) were more abundant in the graft than in the original specimen, and B cells (CD20+) were relatively less abundant. Plasma cells (CD138+) appeared between days 14 and 30. In contrast to specimen J, the CD20+ cells of specimen W coexist with the CD138+ forms. Furthermore, there was a consistent peripheral distribution of the plasma cells (see day 30, CD138). By day 30, the Ki67 appears to be decrementing. Tissue marked with asterisks are pancreas; original magnification of all images ×40.
Plasma cells that develop in specific tumors are consistently either clonal or nonclonal. Plasma cell clonality can be assessed from the ratio of κ to λ light chain expression (top 4 panels; original magnification ×10 [J] and ×4 [W]). IHC was titered to detect the abundant cytoplasmic expression of light chains that is characteristic of plasma cells and their immediate precursors (plasmablasts) while not detecting the surface expression found on mature B cells. The bulk of plasma cells in specimen J were polyclonal, whereas the plasma cells in specimen W uniformly expressed κ light chain but did not express λ light chain and were therefore clonal. At least 3 xenografts of each specimen were stained, and all showed identical results. Typical plasma cell morphology is seen at high power in both specimens (original magnification ×100; H&E stain).
Plasma cells that develop in specific tumors are consistently either clonal or nonclonal. Plasma cell clonality can be assessed from the ratio of κ to λ light chain expression (top 4 panels; original magnification ×10 [J] and ×4 [W]). IHC was titered to detect the abundant cytoplasmic expression of light chains that is characteristic of plasma cells and their immediate precursors (plasmablasts) while not detecting the surface expression found on mature B cells. The bulk of plasma cells in specimen J were polyclonal, whereas the plasma cells in specimen W uniformly expressed κ light chain but did not express λ light chain and were therefore clonal. At least 3 xenografts of each specimen were stained, and all showed identical results. Typical plasma cell morphology is seen at high power in both specimens (original magnification ×100; H&E stain).
Discussion
We used a robust and quantifiable xenograft system for NHLs to identify the properties of the neoplastic cells that are influenced by the TE. The robust nature of the OTX model allowed us to observe patient-specific variation in the dependence on the TE: in some tumors (J, L), the nonneoplastic B cells are responsive to the proliferation and survival cues present in the xenograft environment, whereas the neoplastic B cells are not; in other tumors (M,W), the neoplastic B cells engrafted effectively. The relative failure of neoplastic cells from tumors J and L to engraft compared with nonneoplastic B cells in the same specimens is all the more surprising, given that these neoplastic cells are positive for the IGH:BCL2 translocation, which presumably would make these cells relatively resistant to apoptosis. Given the robust nature of the model and the internal control comprised of passenger, benign B cells, these negative data for tumors J and L suggest there is some critical environmental factor (whether cellular, humoral, or otherwise) present in the patient that did not survive transfer to the mouse and that the factor or factors is critical to the expansion of neoplastic, but not nonneoplastic, B cells. Furthermore, uniform differentiation of the neoplastic B cells into plasma cells in several tumors (M, W, C, E) indicates the differentiation of the neoplastic cells is responsive to environmental cues, findings that parallel those of a recent similar xenograft study of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.13 Therefore, this PDX approach identifies specific patients as having tumors in which the survival and/or the differentiation of the neoplastic cells is dependent on the TE.
We find that the differentiation of neoplastic cells is not cell autonomous, an observation that is consistent with well-described histologic features of some B-cell tumors. MZL, mantle cell lymphomas, and even FLs may be associated in patients with significant numbers of plasma cells that are derived from the neoplastic B cells.14-16 In the case of MZL, these plasma cell accumulations may be so marked that the neoplasm mimics a plasmacytoma or creates an amyloidoma. More subtle accumulations of clonal plasma cells occur in MZLs arising at mucosal sites: the clonal plasma cells are enriched at the most superficial sites, visually suggesting that the environment is modulating either the differentiation of the tumor cells or that cells with plasmacytic differentiation preferentially traffic to specific locations. In the OTX system, all 17 original cell suspensions lacked significant numbers of plasma cells, whereas the grafts showed a time-dependent accumulation of plasma cells; in 4 tumors (M, W, C, E), the plasma cell population was definitively clonal, and in another 13 tumors, the plasma cell population was substantially or perhaps entirely derived from nonneoplastic B cells. Similarly, chronic lymphoma leukemia specimens uniformly undergo plasma cell differentiation in a T-cell-dependent xenograft system, despite the relative rarity of plasma cell differentiation in patient samples of this tumor.13 In summary, our data suggest that the plasma cells associated with some NHLs in patients are a result of a microenvironment-induced differentiation of neoplastic B cells, and more generally, that the microenvironment modulates the differentiation to plasma cells in a wide range of mature B-cell neoplasms.
The reliability of the OTX model creates opportunities to perform “personalized” studies of the role of the tumor microenvironment in tumor biology and therapeutic response. Xenograft models of NHL have been typically limited to higher-grade types of NHL in which the TE effects are limited.1 Our work also shows that the OTX model is practical: 17/20 unselected primary specimens engrafted in some manner; 13 of which are lower-grade forms (mantle, marginal, and follicular); engraftment was rapid (histologically detectable at 1-2 weeks) and quantifiable; and mice were viable with no deaths from disease burden for at least 1 month, allowing time for experimental interventions. Because primary tumor specimens are typically the limiting resource for the production of xenografts, much attention has been focused on the development of the genetic mouse models of lymphoma17-21 or xenograft systems that allow for serial transplant.5,22 Despite the utility of both these approaches, neither captures patient-specific, environmental features. Our approach contrasts particularly with the PDX models that allow serial transplant; it is unclear whether these serial transplant models represent selected tumors and to what extent these serially transplanted tumors are dependent on the host or tumor microenvironment. In contrast, we show that the OTX is robust even when used for unselected low-grade NHL specimens.
Our data are consistent with prior work indicating a key role for CD4+ T cells in the survival of normal and malignant cells both in culture and, in the case of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, on transplant.13,23,24 In contrast to prior studies that have emphasized the efficacy of CD4+ T cells to support primary follicular lymphoma specimens in culture,25 we found that in some cases (J, L), tumor-derived CD4+ preferentially supported engraftment of nonneoplastic as opposed to neoplastic B cells. In addition, we found no definitive evidence of an effect of removing and supplementing specific T-cell subsets (T follicular helper and T regulatory cells). We did not examine the dependence on macrophages or dendritic cells because the flow cytometry performed at the time of diagnosis did not contain the relevant markers, and subsequent, research grade, flow studies (at thaw) of selected specimens did not detect these populations. Therefore, our data do not exclude that these cell types could support engraftment in the absence of CD4+ T cells.
Given the time-dependent changes in the tumor composition for the low-grade lymphomas, we did not systematically attempt to develop long-term xenografts or to serially transplant any lymphomas. At times greater than 30 days, xenografts of 37 lymphoma specimens (largely distinct from those described here) often showed a proliferation of T cells at distant sites suggestive of graft-versus-host disease (data not shown). Analogous to the recent study of chronic lymphocytic leukemia xenografts by Patten et al, some mice appeared to lose the tumor graft.13 Our preliminary observations at points beyond a month suggest the engraftment process for low-grade NHLs is inherently unpredictable, as the same tumor specimen could either entirely regress or result in an aggressive process similar to graft-versus-host disease. Regardless, the patient-specific behaviors of the xenografts in the OTX system were highly predictable for times up to 1 month, allowing the OTX model to be used for quantitative assessment of experimental manipulations.
To successfully exploit the OTX model, there are several features potential users should bear in mind. First, although each tumor specimen had a characteristic time course for histologically detectable engraftment (ranging from earliest point examined at 2 days-1 week), all showed visible omental masses by 2 weeks, although some tumors required injection of greater numbers of cells to form a visible mass by 2 weeks (data not shown). In practice, when working with primary specimens, the number of cells needed likely reflects details of the harvest and preparation of individual specimens, which cannot be controlled in a clinical setting. Regardless, the tumor size and composition for the xenografts from each source showed a highly consistent time course across mice up to at least 1 month, allowing quantitative experiments once these parameters are established. Second, a process histologically resembling graft-versus-host disease occurred by 4 weeks in a subset of tumors, occasionally becoming severe by 6 to 8 weeks. This T-cell proliferation, presumably driven by xeno-antigens, likely alters the T-cell composition and activity from that seen in the patient. Furthermore, this T-cell proliferation can be profound and may obscure the neoplastic cells. Third, some components of the TE were not clearly reestablished in the xenografts. For example, no overtly nodular structures were seen and no evidence was detected of follicular dendritic cell networks in any of the FL xenografts, using routine staining for CD21 and CD23. Regardless, the reliability and relative ease of the OTX approach will allow investigators to assess the several parameters needed to optimize the approach.
The ability to reliably xenograft NHL specimens led us to observations regarding what properties are intrinsic to the neoplastic cells, as opposed to those that are modulated by the environment. Given the ability of the xenograft to support nonmalignant B-cell survival in the same specimens, the failure of the FL B cells to survive [despite the presence of t(14;18) and the resultant overexpression of BCL2] indicates that additional environmental factors beyond CD4+ T-cells must be responsible for maintaining FL. The propensity of neoplastic B cells to undergo plasmacytic differentiation indicates that the differentiation of the neoplastic cells are substantially the result of environmental cues. Although much recent attention has focused on how the TE may modify tumor-directed immunity, our observations underscore the potential roles of the TE in directly modulating the properties of tumor cells.
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Lymphoma Research Foundation 285230 (W.R.B.) and National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute Cancer Core grant CA034196 to the Jackson Laboratory (L.D.S.).
Authorship
Contribution: W.R.B. designed research, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; G.N.S., P.J.R., and S.A.S. performed research; J.P.S. analyzed data; J.M.S. designed and performed research and analyzed data; L.D.S. contributed vital reagents and designed research; and R.B.B. and S.H.B. designed research.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: W. Richard Burack, University of Rochester, 601 Elmwood Ave, Box 626, Rochester, NY 14642; e-mail: richard_burack@urmc.rochester.edu.


![Figure 2. Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires tumor-associated non-B cells. A representative experiment using tumor J (FL; 68% B cells in the thawed aliquot of tumor tissue) is shown. The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days postinjection; each panel is a representative section from 1 of 3 mice in each experimental group. Qualitatively similar results were obtained using tumor W (MZL; data not shown). The images show representative sections for each graft, which include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells made up 28% of the specimen, B cells and other cell types made up 72% of the specimen, and viability was higher than 80%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (cell number for injection, 7 × 106 with 94% viability was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. (C) The nonneoplastic T-cell fraction of the B-cell tumor can engraft despite removal of the B cells (cell number for injection, 3 × 106 [85% viable], was matched to the number of non-B cells injected in A). Note that although tumor volume is clearly decreased compared with the mock-depleted specimen (A), there are definitive foci of lymphoid tumor marked by the green arrows (immunohistochemical studies indicate that these foci are >90% T cells, with no evidence of B cells; data not shown). (D) The non-B-cell fraction rescues engraftment of the B-cell fraction. The fractions used in B and C were mixed in appropriate proportions to recapitulate the composition of the mock-depleted specimen (cell number for injection, 1 × 10 7 [91% viable] was matched to the number injected in A). The reconstitution suggests that the failure of B cells to engraft in B is a result of loss of a cellular component in the non-B-cell fraction as opposed to any other nonspecific effect of the bead-based manipulation. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); each treatment with each tumor was assessed with 3 mice; the entire set of studies using tumor J was conducted twice, and the studies of tumor W were conducted once, all with essentially indistinguishable results.)](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/bloodadvances/1/16/10.1182_bloodadvances.2017005892/3/m_advances005892f2.jpeg?Expires=1765473013&Signature=2fPapRX0HD2~DxcXdyHHv5-TYMVm9wFpAoZcDzC6K~xAAfBMWOGHzzzQem0OUSDscQCwOgmHbajXZu4OaqTYHixcGf-8LndvMzcO6NQF5I4W~GjF5OBhYT7JSxSEph7jiHwUPM7vi0lvu5JanzyoDkOquAZgpYkBY-K9Fp6fpEKv997L3VmI~GBmt1MNW85XnxVr2EBLvcjj~B0IQN-b9u4~fzfSDlRISbLgSMU13yha~QvtpXdMBJga9bJrPbfPjPko0JGEeAb~H4mSIxQ9G0pRUNb3w-~A8oxSzsuaDGm9ixkq2da9IcnlLGGUbzWAkMGcvypGnnzGUj0bUWiqbw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)




![Figure 7. Plasma cells that develop in specific tumors are consistently either clonal or nonclonal. Plasma cell clonality can be assessed from the ratio of κ to λ light chain expression (top 4 panels; original magnification ×10 [J] and ×4 [W]). IHC was titered to detect the abundant cytoplasmic expression of light chains that is characteristic of plasma cells and their immediate precursors (plasmablasts) while not detecting the surface expression found on mature B cells. The bulk of plasma cells in specimen J were polyclonal, whereas the plasma cells in specimen W uniformly expressed κ light chain but did not express λ light chain and were therefore clonal. At least 3 xenografts of each specimen were stained, and all showed identical results. Typical plasma cell morphology is seen at high power in both specimens (original magnification ×100; H&E stain).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/bloodadvances/1/16/10.1182_bloodadvances.2017005892/3/m_advances005892f7.jpeg?Expires=1765473013&Signature=U65hJNnHOawFUhsbtWRijkzqSWIufsFHX4RuKhjWpLt5UemUMdNpTRcjnWMu8MAECJd-aU2XmNoZkOMcE9YKo193TFJGRS5lLoIMEOo8MphJ7~~i5PuF5IMygAuyhMb1-Q15CRNEScuFBq19iHO-We0KWQqR36q1QoDsPxDpwuzzytL28WtdVV8~mTVevD3yyBRjyN59UORF3YjgJ4D0ySRh12hds4rsHPaVNvYbqGYct6s~ApUVtqKoHVPGo-P81fisi0GrINO-7TL4mYNI3JPJl5BJqFyZDugChb4scEFOm2~r6PMZasVewXlVSNZgvVrIWn3CGJyHbnbqIVByAA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)


![Figure 2. Engraftment of B-cell tumors requires tumor-associated non-B cells. A representative experiment using tumor J (FL; 68% B cells in the thawed aliquot of tumor tissue) is shown. The flow cytometry shows the cellular composition at the time of injection. The omentum with associated mesentery and organs was harvested at 14 days postinjection; each panel is a representative section from 1 of 3 mice in each experimental group. Qualitatively similar results were obtained using tumor W (MZL; data not shown). The images show representative sections for each graft, which include the omentum (black outline), spleen (yellow), and pancreas (orange). Several examples of the lymphoid tumor within the omental areas are marked with green arrows. (A) Robust engraftment of a tumor that has undergone mock depletion (beads without antibody). After mock depletion and before injection, T cells made up 28% of the specimen, B cells and other cell types made up 72% of the specimen, and viability was higher than 80%. Next, 1 × 107 cells were injected i.p., and mice were necropsied at 14 days. (B) Removal of non-B cells from the specimen ablated engraftment (cell number for injection, 7 × 106 with 94% viability was matched to the B-cell number injected in A). The high-power inset shows that the omental areas consist entirely of adipose tissue with a few small vessels, and no tumor is present. (C) The nonneoplastic T-cell fraction of the B-cell tumor can engraft despite removal of the B cells (cell number for injection, 3 × 106 [85% viable], was matched to the number of non-B cells injected in A). Note that although tumor volume is clearly decreased compared with the mock-depleted specimen (A), there are definitive foci of lymphoid tumor marked by the green arrows (immunohistochemical studies indicate that these foci are >90% T cells, with no evidence of B cells; data not shown). (D) The non-B-cell fraction rescues engraftment of the B-cell fraction. The fractions used in B and C were mixed in appropriate proportions to recapitulate the composition of the mock-depleted specimen (cell number for injection, 1 × 10 7 [91% viable] was matched to the number injected in A). The reconstitution suggests that the failure of B cells to engraft in B is a result of loss of a cellular component in the non-B-cell fraction as opposed to any other nonspecific effect of the bead-based manipulation. (Original magnification ×12.5 and ×400 (insets); each treatment with each tumor was assessed with 3 mice; the entire set of studies using tumor J was conducted twice, and the studies of tumor W were conducted once, all with essentially indistinguishable results.)](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/bloodadvances/1/16/10.1182_bloodadvances.2017005892/3/m_advances005892f2.jpeg?Expires=1765473014&Signature=1ApGL-9oB2V8hG7L5JnnfV068KHz6sD9j2u5HBsIZgc8IbmNsQ5SdpzE~Rjao~n~KmwWuXQ4n7dOBJorjl~g5dXFE8mIV-vnh1Y1Z5yNQst7IeV3fCOn8wI91NCmR1OoyfBiv-d-OL8CblQjVSphq0xZ1dtZMhRYUzqlAUdaSATzSA0tw27Hwbxj7HeUySXFtVDXAYI-FEXu5mOFV9D3dh6Kb-MgpeAYBlapZLSkZow7mz1cKrFDacWDI7YQfutylh~IwAnEva3eTxsVvwcEMXRzhtRzx6~UCmtrSybg-KWr28LNUxpU0zgFHiQ1ZiAeXYIJ8yLJ9AGKuFD27O7zQw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)



![Figure 7. Plasma cells that develop in specific tumors are consistently either clonal or nonclonal. Plasma cell clonality can be assessed from the ratio of κ to λ light chain expression (top 4 panels; original magnification ×10 [J] and ×4 [W]). IHC was titered to detect the abundant cytoplasmic expression of light chains that is characteristic of plasma cells and their immediate precursors (plasmablasts) while not detecting the surface expression found on mature B cells. The bulk of plasma cells in specimen J were polyclonal, whereas the plasma cells in specimen W uniformly expressed κ light chain but did not express λ light chain and were therefore clonal. At least 3 xenografts of each specimen were stained, and all showed identical results. Typical plasma cell morphology is seen at high power in both specimens (original magnification ×100; H&E stain).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/bloodadvances/1/16/10.1182_bloodadvances.2017005892/3/m_advances005892f7.jpeg?Expires=1765473014&Signature=HzjPJqNZPY~v7N7vIe1FI5vTT~ipbLw1INcV4i97lFXFntlkyiA3GCQERpB4TioOs8p2FpzRvtmxlY0oksEhu3uaRqYJQ8puqIWj65GUgCUfAlCr4VMuEI5FAM-DrkzIUiKO0rF7GIlM1BO~sojQQe-iTbCWVMHY~JGwAlgs5RNPDXV1W0hkA-m-dMm5i9YQ0aF9e6y4r21wCai6y-bneJoImeTFnp~kuErBW8OheTXgwHvhcy38X--KIMppM7d43Z5FYUa0et0g3DrwgOHoieHhSYhItJGnJhh4cCYq7c4anRYLLUG7tN2B6gaF04ecXCqtB8y3lycyHDMQPquZOA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)