Abstract
Hemophilic arthropathy (HA) is characterized by joint damage following recurrent joint bleeds frequently observed in patients affected by the clotting disorder hemophilia. Joint bleeds or hemarthroses trigger inflammation in the synovial tissue, which promotes damage to the articular cartilage. The plasminogen activation system is integral to fibrinolysis, and the urokinase plasminogen activator, or uPA in particular, is strongly upregulated following hemarthroses. uPA is a serine protease that catalyzes the production of plasmin, a broad-spectrum protease that can degrade fibrin as well as proteins of the joint extracellular matrix and cartilage. Both uPA and plasmin are able to proteolytically generate active forms of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). The MMPs are a family of >20 proteases that are secreted as inactive proenzymes and are activated extracellularly. MMPs are involved in the degradation of all types of collagen and proteoglycans that constitute the extracellular matrix, which provides structural support to articular cartilage. The MMPs have an established role in joint destruction following rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They degrade cartilage and bone, indirectly promoting angiogenesis. MMPs are also implicated in the pathology of osteoarthritis (OA), characterized by degradation of the cartilage matrix that precipitates joint damage and deformity. HA shares a number of overlapping pathological characteristics with RA and OA. Here we discuss how the plasminogen activation system and MMPs might exacerbate joint damage in HA, lending insight into novel possible therapeutic targets to reduce the comorbidity of hemophilia.
Hemophilic arthropathy (HA)
Hemophilia A and B are X-linked diseases that affect genes controlling the production of coagulation proteins factor VIII and factor IX. This causes a spectrum of deficiency of coagulation factors resulting in impaired hemostasis. Severe hemophilia is associated with spontaneous bleeding in various anatomical locations, including joints, muscle, and brain parenchyma. In the event of trauma, impaired coagulation also results in increased severity of bleeding accompanied by the associated complications if left untreated.1
Hemophilia was conventionally managed by the replacement of coagulation factors aimed at reducing bleeding episodes. Recent development has expanded the options of management. Extended half-life coagulation factors2,3 have decreased the frequency of treatment required, potentially improving adherence to treatment and improving the quality of life in people with hemophilia. The bispecific antibody emicizumab that does not replace factor VIII but rather replaces the activity of factor VIII in the process of coagulation4 offers additional options, especially in cases of management in people with hemophilia who develop endogenous inhibitors.
HA is the term describing the joint destruction caused by repeated damage from recurrent bleeding into joints (hemarthroses). HA causes significant joint deformity, leading to reduced quality of life in people with hemophilia.5 Although access to prophylaxis has decreased the frequency of HA because reduced joint bleeding preserves joint health,6 joint damage can still result from only a small number of hemarthroses.7 Therefore, it remains prominent in Europe and the United States, where fair access to replacement therapy is routinely practiced on a prophylactic basis. Treatment for HA continues to be an unmet need in the developing world with poor access to coagulation factor replacement.8 There are no effective treatments to minimize the adverse events following bleeding into the joint or to prevent the development of arthropathy. Targeting these mechanisms separately but concurrently to the bleeding events could provide a “second line of defense” to produce better outcomes in the care of people with hemophilia.9
The current understanding of the pathogenesis of HA is that hemarthroses result in hemosiderin deposition that triggers inflammatory and enzymatic processes and fibrosis, leading to cartilage damage. Repetitive bleeding in the joints creates a microenvironment wherein dysregulation of hemostasis causes unregulated fibrinolysis while blood products interact with and stimulate synovial fibroblasts. These cells, in turn, secrete proinflammatory cytokines as well as collagen-degrading proteases that enhance cartilage damage.10 In this review, we will discuss how altered hemostasis as well as elevated proteolytic activity as a result of synovial inflammatory changes might be key events underpinning cartilage damage in HA.
Synovial joints
Synovial joints consist of a membranous structure, the synovium, that covers the surface of the joint capsule, intraarticular tendons, and ligaments but spares articular cartilage. The synovium is divided into the synovial lining (intima) and the sublining (subintima). The intima is made up of synoviocytes, a heterogeneous cell population consisting of mainly type A (macrophage-like) and type B (fibroblast-like) synoviocytes. The type A synoviocytes scavenge blood and other substances from the joint space, while type B synoviocytes synthesize specialized matrix constituents, including hyaluronan, collagens, and fibronectin, for the subintima and synovial fluid.11 The subintima is made up of fibrovascular connective tissue that provides oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors to the synovium and the articular cartilage.12 It is likely to be the main site of articular bleeding.13
The bone surfaces that abut to form a synovial joint are encapsulated by a thin layer of articular cartilage that consists of a dense extracellular matrix (ECM) with highly specialized cells called chondrocytes. The ECM is made up of the basement membrane underlying endothelial and epithelial cells and the interstitial matrix, a scaffold-like structure that maintains tissue integrity.14 The ECM of the articular cartilage is made up of 90% to 95% collagen II, which is intertwined with proteoglycans to form fibrils and fibers. The basement membrane is also composed of collagen IV,15 while the interstitial matrix is made up of collagen I, III, V, and VI.16
Haemarthroses tend to target larger synovial joints and are triggered by a combination of mechanical and enzymatic processes.17 Synovial tissue actively clears waste from the synovial cavity, including blood that enters the cavity during a joint bleed. However, clearance of blood and the hemoglobin breakdown product hemosiderin also triggers synovial proliferation and hypervascularization of the subintima, promoting inflammation and neoangiogenesis, which increases the risk of subsequent bleeds.18,19 In vitro studies by Wen and colleagues demonstrated iron can increase human synovial fibroblast proliferation as well as expression of proto-oncogene c-myc expression.20 Hakyoban and colleagues later demonstrated increased expression of p53-binding protein mdm2 in mouse joints with hemophilic synovitis. This has led to the conclusion that iron derived from red cells accumulating after an intraarticular bleed facilitates synoviocyte proliferation by blockade of transcription factors c-myc and mdm2, leading to the formation of synovial pannus.21
Under normal conditions, the cartilage does not have a blood or nerve supply. Although metabolically inactive after having established the original cartilage matrix, chondrocytes are not entirely quiescent and receive oxygen and nutrients through the synovial fluid.22 When the synovial fluid is contaminated with red blood cells, plasma, and other constituents from the blood, including white blood cells, a range of inflammatory processes are initiated.11,23 As a result, chondrocytes are exposed to proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors as well as iron-catalyzed reactive oxygen species that induce chondrocyte apoptosis, making articular cartilage the primary target for the development of HA.18
Fibrinolytic and proteolytic mechanisms of joint damage in HA
Joint bleeding in hemophilia occurs due to defective thrombin generation and relatively low tissue factor expression. Subsequent delayed bleeding occurs due to malformed fibrin structures forming clots that are unstable and susceptible to premature degradation by fibrinolytic enzymes that are part of the plasminogen activation system.24
Plasminogen activation system
The fibrinolytic pathway describes the coordinated breakdown of fibrin formed as the result of coagulation. In this pathway, substrates, activators, inhibitors, and cofactors interact to remove fibrin deposits.25 Plasmin is the major fibrinolytic protease and circulates as a zymogen plasminogen that is converted to active plasmin by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). The primary substrate fibrin binds plasminogen and tPA on its surface to enhance plasmin generation, mainly in circulation. tPA significantly increases catalytic efficiency for plasminogen in the presence of fibrin. uPA is another serine protease that acts on plasminogen but is also involved in ECM degradation.26 uPA binds to urokinase receptor (uPAR) for enhanced activation of plasminogen.27 Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) blocks fibrinolysis by removing C-terminal lysine residues on partially degraded fibrin, which serve as a cofactor for plasminogen activation. Plasminogen activation is also inhibited by PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor 1) or by α2AP (α2 antiplasmin) or α2 MG (α2 macroglobulin).26 Remarkably, plasminogen expression is not seen in articular cartilage but is strongly detected in synovial fluid28 ; uPA is also highly expressed in synovial fluid and implicated in various pathological mechanisms of arthritis,29 as discussed in subsequent sections.
Human synovial membranes typically have an anticoagulant milieu defined by low levels of tissue factor (TF) and high levels of TF pathway inhibitor to dampen the extrinsic coagulation pathway.30 In patients with hemophilia, the synovial fluid contains high levels of thrombomodulin, possibly because neutrophil activation during chronic synovitis promotes secretion of thrombomodulin. Thrombomodulin typically binds thrombin in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio and then activates protein C, a zymogen that inhibits blood clotting via active coagulation factor V (FVa) and FVIIIa degradation. Accordingly, elevated thrombomodulin in HA synovial fluid was shown to inhibit thrombin generation in plasma samples from normal controls ex vivo.31
In vitro studies have shown that TAFI activation is defective in plasma from hemophilia patients, and therefore, there is a deficiency in the intrinsic feedback loop for thrombin generation, especially due to low TF levels. Lack of TAFI activation, in turn, enhances fibrinolysis and consequent clot instability leading to premature clot lysis.32 In F8−/− mice subjected to hemarthroses, TAFI activation is impaired, which leads to a promotion of uPA-induced fibrinolysis, a key event causing joint bleeding. This suggests that maintenance of clots is as important as the promotion of clot formation when considering the development of therapies for HA.24 In vitro, chondrocytes produce uPA constitutively, while synoviocytes upregulate uPA following stimulation with proinflammatory cytokines, in particular, interleukin-6 (IL-6).33 Joint bleeding in HA has been shown to boost the production of uPA and, therefore, plasmin by synoviocytes. While this naturally promotes bleeding, uPA can bind to uPAR to stimulate chemotaxis, angiogenesis, proliferation, and bone and cartilage damage.34 Indeed, intraarticular antiplasmin but not direct inhibition of uPA by amiloride is protective in a mouse model of joint bleeding by reducing synovitis and cartilage damage.35 Plasmin itself is a broad-spectrum protease that can catabolize components of the ECM, including fibronectin, glycoproteins, and proteoglycans. Plasmin can also activate numerous matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).27 Collectively, this leads us to hypothesize that uncontrolled uPA-mediated plasminogen activation could be a trigger for proteolytic activation and MMP activation, in particular, in hemophilic joints.
Activity and regulation of MMPs in joints
MMPs are zinc endopeptidases crucial for extracellular matrix turnover and usually consist of a propeptide and a zinc-dependent catalytic domain. MMPs are synthesized as preproenzymes, with the signal peptide removed during translation to yield pro-MMPs. Tissue and plasma proteases can cleave the propeptide to produce active MMPs, but they can also be activated by bacterial proteinases, or MMP intermediates, other MMPs, reactive oxygen, and chemical agents.36 MMPs together with disintegrin–metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTSs) have varied and sometimes overlapping functions in regulating cell migration, differentiation, growth, inflammation, neovascularization, and apoptosis.37
MMPs are classified into groups based on their substrate specificity. There are 23 MMPs in humans that mainly function to degrade or remove ECM components. Collagenases (MMPs 1, 8, and 13) degrade fibrillar collagen types I, II, and III, while stromelysins (MMP-3 and -11) break down proteoglycans as well as nonhelical regions of collagens. Collagenases and stromelysins have broader substrate specificity than gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) that specifically catabolize gelatin (degraded collagen). Collagen types IV, V, and XI are gelatinase substrates.38 Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are natural endogenous inhibitors of MMPs. TIMP-1 inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9, and TIMP-2 inhibits proMMP-2, although low levels of TIMP-2 are needed to activate MMP-2. TIMP-3 is the natural inhibitor of MMP-2 and -9, while TIMP-4 inhibits all MMPs.39
In the joints, MMPs facilitate the remodeling of the chondrocyte ECM; under physiological conditions, a delicate balance in the expression of MMPs and TIMPs regulates the remodeling and degradation of the ECM. Arthritis appears to tip this balance by promoting the degradative potential of MMPs within the joint environment leading to chronic joint destruction.37 IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-15, IL-17, tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β, vascular-derived endothelial growth factor (VEGF), histamine, EMMPRIN/CD147, serum amyloid S, and β-microglobulin are all known stimulators of MMPs in the joint.40 Chubinskaya and colleagues showed that MMP-1, -2, -13, and -14 mRNA expression is detectable in adult human cartilage while MMP-3 and -8 are upregulated in damaged cartilage.41 MMP-2, -11, and -19 are constitutively expressed in the synovium.36
MMP-1 is an interstitial collagenase (collagenase 1) produced by synovial cells within the joint, while MMP-2 is secreted by stromal cells under the synovial cell layer and degrades aggrecan, proteoglycan, and collagen I, II, and III. Being highly ubiquitous, MMP-2 also regulates angiogenesis and tissue repair and regeneration. MMP-2 is constitutively expressed by synovial fibroblasts and has a key role in the degradation of ECM and other cellular proteins in the joint.42 Unlike several other MMPs, its transcription is not induced in response to TNF-α and IL-1; rather, it is mostly regulated posttranslationally. Although MMP-2 is also produced as a proenzyme, its activation is regulated locally by MMP-14 activation and TIMP-2 inhibition.43 MMP-14 converts the 72 kDa proMMP-2 to an intermediate 64 kDa protein, which is then activated by plasmin following conversion to a 62 kDa molecule.44 MMP-3 or stromelysin-1 specifically degrades ECM components, including elastin, fibronectin, laminin, collagen III, IV, IX, and X, and cartilage proteoglycans including versican and aggrecan.38 Pro–MMP-3 can be activated by MT-MMPs, and active MMP-3 can, in turn, activate MMP-1, -7, and -9.38 MMP-7 (matrilysin) cleaves proteoglycans, fibronectin, and elastin. Active MMP-7, in turn, also activates pro-MMPs 1, 2, and 7. MMP-8 is best known as neutrophil collagenase and, akin to MMP-9, is secreted by neutrophils. Macrophages and synovial cells are additional sources of MMP-9. Macrophages also release MMP-12, which can degrade collagen type IV, proteoglycan, and other ECM proteins. Chondrocytes produce MMP-13 that specifically catabolizes collagen II and also has the ability to degrade collagen I/III and aggrecan.39
Current knowledge about the role of MMPs in HA
A recent paper showed increased levels of MMP-1, -2, and -3 in ligament tissues of patients with HA when compared with similar tissues from patients with OA.45 In F8−/− rats, induction of hemarthroses led to serological elevations in markers of basement membrane turnover, alterations in the interstitial matrix, and cartilage degradation evidenced by accumulation of degraded collagen II. Given that ECM proteolysis is primarily regulated by MMPs, this indicates that MMPs are strongly involved in cartilage destruction after HA.46 Sogi and colleagues used an F8 independent model of HA to document a critical role for MMPs in the pathophysiology of this condition. They developed a rat model in which joints were first immobilized for a number of days and then injected with blood and demonstrated that when joint hemorrhage was mimicked, articular cartilage degeneration occurred to chondrocyte destruction. Increased iron deposition in the synovium together with synovial inflammation were evident until 8 weeks after blood injection, and all these events were associated with increased expression of MMP-8 and MMP-13 in the cartilage.47 Further, Carrulli and colleagues found that intraarticular hyaluronic acid injections in knee joints of patients with HA had a therapeutic benefit, the possible mechanism for which is via blockade of MMP-13.48 Acharya and colleagues have documented a fourfold increase in MMP-9 as well as other proangiogenic factors such as VEGF, and HIF-1α in peripheral blood of patients with HA. MMP-9+ cells were detected in the vascular endothelium, and moderate expression was seen in parts of the synovium.49
While there is limited data on the role of MMPs in HA, it is evident that unregulated MMP activation has the potential to cause joint destruction. In support of this hypothesis is the wealth of data showing the role of this protease system in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)37 and osteoarthritis (OA).50 Although the specific sites and initiating mechanisms might differ between HA, OA, and RA, the metabolic and proinflammatory responses appear to be similar,51 whereby a proinflammatory cytokine trigger catabolic processes that bring about joint damage. These apparent similarities are detailed in Table 1, together with a summary of the known involvement of MMPs in each condition.
Comparison between RA, OA, and HA
| . | RA . | OA . | HA . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Inflammatory joint lesions caused due to an autoimmune response (e.g. citrullination, infection). “Second hit” may be required. Antigen presentation promotes antibody generation in B cells. Reviewed by Smolen et al.77 | Degenerative joint injury is caused by multiple factors, including aging, direct injury, and biomechanical overloading. These events alter articular cartilage, subchondral bone, ligaments, capsule, and synovial membrane that culminate in joint failure. Reviewed by Martel-Pelletier et al.78 | Degenerative joint damage as seen in OA as well as chronic inflammation as in RA. Synovial lesions triggered by iron deposition due to bleeding in the joint that activates proteases and inflammatory cytokines. Reviewed by Zhu et al.79 |
| Intraarticular mechanisms | 1) Synovial tissue proliferation as an inflammatory response, resulting in the production of IL1, IL-6, TNF, MMPs, prostaglandins, and RANKL. Cartilage invasion from invasive synovial tissue (pannus) occurs. 2) Cartilage damage is caused by proteases (eg, MMPs, aggrecanases, collagenases, and stromelysins). 3) Propagation of inflammation by antigen-presenting cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages, producing CCL19, CCL21, TNF, IL1, IL6, and RANKL. 4) Bone erosion via activation of osteoclasts by RANKL by IL1 and IL6. Reviewed by Smolen et al.77 | 1) Chondrocyte and synovial activation through cytokines, including DAMPs, IL-1β, CCL19, TNFα, IL15, and MCP-1. 2) Activated chondrocytes produce proteases, including MMPs, aggrecanases, serine, and cysteine proteinases. Extracellular matrix fragments further stimulate synovial cells. 3) Bone remodeling through TGF β, BMP2, IL6, IL8, and RANKL results in osteophyte formation. Reviewed by Martel-Pelletier et al.78 | 1) Synovial tissue is stimulated through iron to produce IL1β, IL6, TNFα, CCL2 and CXCL1, MMPs, and aggrecanases. 2) Iron causes direct damage to cartilage by reacting with H2O2 to produce reactive oxygen species, in addition to propagating inflammation through IL1β, IL6, and TNFα. Subsequently, monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils, and activated T cells are recruited to the site of bleeding. 3) Tissue hyperplasia promotes neoangiogenesis. The instability of new vessels formed further increases the risk of intraarticular hemorrhage. 4) Bone degeneration progresses more rapidly and severely than RA and OA. Bone turnover is likely mediated by RANKL/ osteoprotegerin and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Reviewed by Zhu et al.79 |
| MMP involvement | |||
| MMP-1 | Levels correlate with the degree of synovial inflammation in the joint in RA.80 | Upregulated in joint fluid but not as high as that seen in RA.42 High expression in chondrocytes cultured from OA patient cartilage explants.81 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 |
| MMP-2 | Patients with erosive disease have higher synovial active MMP-2 levels, strongly implicating MMP-2 in synovial tissue as a marker for aggressive synovitis.43 Although MMP-2 is upregulated in arthritic joints, MMP-2–deficient mice are more susceptible to antibody-induced arthritis, indicating that MMP-2 may play a suppressive role in the progression of arthritis, possibly due to its ability to cleave and inactivate IL-17, that regulates migration and invasion and inflammation of RA synovial fibroblasts.57 | MMP-2 expression in the ECM of subchondral bone during OA causes degradation of type I and other fibrillar collagens, and increased collagen turnover potentiates cartilage damage that affects joint morphology, thereby worsening OA.82 Immunopositive staining in plica and pannus-like tissue of late-stage OA knee joints.50 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 |
| MMP-3 | Strongly expressed in the joint cavities in patients with RA.36 Correlates with disease severity.74 Upregulated in the early–mid stages of RA.74 | Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 Expression induced after knee injury in F8−/− mice.84 |
| MMP-8 | Protective, as deficiency leads to enhanced synovial inflammation and bone degradation in a mouse model.85 | Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 | Increased expression in an autologous blood injection mouse model of HA.47 |
| MMP-9 | Mice deficient in MMP-9 are less severely affected in a model of antibody-induced arthritis.57 | Increased; MMP-9 levels correlate with synovial fluid VEGF levels implicating MMP-9 in the regulation of angiogenesis during OA.42 Immunopositive staining in plica and pannus-like tissue of late-stage OA knee joints.50 | High and moderate expression in the vascular endothelium and in synovial cells, respectively, in human tissue.49 |
| MMP-10 | Strongly expressed in synovial fluid.63 Under inflammatory conditions, both synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes express MMP-10.63 Further able to activate procollagenases, including MMP-1, -8, and -13, which also promote cartilage degradation.63 | Strongly expressed in synovial fluid.63 | No involvement documented to date. |
| MMP-13 | Implicated in RA-associated joint disease—degrades collagen II and aggrecan.36 MMP-13 increased in joint fluid of RA patients.74 High immunopositivity staining in synovium correlates with severity of inflammation.75 Suppression associated with joint protection in a mouse model.86 | Critical role in induction and pathogenesis. Degrades articular cartilage and triggers synovial hyperplasia, synovitis with marked immune cells infiltration in synovial joints, as well as cartilage erosion.40 Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 Associated with structural cartilage damage in a rodent model of OA.87 | Expression induced after knee injury in F8−/− mice.84 |
| MMP-14 (MT-MMP1), activator for pro–MMP-2 | Significantly higher, and TIMP-2 expression was reduced in synovial tissue.43 | Highly expressed in chondrocytes during OA.62 | No involvement documented to date. |
| . | RA . | OA . | HA . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Inflammatory joint lesions caused due to an autoimmune response (e.g. citrullination, infection). “Second hit” may be required. Antigen presentation promotes antibody generation in B cells. Reviewed by Smolen et al.77 | Degenerative joint injury is caused by multiple factors, including aging, direct injury, and biomechanical overloading. These events alter articular cartilage, subchondral bone, ligaments, capsule, and synovial membrane that culminate in joint failure. Reviewed by Martel-Pelletier et al.78 | Degenerative joint damage as seen in OA as well as chronic inflammation as in RA. Synovial lesions triggered by iron deposition due to bleeding in the joint that activates proteases and inflammatory cytokines. Reviewed by Zhu et al.79 |
| Intraarticular mechanisms | 1) Synovial tissue proliferation as an inflammatory response, resulting in the production of IL1, IL-6, TNF, MMPs, prostaglandins, and RANKL. Cartilage invasion from invasive synovial tissue (pannus) occurs. 2) Cartilage damage is caused by proteases (eg, MMPs, aggrecanases, collagenases, and stromelysins). 3) Propagation of inflammation by antigen-presenting cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages, producing CCL19, CCL21, TNF, IL1, IL6, and RANKL. 4) Bone erosion via activation of osteoclasts by RANKL by IL1 and IL6. Reviewed by Smolen et al.77 | 1) Chondrocyte and synovial activation through cytokines, including DAMPs, IL-1β, CCL19, TNFα, IL15, and MCP-1. 2) Activated chondrocytes produce proteases, including MMPs, aggrecanases, serine, and cysteine proteinases. Extracellular matrix fragments further stimulate synovial cells. 3) Bone remodeling through TGF β, BMP2, IL6, IL8, and RANKL results in osteophyte formation. Reviewed by Martel-Pelletier et al.78 | 1) Synovial tissue is stimulated through iron to produce IL1β, IL6, TNFα, CCL2 and CXCL1, MMPs, and aggrecanases. 2) Iron causes direct damage to cartilage by reacting with H2O2 to produce reactive oxygen species, in addition to propagating inflammation through IL1β, IL6, and TNFα. Subsequently, monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils, and activated T cells are recruited to the site of bleeding. 3) Tissue hyperplasia promotes neoangiogenesis. The instability of new vessels formed further increases the risk of intraarticular hemorrhage. 4) Bone degeneration progresses more rapidly and severely than RA and OA. Bone turnover is likely mediated by RANKL/ osteoprotegerin and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Reviewed by Zhu et al.79 |
| MMP involvement | |||
| MMP-1 | Levels correlate with the degree of synovial inflammation in the joint in RA.80 | Upregulated in joint fluid but not as high as that seen in RA.42 High expression in chondrocytes cultured from OA patient cartilage explants.81 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 |
| MMP-2 | Patients with erosive disease have higher synovial active MMP-2 levels, strongly implicating MMP-2 in synovial tissue as a marker for aggressive synovitis.43 Although MMP-2 is upregulated in arthritic joints, MMP-2–deficient mice are more susceptible to antibody-induced arthritis, indicating that MMP-2 may play a suppressive role in the progression of arthritis, possibly due to its ability to cleave and inactivate IL-17, that regulates migration and invasion and inflammation of RA synovial fibroblasts.57 | MMP-2 expression in the ECM of subchondral bone during OA causes degradation of type I and other fibrillar collagens, and increased collagen turnover potentiates cartilage damage that affects joint morphology, thereby worsening OA.82 Immunopositive staining in plica and pannus-like tissue of late-stage OA knee joints.50 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 |
| MMP-3 | Strongly expressed in the joint cavities in patients with RA.36 Correlates with disease severity.74 Upregulated in the early–mid stages of RA.74 | Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 | Expression detected in ligaments of patients.45 Expression induced after knee injury in F8−/− mice.84 |
| MMP-8 | Protective, as deficiency leads to enhanced synovial inflammation and bone degradation in a mouse model.85 | Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 | Increased expression in an autologous blood injection mouse model of HA.47 |
| MMP-9 | Mice deficient in MMP-9 are less severely affected in a model of antibody-induced arthritis.57 | Increased; MMP-9 levels correlate with synovial fluid VEGF levels implicating MMP-9 in the regulation of angiogenesis during OA.42 Immunopositive staining in plica and pannus-like tissue of late-stage OA knee joints.50 | High and moderate expression in the vascular endothelium and in synovial cells, respectively, in human tissue.49 |
| MMP-10 | Strongly expressed in synovial fluid.63 Under inflammatory conditions, both synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes express MMP-10.63 Further able to activate procollagenases, including MMP-1, -8, and -13, which also promote cartilage degradation.63 | Strongly expressed in synovial fluid.63 | No involvement documented to date. |
| MMP-13 | Implicated in RA-associated joint disease—degrades collagen II and aggrecan.36 MMP-13 increased in joint fluid of RA patients.74 High immunopositivity staining in synovium correlates with severity of inflammation.75 Suppression associated with joint protection in a mouse model.86 | Critical role in induction and pathogenesis. Degrades articular cartilage and triggers synovial hyperplasia, synovitis with marked immune cells infiltration in synovial joints, as well as cartilage erosion.40 Immunopositive chondrocytes are visible in the superficial zone in human articular cartilage tissue.83 Associated with structural cartilage damage in a rodent model of OA.87 | Expression induced after knee injury in F8−/− mice.84 |
| MMP-14 (MT-MMP1), activator for pro–MMP-2 | Significantly higher, and TIMP-2 expression was reduced in synovial tissue.43 | Highly expressed in chondrocytes during OA.62 | No involvement documented to date. |
These conditions have different triggers and hypothesized initiation factors. However, an overlapping pathology is seen through inflammatory processes, resulting in changes to synovium, cartilage, and bone that result in an increase in similar tissue-modifying proteins that lead to articular cartilage and bone damage as a common consequence.
CCLs, chemokine ligand; MCP1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor κ B ligand.
MMPs promote joint destruction in OA and RA
RA is a polyarthritis affecting small articular joints and also has wide-ranging multiorgan complications.52 In this complex disease that involves multiple mechanisms, synovial inflammation, hypertrophy, and invasion are the main features that then result in pannus formation and cartilage degradation, culminating in joint destruction.53 The major population of cells driving the proinflammatory actions in RA synovitis is macrophages, through increasing TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, IL-15, IL-23, and IL-8, and complement activation54,55 driving a T-cell response. The inflamed synovium becomes an invasive structure accompanied by the influx of monocytes, dendritic cells, mast cells, T helper cells, and plasma cells. Loss of fibrillar (collagens) and nonfibrillar components of the ECM mediated by proteolytic enzymes, including MMPs and aggrecanases with disintegrin domains, causing ECM degradation in cartilage, bone, and soft tissues of the joint is crucial to joint destruction in RA.56 In RA, MMPs have been directly implicated in synoviocyte migration and invasion, synovial hypertrophy-related neoangiogenic responses, and destructive synovitis.38 MMP-3 is strongly expressed in the joint cavities in patients with RA. MMP-14, an activator for pro-MMP-2, has been shown to be significantly higher, and TIMP-2 expression is reduced in synovial tissue of RA patients. In the same study, patients with erosive disease had higher synovial active MMP-2 levels, strongly implicating activated MMP-2 levels in synovial tissue as a marker for more aggressive synovitis.43 Mice deficient in MMP-9 are less severely affected in a model of antibody-induced arthritis. Although MMP-2 is upregulated in arthritic joints, MMP-2 deficient mice are more susceptible to antibody-induced arthritis, indicating that MMP-2 may play a suppressive role in the progression of arthritis, possibly to due to its ability to cleave and inactivate IL-17, which regulates migration and invasion and inflammation of RA synovial fibroblasts.57 Other MMPs strongly implicated in RA-associated joint disease include MMP-13, which degrades collagen II and aggrecan, and MMP-15, which activates proMMP-2 and proMMP-13 and is involved in TNFα processing.36
OA is traditionally considered a degenerative disease of joints58 that progresses slowly initially, changing the joint by damaging cartilage and bone.59 OA is initiated by aberrant chondrocyte responses in articular cartilage. These chondrocytes produce MMPs that degrade the pericellular and interterritorial proteins of the cartilage ECM.40 While a role for the ADAMTS enzymes in OA progression is well known, accumulating data has implicated MMP gene upregulation in the destruction of articular cartilage and subsequent joint failure. These data include reports of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13, and MT1-MMP in sera and synovial fluid of OA patients. The same proinflammatory cytokines that have a role in RA and HA (ie, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) are also elevated in sera and synovial fluid of OA patients, further affirming the mechanistic similarities in all 3 conditions.38 Both IL-1β and TNF-α have been shown to stimulate chondrocytes and synoviocytes to produce MMPs that promote ECM degradation in explant cultures of articular cartilage sourced from OA patients who underwent arthroplasty.60
MMP-3 is abundant in the synovium and cartilage of knee joints and pannus-like tissue of OA patients and, unlike in the case of RA, stays elevated during the course of the disease. It is known to promote angiogenesis within cartilage tissue and also causes synovitis due to cartilage degradation and consequent inflammation. Synovitis, in turn, triggers further expression of MMP-3, thereby worsening the progression of OA.61 MMP-13 also has a critical role in the induction and pathogenesis of OA. It degrades articular cartilage and triggers synovial hyperplasia, synovitis with marked immune cells infiltration in synovial joints, as well as cartilage erosion.40
MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression are increased in the cartilage of patients with OA and are associated with chondrocyte IL-1α secretion. That MMP-9 concentrations correlate with synovial fluid VEGF concentrations further suggests a role for MMP-9 in the regulation of angiogenesis during OA.42 MMP-2 expression in the ECM of subchondral bone during OA causes degradation of type I and other fibrillar collagens, and increased collagen turnover potentiates cartilage damage that affects joint morphology, thereby worsening OA. MT-MMP 1, an activator of MMP-2, is also highly expressed in the chondrocytes during OA.62
While MMP-9 correlates with MMP-13 concentrations, and both are reported to be similar in synovial fluid from RA and OA patients, total MMP-1 appears to be significantly higher in the RA group when compared with the OA group.42 MMP-10 is strongly expressed in synovial fluid extracted from knee joints of both RA and OA patients. MMP-10 is further able to activate procollagenases, including MMP-1, -8, and -13, which also promote cartilage degradation. Together with findings that under inflammatory conditions, both synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes express MMP-10, this strongly implicates MMP-10 in the cartilage degradome during arthritis.63 Table 1 provides a summary of the known role of MMPs in the pathogenesis of RA and OA and the current literature providing evidence for their involvement in HA.
uPA and plasmin trigger MMP activation in RA and OA
The uPA/plasmin system has been directly implicated in the pathology of RA and OA. uPA is significantly upregulated in the synovial lining area of proliferative and invasively growing synovial tissue in RA patients and is virtually undetectable in synovial extracts of OA patients. However, t-PA antigen levels have an opposite expression pattern, suggesting that reduced t-PA–mediated plasminogen activation might cause a delay in intraarticular fibrin clearance in RA patients.64 Jin and colleagues showed that injection of uPA into the joints of healthy mice induces arthritis with significant synovial inflammation and some cartilage destruction, suggesting a central role of uPA in causing arthritis.
Pro MMPs 1, 3, 7, 9, 10, and 13 are known to be activated by plasmin in vitro.27 uPA has also been shown to activate pro–MMP-2 in vitro.65 Plasmin is a potent MMP-3 activator through sequential proteolysis of the pro–MMP-3 peptide. In a purified system, MMP-3 can, in turn, hydrolyze uPA and plasminogen to downregulate cell-associated plasmin activity.66 Stimulation of synovial fibroblasts with IL-6 increases uPA levels but also IL-1, which in turn stimulates the production of MMP-1 and MMP-3.33
IL-α, TNF-α, and LPS treatment of cells obtained from hypertrophic synovia in knees of patients with early OA undergoing arthroscopy triggered abundant MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion. That this process could be blocked by the plasmin inhibitor aprotinin strongly implicates a role for plasmin-mediated MMP-2 and MMP-9 activation in OA.67
Kim and colleagues showed that total MMP-1 is upregulated joint fluid from RA and OA patients while MMP-13 is selectively increased in the RA group; this increase correlated with an increase in MMP-9 and uPA. As pro–MMP-13 is a plasmin substrate, there is a strong case for uPA-mediated plasminogen activation in the pathogenesis of RA.68 Accordingly, uPA-deficient and plasminogen-deficient mice have both been found to be resistant to collagen II antibody-induced arthritis. MMP-3, MMP-9, and MMP-13 expression levels were shown to be increased in joints from arthritic wild-type mice when compared with uPA−/− mice,69 demonstrating a correlation between uPA levels and MMP gene expression. For plasminogen-deficient animals, the phenomenon could be reversed by injecting mice with plasminogen, indicating that active plasmin is a trigger for pathogenic joint inflammation in this model.70 However, the protective role of uPA has also been described in antigen-induced arthritis (AIA), whereby uPA-deficient (uPA−/−) mice showed increased intraarticular fibrin deposition and more severe disease.71 Hence there is mounting evidence that uPA mediated plasminogen activation and caused MMP activation, thereby precipitating cartilage damage in both RA and OA.
Plasminogen activation and MMP-mediated joint destruction as a plausible pathway for joint damage in HA
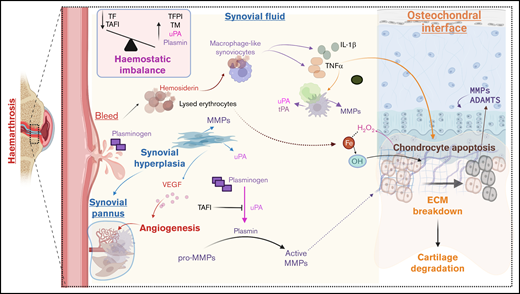
While the above literature supports the role of protease activation in the pathophysiology of HA, it remains to be studied in experimental and clinical settings. However, there are several known features of HA that corroborate this hypothesis, as illustrated in Figure 1. Bleeding into the joint activity creates the influx of hemosiderin that catalyzes the production of reactive oxygen species, leading to chondrocyte apoptosis. Type A synoviocytes incorporate hemosiderin and produce proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α, leading to an intraarticular cytokine storm that worsens cartilage and bone damage. These cytokines promote the recruitment and activation of monocytes and macrophages, which are known to stimulate the production of nitric oxide and proteases, including MMPs, uPA, etc.13 A hemostatic imbalance characterized by low TF and high TAFI levels would lead to uncontrolled uPA and tPA activity.24 The influx of blood would expose the synovium to abundant quantities of plasminogen,72 thereby creating an ideal environment for uPA-mediated plasminogen activation, resulting in plasmin production. Fibrin deposition is commonly observed in the cavity of inflamed joints,73 and being a cofactor for tPA-mediated plasminogen activation, significant plasmin generation would occur. uPA and plasmin can both cleave pro-MMPs to produce active MMPs.29 Based on the arthritis literature, MMP-1 and MMP-3 could be produced by synovial lining cells, and MMP-2 is secreted by stromal cells in the sublining synovial layer. Neutrophil infiltration could lead to the production of MMP-8 and MMP-9, while macrophage-like cells and synovial cells could produce MMP-9.74 Activation of cytokines such as IL-1 and TNFα due to hemosiderin uptake by macrophage-like synoviocytes would lead to the release of MMP-1063 and MMP-13,47,75 collagenases capable of catabolizing articular cartilage. Chronic inflammation of the synovial membrane also leads to synovial hypertrophy and triggers an increase in blood flow due to increased oxygen demand to help clear debris from the joint effectively. As a result, growth factors like VEGF are released to promote neoangiogenesis,76 and this could be further boosted by MMP-9– and -13–mediated VEGF stimulation.42 The highly vascular synovial tissue formed is prone to friction between the articular surfaces, creating new bleeding episodes. The inflamed synovium and activated synovial fibroblasts, pannus tissue, and infiltrated inflammatory T cells further degrade the ECM of cartilage, triggering the onset of degenerative joint disease (Figure 1).5
Conclusions
It is well-known that proteases regulate the catabolism of ECM components as a part of normal tissue remodeling. However, dysregulation of their proteolytic activity due to local signaling mediators such as cytokines and growth factors causes cartilage and bone destruction in inflammatory arthritis. The patterns and levels of MMP expression by activated cells in arthritic joints are adequate to degrade the structural collagens that comprise 98% of the articular cartilage, as well as the adjacent bones and tendons, and also noncollagen matrix molecules.37,40 Various cell types in arthritic joints produce plasminogen activators and their inhibitors, especially in response to inflammatory cytokine stimulation in vitro. These in vitro studies are validated by a range of in vivo studies showing that uPA-mediated plasmin activity is a major driver of joint damage in arthritis. It occurs both indirectly by plasmin-mediated activation of pro-MMPs or directly through plasmin-mediated cartilage collagen and proteoglycan catabolism.69 The role of plasmin and MMP activation in HA is not characterized. However, there is an abundance of literature highlighting the role of these proteases in inflammatory arthritis, and there are several known overlapping pathogenic triggers between arthritis and HA. This creates a strong case for further research into how the PA and MMP systems affect the progression of HA. Future research should aim to characterize the profile of MMPs and plasminogen activators in synovial fluid from HA patients. Simultaneous studies should use in vitro models of synovial fibroblast and chondrocyte cocultures to assess the effect of plasminogen activation on MMP secretion and chondrocyte apoptosis. The effect of iron uptake on MMP secretion should also be considered. In vivo experiments involving F8−/− mice and well-characterized models of HA can be designed to assess whether blockade of MMPs and/or plasminogen activation can hamper the progression of HA. These studies will help determine whether readily available MMP and plasmin or plasminogen activator inhibitors can be adjuvant treatments to alleviate joint destruction in HA.
Potential role of proteases in HA. During hemarthroses, blood comes into contact with joint structures. The introduction of blood causes an influx of iron (Fe), interacting with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by chondrocytes, resulting in hydroxyl radicals (OH), causing chondrocyte apoptosis. Type A synoviocytes incorporate hemosiderin and produce proinflammatory cytokines IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α, leading to an intraarticular cytokine storm that worsens cartilage and bone damage. These cytokines promote the recruitment and activation of monocytes and macrophages, prompting of production of MMPs and plasminogen activators (uPA and tPA). Synovial tissue proliferation occurs under inflammatory conditions to produce pro-MMPs and upregulate uPA, while angiogenesis occurs under the influence of VEGF, leading to the formation of synovial pannus. There is a hemostatic imbalance in the synovial fluid of patients with hemophilia. It is characterized by high levels of thrombomodulin and impaired TAFI activation due to low TF levels. Lack of TAFI activation, in turn, enhances uPA-mediated fibrinolysis and consequent clot instability leading to premature clot lysis. The influx of plasminogen occurs with blood and is converted to plasmin by uPA. Plasmin activates MMPs to degrade cartilage and bone. ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motifs; MMP: matrix metalloprotease; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TM, thrombomodulin. Created with Biorender.com.
Potential role of proteases in HA. During hemarthroses, blood comes into contact with joint structures. The introduction of blood causes an influx of iron (Fe), interacting with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by chondrocytes, resulting in hydroxyl radicals (OH), causing chondrocyte apoptosis. Type A synoviocytes incorporate hemosiderin and produce proinflammatory cytokines IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α, leading to an intraarticular cytokine storm that worsens cartilage and bone damage. These cytokines promote the recruitment and activation of monocytes and macrophages, prompting of production of MMPs and plasminogen activators (uPA and tPA). Synovial tissue proliferation occurs under inflammatory conditions to produce pro-MMPs and upregulate uPA, while angiogenesis occurs under the influence of VEGF, leading to the formation of synovial pannus. There is a hemostatic imbalance in the synovial fluid of patients with hemophilia. It is characterized by high levels of thrombomodulin and impaired TAFI activation due to low TF levels. Lack of TAFI activation, in turn, enhances uPA-mediated fibrinolysis and consequent clot instability leading to premature clot lysis. The influx of plasminogen occurs with blood and is converted to plasmin by uPA. Plasmin activates MMPs to degrade cartilage and bone. ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motifs; MMP: matrix metalloprotease; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TM, thrombomodulin. Created with Biorender.com.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Project grant APP1141046 awarded to H.H.N.
Authorship
Contribution: M.S. and W.W.S.H. wrote the manuscript; J.S.J.C. developed the figure and assisted with drafting the manuscript; and M.S. and H.H.N. edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for M.S. is Monash AMREP building, Level 1, Walkway, via The Alfred Centre, Melbourne, VIC, Australia.
Correspondence: Maithili Sashindranath, Australian Centre for Blood Diseases, Central Clinical School, Monash University, Level 1, 89 Commercial Rd, Melbourne, VIC 3004, Australia; e-mail: maithili.sashindranath@monash.edu.