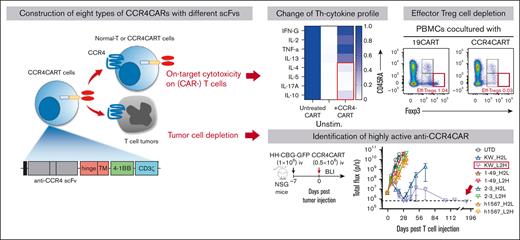
Key Points
CCR4 CAR is active against T-cell lymphoma.
Fratricide induced by CCR4 CAR selectively depletes Th2, Th17, and Treg while sparing Th1.
Abstract
A challenge when targeting T-cell lymphoma with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is that target antigens are often shared between T cells and tumor cells, resulting in fratricide between CAR T cells and on-target cytotoxicity on normal T cells. CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) is highly expressed in many mature T-cell malignancies, such as adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), and has a unique expression profile in normal T cells. CCR4 is predominantly expressed by type-2 and type-17 helper T cells (Th2 and Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg), but it is rarely expressed by other T helper (Th) subsets and CD8+ cells. Although fratricide in CAR T cells is generally thought to be detrimental to anticancer functions, in this study, we demonstrated that anti-CCR4 CAR T cells specifically depleted Th2 and Tregs, while sparing CD8+ and Th1 T cells. Moreover, fratricide increased the percentage of CAR+ T cells in the final product. CCR4-CAR T cells were characterized by high transduction efficiency, robust T-cell expansion, and rapid fratricidal depletion of CCR4-positive T cells during CAR transduction and expansion. Furthermore, mogamulizumab-based CCR4-CAR T cells induced superior antitumor efficacy and long-term remission in mice engrafted with human T-cell lymphoma cells. In summary, CCR4–depleted anti-CCR4 CAR T cells are enriched in Th1 and CD8+ T cells and exhibit high antitumor efficacy against CCR4–expressing T-cell malignancies.
Introduction
CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) is a G protein-coupled 7 transmembrane domain chemokine receptor that binds to the chemokines CCL17/TARC and CCL22/MDC.1 CCR4 is a potential target for the treatment of mature T-cell malignancies, as it is highly expressed in the majority of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL),2,3 cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL),4,5 and 30 to 40% of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) cases.6,7 All these T-cell malignancies show poor prognosis and curative treatment is rare.8,9 In addition, CCR4 in tumors is functional, and its expression is associated with a poorer disease outcome.2 Notably, in normal T cells, CCR4 is predominantly expressed by helper T cells (Th), Th2 and Th17, effector-type Tregs, and cutaneous lymphocyte antigen+ skin-homing T cells but is rarely expressed by other Th subsets and CD8+ T cells.
The feasibility of targeting CCR4 in T-cell lymphoma therapy has been demonstrated by the clinical use of mogamulizumab (KW-0761), a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody that can enhance antibody–dependent cellular cytotoxicity.10,11 A phase 1/2 trial of mogamulizumab for CTCL and ATLL showed an acceptable safety profile and some efficacy,12-14 and, a phase 3 trial demonstrated that mogamulizumab significantly prolonged the progression-free survival of patients with CTCL compared with the HDAC inhibitor vorinostat, which is 1 of the standard therapies for CTCL.15 Mogamulizumab-related adverse events were comparable to those of vorinostat, and most of them were manageable. Based on these trials, mogamulizumab was approved by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency for the treatment of refractory ATLL, CTCL, and PTCL in Japan and by the FDA in the United States for CTCL. However, most patients treated with mogamulizumab experience refractory or relapsed disease.12-15 Therefore, we sought to develop a more potent anti-CCR4 immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR T cells). The efficacy of CAR T cells in cancer therapy has been established using multiple products approved for B-cell leukemia and lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.16-19
Shared target antigen expression between normal T cells and tumor cells presents a major challenge when designing CAR T-cell therapies to treat T-cell malignancies. In general, targeting pan–T-cell antigens can result in failure of T-cell transduction and expansion due to fratricide. For example, targeting CD5 with CAR T leads to the downregulation of CD5 in CAR T cells.20,21 Moreover, deletion or blocking of CD7 can reduce fratricide in anti-CD7 CAR T cells.21-24 However, the complexity, cost, and unpredictable genotoxicity of genetic engineering may diminish clinical feasibility.25,26 Another approach to targeting CD70 is to use naturally selected anti-CD7 CAR T cells.27 This approach is currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
Unlike pan–T-cell antigens, CCR4 is expressed only in a restricted subset of T cells, including CD4+Th2 and Tregs.1 A previous report suggested that functional CCR4-redirected CAR (CCR4-CAR) T cells can be established; however, the effect of fratricide and its relevance to CAR T-cell expansion, transduction, functions, target sensing, phenotype, and antitumor efficacy remains unclear.28 In addition, optimization of the anti-CCR4 CAR construct, particularly scFv, has not yet been investigated as a strategy to enhance CAR T-cell potency. Therefore, we aimed to develop highly effective CCR4-CAR T cells for the treatment of selected T-cell malignancies and investigate the impact of CCR4-CAR–mediated fratricide on CAR T-cell products and normal T cells.
Materials and methods
Generation of CCR4-CAR T cells
Anti-CCR4 scFvs were constructed using 4 different anti-CCR4 mAbs. Each heavy chain variable region (H) and light chain variable region (L) were fused in either the H to L or L to H orientations via standard linkers (Table 1), resulting in 8 constructs. ScFvs were subcloned into the second-generation backbone CAR containing 4-1BB and CD3ζ (supplemental Figure 2A). A control CD19-CAR containing 4-1BB and CD3ζ was constructed as previously described.29 T cells were stimulated with magnetic polymer beads coated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies (ThermoFisher Scientific) and transduced with the CARs using lentivirus at a multiplicity of infection of 4 on the next day of stimulation. The beads were removed using a magnetic field 5 days after stimulation. Cells were counted and diluted to 0.7 × 106 cells/mL by adding fresh media every day or on alternate days and harvested when the T-cell size decreased to 350 μm3 for subsequent experiments.
List of CCR4-CARs and their original mAbs
| # . | CAR . | scFv . | mAb clone . | Affinity (Kd) . | CCR4 epitope . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KW_H2L | H to L | KW-0761 | ND (slow dissociation) | NT 12 to 29 (DESIYSNYYLYESIPKPC) | 11 |
| 2 | KW_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 3 | 1-49_H2L | H to L | mAb 1-49 | 77.98 nM | ND (combinatorial of NT and ECL) | 29 |
| 4 | 1-49_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 5 | 2-3_H2L | H to L | mAb 2-3 | 1.39 nM | ||
| 6 | 2-3_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 7 | h1567_H2L | H to L | h1567 | 2.54 nM | ||
| 8 | h1567_L2H | L to H |
| # . | CAR . | scFv . | mAb clone . | Affinity (Kd) . | CCR4 epitope . | Reference . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KW_H2L | H to L | KW-0761 | ND (slow dissociation) | NT 12 to 29 (DESIYSNYYLYESIPKPC) | 11 |
| 2 | KW_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 3 | 1-49_H2L | H to L | mAb 1-49 | 77.98 nM | ND (combinatorial of NT and ECL) | 29 |
| 4 | 1-49_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 5 | 2-3_H2L | H to L | mAb 2-3 | 1.39 nM | ||
| 6 | 2-3_L2H | L to H | ||||
| 7 | h1567_H2L | H to L | h1567 | 2.54 nM | ||
| 8 | h1567_L2H | L to H |
Kd values are from data as antibodies but not as scFvs.
ECL, extracellular loop; ND, not determined; NT, N-terminus.
Cell lines
The T-cell lymphoma-derived cell lines HH (American Type Culture Collection [ATCC] CRL-2105), MJ (ATCC CRL-8294), and HuT78 (ATCC TIB-161) were obtained from the ATCC. The ATN-1 cell line was a gift from Takashi Ishida at Nagoya University. A B-ALL–derived cell line, Nalm6, was a gift from Joseph A. Fraietta at the University of Pennsylvania. Cell lines were transduced with lentivirus to express click beetle luciferase green and green fluorescent protein (CBG-GFP). HH cells were further transduced to express truncated CD19 (HH-CBG-GFP-t19) and sorted using an INFLUX cell sorter (BD Biosciences) for purification. To mimic a CCR4 and CAR double-positive T-cell population, HH cells were transduced with either CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR or CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR using the same lentivirus used for normal T-cell transduction, HH-CCR4(KW_L2H) CAR and HH-CCR4(h1567_L2H) CAR, respectively. All cell lines were authenticated by the University of Arizona Genetics Core and tested for mycoplasma contamination using a MycoAlert Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Lonza). HH, ATN-1, and Nalm6 were maintained in culture with RPMI (Gibco, Life Technologies) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Seradigm), and MJ and HuT78 were maintained in culture with Iscove modified Dulbecco medium (Gibco, Life Technologies) supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum.
Luciferase–based killing assay
Luciferase-based assay has been optimized for the evaluation of CAR T-cell–mediated killing activity, based on previous reports.30,31 CAR T cells and 1 × 104 target cells expressing luciferase were cocultured at the indicated effector target ratio (E:T ratio) in round bottom 96 well plates (Coster). Triton X-100 was added as a total lysis control. After 16-hour coculture, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and lysed with 100 μL luciferase cell culture lysis buffer (Promega), followed by 1 cycle of freezing and thawing to obtain complete lysis. Lysates were analyzed for luciferase activity with a Synergy H4 plate reader (BioTek) using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega). Percent specific lysis was calculated using the following formula: % specific lysis = [(experimental lysis – spontaneous lysis)/(maximum lysis – spontaneous lysis)] × 100.
51Cr release assay
The target cells were labeled for 2 hours with 51Cr (PerkinElmer) and washed twice with the RPMI medium. CAR T cells and 1 × 104 labeled cells were cocultured at the indicated E:T ratio in 96 well round bottom plates for 4 hours. Sodium dodecyl sulfate was added to the total cell lysis control. The supernatant from each well was transferred to a LumaPlate-96 (PerkinElmer) and the amount of radiation emitted by 51Cr was determined as counts per minute (cpm) using a TopCount plate reader (PerkinElmer). The percent specific lysis was calculated using the following formula: % specific lysis = [(experimental cpm – spontaneous cpm)/(maximum cpm – spontaneous cpm)] × 100.
Coculture assay (FCM–based killing assay)
Target cells (peripheral blood mononuclear cells or primary tumor cells) were labeled with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester according to the manufacturer’s instructions and cocultured with CAR T cells at the indicated E:T ratios in 96 well round bottom or 24 well plates for 18 hours. Cells were stained with an amine-reactive viability dye for dead cell detection and surface and intracellular molecules (only for the experiment to identify Treg cell populations). The samples were analyzed by flowcytometry (FCM) using counting beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Percent specific lysis was calculated using the following formula: % specific lysis = [(experimental lysis – spontaneous lysis)/(maximum lysis – spontaneous lysis)] × 100.
Collection of patient samples
Clinical samples (tumors) were obtained from the clinical practices of the University of Pennsylvania under an Institutional Review Board–approved protocol. All subjects provided written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Mouse experiments and bioluminescence imaging (BLI)
Five- to 7-week old NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice (Jackson Laboratories) were intravenously inoculated with HH-CBG-GFP or HH-CBG-GFP-t19 and treated with either 0.5 or 2 × 106 CAR-positive T cells or untransduced (UTD) T cells on day 7 after tumor inoculation. Tumor burden was followed by BLI using a Xenogen IVIS-200 Spectrum camera (Caliper Life Sciences), and data were analyzed using the LivingImage software (PerkinElmer). The University of Pennsylvania Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all animal experiments and all animal procedures were performed in the animal facility at the University of Pennsylvania, in accordance with the requirements of the Federal and Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Mouse peripheral blood analysis
Peripheral blood was obtained by retro-orbital bleeding or cardiac puncture and the cell numbers of each T-cell subset (total T cells, CD4, and CD8) were quantified by FCM using TruCount tubes (BD Biosciences). Cytokines in serum were analyzed using a high-sensitivity LUMINEX assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Merck Millipore).
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was performed on the paraformaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples. An antibody specific to CCR4 (clone: polyclonal, catalog #: HPA031613) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The stained slides were scanned at ×20 magnification.
FCM analysis and antibodies
The antibodies used for the FCM analysis are listed in supplemental Table 1. Dead cells were gated by staining with the violet amine-reactive viability dye, LIVE-DEAD violet (Invitrogen). Intracellular staining was performed using the Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Kit (Affymetrix) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. CCR4-CAR and CD19-CAR expression was detected using biotinylated anti-human Fab and anti-mouse Fab antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch), respectively. The purified anti-CCR4 mAb (clone KW-0761) was conjugated with Alexa Fluor 680 using an Alexa Fluor 680 Antibody Labeling Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Data were collected using an LSRFortessa Cell Analyzer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using FlowJo version 10 software (TreeStar).
Degranulation and intracellular cytokine production assay
T cells were stimulated either with control media, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and ionomycin (PMA-Iono) (Sigma-Aldrich), or tumor cells at a 1:1 responder: stimulator (R:S) ratio in the presence of monensin (BD Biosciences) and CD107a detection antibody. Cells were stained for LIVE-DEAD violet, surface antigen, and intracellular cytokines at 6 hours of coculture, as described in the FCM and antibodies section.
Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 8 (GraphPad Software). A 2-tailed t test was used to compare the 2 groups and 1-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test was used to compare 3 or more groups. Survival curves were drawn using the Kaplan-Meier method and the differences between the 2 curves were compared using the log-rank test. P values <.05 were considered significant.
Results
Evaluation of CCR4 as a target for CAR T-cell immunotherapy
High expression of a tumor antigen in normal tissues potentially induces on-target off-tumor toxicity. The CCR4 expression profile has been well-determined in previous reports and public databases. Beside normal CD4 T cells described above, CCR4 expression in normal organs is reported in RNA expression levels including kidney, lung, and pancreas in some databases32 including the human protein atlas (https://www.proteinatlas.org/), but fortunately its expression levels are low and severe organ specific adverse effects other than a manageable thrombocytopenia are not reported in the clinical studies of mogamulizumab.12-15 We also evaluated CCR4 expression in skin lesions from patients with CTCL and compared it with that in normal tissues using a tissue microarray derived from 27 organs (supplemental Figure 1A-B). Cutaneous tumor cells from all the patients were highly positive for CCR4, whereas normal tissues rarely expressed CCR4. This is consistent with the previously reported acceptable safety profile of anti-CCR4 mAb (mogamulizumab) therapy in the clinic.
Evaluation and lead selection of multiple anti-CCR4 CAR constructs
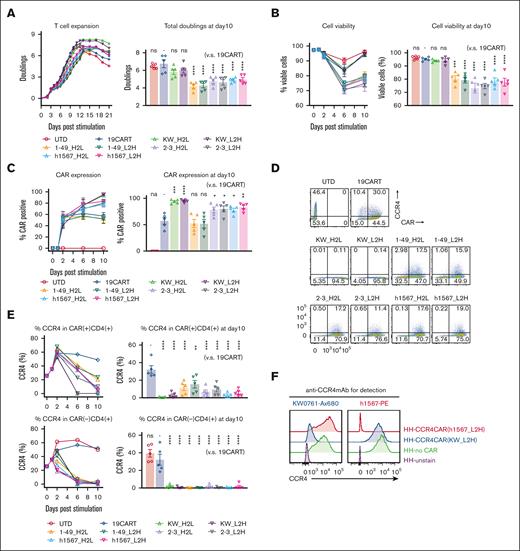
Our goal was to generate CAR-targeting CCR4 for adoptive cell therapy of T-cell lymphoma. To accomplish this, we engineered a panel of 8 anti-CCR4 CARs constructs, each with a different spatial combination of H- and L-binding domains resulting from the humanized anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibodies KW-0761(mogamulizumab),11 h1567, and its affinity-enhanced and decreased derivatives (mAb2-3 and mAb1-49, respectively).33 The constructed scFvs were cloned into the pTRPE CAR backbone plasmid which includes a 4-1BB costimulatory domain and CD3ζ signaling domain (Table 1; supplemental Figure 2A).29 We compared CAR transduction efficiency, T-cell expansion, and phenotype of CCR4-CAR T cells to the CD19-CAR T-cell control. All versions of CCR4-CAR T cells expanded with the anti-CD3/28 bead stimulation; however, T cells expressing KW-0761 derived scFvs, CCR4(KW_H2L/L2H)-CAR T cells, showed superior expansion, resulting in the highest CAR T-cell product yield (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 2B). The volume of CCR4(KW_ L2H)-CAR T cells after CAR transduction and T-cell expansion was the smallest among the 8 types of CCR4-CAR T cells (supplemental Figure 2C), suggesting a less activated status. Superior T-cell expansion was associated with high T-cell viability (Figure 1B). All CCR4-CAR T cells maintained a less differentiated central memory phenotype than CD19-CAR T cells and UTD cells (supplemental Figure 2D). This suggests that mutual CCR4 recognition via CAR-induced 4-1BB signaling, which is known to promote central memory differentiation and persistence of CAR T cells.34 Interestingly, autoselection of CAR-positive cells was observed to differing degrees in 6 out of 8 CCR4-CAR T-cell products. In particular, anti-CCR4 CAR T cells with KW_H2L/L2H scFv cells exhibited nearly 100% CAR expression on day 10, even though the transduction efficacy was comparable with or lower than that of the other CCR4-CAR T cells on day 2 (Figure 1C; supplemental Figure 2E).
CCR4-CAR T cells can expand while depleting CCR4-expressing T cells. (A) Expansion of T cells transduced with CCR4-CAR for 21 days (left panel) and total doublings at day 10 (right panel). The left panel shows representative T-cell expansion curves. T cells were counted and diluted to 0.7 × 106 cells/mL by adding fresh media every other day. T cells were harvested when the T-cell size decreased to 350 μm3 for subsequent experiments when a part of the cells was spared to continue counting. The right panel shows the pooled data of total T-cell expansion on day 10 after anti-CD3/28 stimulation. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and the standard error of the mean (SEM) (5 experiments from 5 donors). (B) Time course analysis of T-cell viability. Cell viability was analyzed by amine-reactive dye staining (LIVE-DEAD staining) and FCM. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM image (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM image (left panel) (5 experiments from 5 donors). Statistical analysis was performed to the data obtained on day 10. (C) Time course analysis of CAR expression in T cells showing CAR-positive cell expansion in some types of CAR T cells. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (left panel) (5 experiments from 5 donors). Statistical analysis was performed to the data obtained on day 10. (D) Representative flow plots showing the expression of CAR and CCR4 on T cells on day 6 after stimulation. The numbers denote the percentage of cells in each quadrant. (E) Representative kinetics of CCR4 expression (left panels) and pooled data of CCR4 expression on day 10 (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (5 experiments with 5 donors). (F) Epitope-specific blocking of CCR4 by CCR4-CAR in HH cells. CCR4 expression detected either with anti-CCR4mAb clone h1567 (left panel) or anti-CCR4 mAb clone KW-0761 (right panel) in HH cells transduced with the indicated CCR4 CAR is shown. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19CART group) using 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test.
CCR4-CAR T cells can expand while depleting CCR4-expressing T cells. (A) Expansion of T cells transduced with CCR4-CAR for 21 days (left panel) and total doublings at day 10 (right panel). The left panel shows representative T-cell expansion curves. T cells were counted and diluted to 0.7 × 106 cells/mL by adding fresh media every other day. T cells were harvested when the T-cell size decreased to 350 μm3 for subsequent experiments when a part of the cells was spared to continue counting. The right panel shows the pooled data of total T-cell expansion on day 10 after anti-CD3/28 stimulation. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and the standard error of the mean (SEM) (5 experiments from 5 donors). (B) Time course analysis of T-cell viability. Cell viability was analyzed by amine-reactive dye staining (LIVE-DEAD staining) and FCM. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM image (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM image (left panel) (5 experiments from 5 donors). Statistical analysis was performed to the data obtained on day 10. (C) Time course analysis of CAR expression in T cells showing CAR-positive cell expansion in some types of CAR T cells. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (left panel) (5 experiments from 5 donors). Statistical analysis was performed to the data obtained on day 10. (D) Representative flow plots showing the expression of CAR and CCR4 on T cells on day 6 after stimulation. The numbers denote the percentage of cells in each quadrant. (E) Representative kinetics of CCR4 expression (left panels) and pooled data of CCR4 expression on day 10 (right panel). Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (5 experiments with 5 donors). (F) Epitope-specific blocking of CCR4 by CCR4-CAR in HH cells. CCR4 expression detected either with anti-CCR4mAb clone h1567 (left panel) or anti-CCR4 mAb clone KW-0761 (right panel) in HH cells transduced with the indicated CCR4 CAR is shown. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19CART group) using 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test.
CCR4(KW_H2L and KW_L2H)-CAR T cells eliminate CCR4-positive cells
To assess whether T-cell fratricide contributed to the enrichment of CCR4-CAR T-cell expression in CCR4-CAR T-cell products, we measured CCR4 expression levels in CAR-positive and CAR-negative populations after CAR T-cell expansion by flow cytometry using the anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody, D8SEE, which does not bind to the same epitope as the monoclonal antibodies used for CCR4-CAR construction (supplemental Figure 3A). Rapid loss of CCR4 expression and a corresponding decrease in the CD4/8 ratio occurred in all CAR-negative T-cell populations (Figure 1D-E; supplemental Figure 3B). The level of surface CCR4 did not change, even with increased antibody concentration (supplemental Figure 3C), and intracellular CCR4 was negative (supplemental Figure 3D), suggesting that the loss of CCR4 represents the lysis of CCR4 expressing cells rather than detection error or CCR4 internalization. Similarly, CCR4(KW_H2L/L2H)-CAR T cells rapidly lost CCR4 expression (Figure 1D-E), suggesting that transient signaling through CAR by recognizing mutual CCR4 and T-cell fratricide contributed to the enrichment of CCR4-CAR–positive T cells in the product. Surprisingly, CCR4(h1567, 1-49)-CAR–positive cell populations were relatively resistant to fratricide, as most of the CCR4-positive cells remained in the CAR-positive population, even on days 6 and 10 (Figure 1D-E), suggesting that the degree of fratricide in the CAR-positive population and CAR signaling by recognizing mutual CCR4 was dependent on the anti-CCR4 scFv.
We then sought to understand why some CCR4-CAR T cells expressing surface-detectable CCR4 failed to kill neighboring CCR4-expressing CCR4-CAR T cells, as opposed to other CCR4-expressing CCR4-CAR T cells that were susceptible to fratricide. To investigate the mechanisms of resistance to fratricide in the CAR-positive T-cell population, a CCR4-positive T-cell line (HH) was transduced with either CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR or CCR4 (h1567_L2H)-CAR to mimic the CCR4-CAR and CCR4 double-positive T-cell populations (supplemental Figure 4). We hypothesized that CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR could not kill CCR4-expressing CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR T cells because recognition of the CCR4 epitope was blocked. We tested the binding of anti-CCR4 clone h1567 and clone KW-0761 monoclonal antibodies to HH cells expressing either CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR or CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR. When HH cells expressed CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR, the anti-CCR4 clone h1567 monoclonal antibody was unable to recognize CCR4 expressed on the surface of the CAR T cell, but the anti-CCR4 clone KW-0761 detected CCR4 surface expression. In HH cells expressing CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR, CCR4 detection was instead present, although reduced, when using the anti-CCR4 clone KW mAb (Figure 1F). These results suggest that CCR4-CAR blocks the CCR4 epitope specifically in cis, thereby causing resistance to fratricide, and indicate that the degree of binding in cis of anti-CCR4 scFv to CCR4 is scFv-dependent. This phenomenon is consistent with a previous finding that the expression of CD19-CAR in CD19-positive cells can block the CD19 epitope in cis, resulting in resistance to CAR-mediated killing.35
CCR4-CAR T cells are enriched for Th1 cells
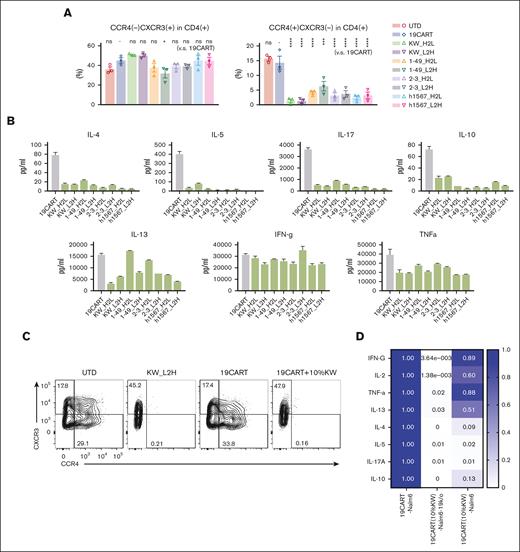
To investigate how CCR4-CAR T-cell fratricide impacts the distribution of CD4+ T-cell subsets in CCR4-CAR T-cell products, we measured the levels of Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg subsets and cytokine profiles. We observed that compared with CD19-CAR T cells, CCR4-CAR T-cell products contained a significantly decreased percentage of the CD4+ Th2-like subset, as defined by the following flow cytometry signature; CD4+ CCR4+ CXCR3– CCR6– CCR10–, but maintained the level of CD4+ Th1-like subset; CD4+ CCR4– CXCR3+ CCR6–, and CCR10– (Figure 2A). Treg subsets, as determined by FoxP3 and CD25, were rare in our CAR T-cell products, and there was no difference between CD19-CAR T cells and CCR4-CAR T-cell products (supplemental Figure 5A). In addition, upon stimulation with PMA-ionomycin, CCR4-CAR T cells produced decreased levels of Th2, Th17, and Treg related cytokines while maintaining a Th1-related cytokine, INF-γ, and proinflammatory cytokine (TNFα) production (Figure 2B). These results suggest that transduction of T cells with CCR4-CAR results in the depletion of CCR4-positive Th2, Th17, and Treg subsets, and maintains the CCR4-negative Th1 CD4+ subset. This depletion may be beneficial as a general strategy for enhancing CAR T-cell therapy. To test this hypothesis, we used CCR4-CAR T cells to make a Th1-rich–CD19-CAR T-cell product. Addition of 10% CCR4-CAR T cells was sufficient to deplete CCR4-positive T-cell subsets in CD19-CAR T cells (Figure 2C), resulting in a relatively Th1 dominant CD19-CAR T-cell product (Figure 2D). To further evaluate the effects of CCR4 CAR T cells on normal Treg cells, we cocultured CCR4-CAR T cells with peripheral mononuclear cells. CCR4-CAR T cells depleted effector Treg cells (Treg fraction II) possessed the highest immunosuppressive capacity, while sparing naïve Treg cells (supplemental Figure 5B).36
Fratricide changes the Th-subset proportion with decreased Th2, Th17, and Treg cytokine production while sparing Th1 cytokine production. (A) Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CAR T-cell products. The Th1-like subset was defined as CD4(+), CXCR3(+), CCR4(–), CCR6(–), and CCR10(–). Th2-like subset was defined as CD4(+), CXCR3(–), CCR4(+), CCR6(–), and CCR10(–) by FCM. Phenotypes were analyzed by gating the CAR-positive population, with the exception of the UTD group. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (3 experiments from 3 donors). ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19-CAR T group) by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. (B) Profiles of cytokine production by CD19- and CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with PMA/Iono. Cytokine levels in the supernatant 24 hours after stimulation were analyzed using the LUMINEX assay. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. Bars represent the mean and standard deviation of technical duplicates. (C) Depletion of CCR4-positive subsets by adding CCR4-CAR T cells to CD19-CAR T cells. T cells were stimulated and transduced with either the CCR4 CAR or CD19 CAR. 10% CCR4-CAR T cells were mixed with CD19-CAR T cells 5 days after stimulation. CCR4 expression in CD19-CAR–positive cells was analyzed on day 10. The numbers denote the percentage of cells in each quadrant. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. (D) Heat map of Th-related cytokine production by CD19-CAR T cells pretreated with CCR4-CAR T cells compared with untreated CD19-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated using the indicated stimulators. The cytokine levels in the supernatant at 24 hours after stimulation were analyzed using LUMINEX assay. The cytokine levels from untreated CD19-CAR T cells were set to 1 and the relative expression levels are indicated. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors.
Fratricide changes the Th-subset proportion with decreased Th2, Th17, and Treg cytokine production while sparing Th1 cytokine production. (A) Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CAR T-cell products. The Th1-like subset was defined as CD4(+), CXCR3(+), CCR4(–), CCR6(–), and CCR10(–). Th2-like subset was defined as CD4(+), CXCR3(–), CCR4(+), CCR6(–), and CCR10(–) by FCM. Phenotypes were analyzed by gating the CAR-positive population, with the exception of the UTD group. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM (3 experiments from 3 donors). ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19-CAR T group) by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. (B) Profiles of cytokine production by CD19- and CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with PMA/Iono. Cytokine levels in the supernatant 24 hours after stimulation were analyzed using the LUMINEX assay. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. Bars represent the mean and standard deviation of technical duplicates. (C) Depletion of CCR4-positive subsets by adding CCR4-CAR T cells to CD19-CAR T cells. T cells were stimulated and transduced with either the CCR4 CAR or CD19 CAR. 10% CCR4-CAR T cells were mixed with CD19-CAR T cells 5 days after stimulation. CCR4 expression in CD19-CAR–positive cells was analyzed on day 10. The numbers denote the percentage of cells in each quadrant. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. (D) Heat map of Th-related cytokine production by CD19-CAR T cells pretreated with CCR4-CAR T cells compared with untreated CD19-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated using the indicated stimulators. The cytokine levels in the supernatant at 24 hours after stimulation were analyzed using LUMINEX assay. The cytokine levels from untreated CD19-CAR T cells were set to 1 and the relative expression levels are indicated. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors.
CCR4-CAR T cells respond to and lyse CCR4-positive T-cell lymphoma cells in vitro
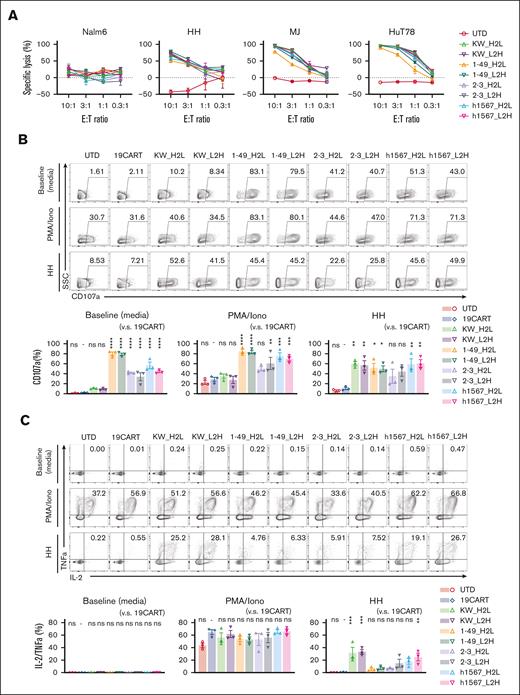
Because target antigen density impacts CAR T-cell responses,37 we tested the lytic activity of our panel of CCR4-CAR T cells against 3 cell lines, HH, MJ, and Hut78 cells derived from patients with T-cell malignancies displaying a range of CCR4 expression (supplemental Figure 5). All CCR4-CAR T-cell products lysed the CCR4-expressing cell lines. No apparent difference in lytic activity was observed between CCR4-CAR T cells and HH, the highest CCR4-expressing cell line. We noted that in both the intermediate and low CCR4-expressing cell lines, MJ and HuT78, CCR4(KW_H2L/L2H)-CAR T cells exhibited the highest killing capacity, whereas CCR4(1-49_H2L/L2H)-CAR T cells had the lowest (Figure 3A). All CCR4-CAR T cells degranulated upon CCR4 stimulation, as reflected by CD107a upregulation; however, CARs derived from clone h1567 and its derivatives showed target-cell–independent degranulation at baseline (Figure 3B). All CCR4-CAR T cells were degranulated at similar levels upon HH cell stimulation. We also analyzed the capacity of multiple cytokine production by FCM as a surrogate of T-cell function.38 All the CARs produced cytokines at similar levels upon PMA/Iono simulation, but there were significant differences in cytokine production upon HH cell stimulation: CCR4(KWL2H/H2L) CAR T cells efficiently produced both IL-2 and TNFa, whereas the other CAR T cells derived from clone h1567, produced decreased IL-2 and TNFa (Figure 3C). This is inversely correlated with baseline degranulation, indicating the induction of T-cell dysfunction with target-cell–independent tonic signaling, as previously reported.39
CCR4-CAR T cells specifically lyse CCR4-positive T-cell lymphoma cell lines and produce cytokines upon stimulation, whereas some CCR4 CAR constructs display ligand-independent T-cell degranulation. (A) Lytic activity of CAR T cells against tumor cell lines. CAR T cells and tumor cells expressing luciferase were incubated at the indicated E:T ratios. Specific lysis after 16 hours of coculture was determined based on the luminescence. Bars represent the means and standard deviation from technical triplicates. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. (B) Degranulation of CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with media, PMA-Iono, or HH cells at a 1:1 R:S ratio with CD107a detecting antibody and incubated for 6 hours. The cells were analyzed by FCM. The upper panels are representative flow plots for CD107a expression, the lower panels are pooled data from 3 experiments, and the 3 donors indicate baseline degranulation of CCR4CART cells derived from h1567 or its derivatives. The numbers in each column indicate the percentage of CD107a-positive populations. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and the SEM, respectively. (C) Cytokine production by CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with media, PMA-Iono, or HH cells at a 1:1 R:S ratio and incubated in the presence of monensin for 6 hours. The cells were analyzed for intracellular cytokines using FCM. The upper panels are representative flow plots for IL-2 and TNFa expression, and the lower panels are pooled data from 3 experiments with 3 donors. The numbers in each column indicate the percentage of IL-2 TNF-a positive populations. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM, respectively. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19-CAR T group) using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
CCR4-CAR T cells specifically lyse CCR4-positive T-cell lymphoma cell lines and produce cytokines upon stimulation, whereas some CCR4 CAR constructs display ligand-independent T-cell degranulation. (A) Lytic activity of CAR T cells against tumor cell lines. CAR T cells and tumor cells expressing luciferase were incubated at the indicated E:T ratios. Specific lysis after 16 hours of coculture was determined based on the luminescence. Bars represent the means and standard deviation from technical triplicates. Data are representative of 3 experiments from 3 donors. (B) Degranulation of CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with media, PMA-Iono, or HH cells at a 1:1 R:S ratio with CD107a detecting antibody and incubated for 6 hours. The cells were analyzed by FCM. The upper panels are representative flow plots for CD107a expression, the lower panels are pooled data from 3 experiments, and the 3 donors indicate baseline degranulation of CCR4CART cells derived from h1567 or its derivatives. The numbers in each column indicate the percentage of CD107a-positive populations. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and the SEM, respectively. (C) Cytokine production by CCR4-CAR T cells. CAR T cells were stimulated with media, PMA-Iono, or HH cells at a 1:1 R:S ratio and incubated in the presence of monensin for 6 hours. The cells were analyzed for intracellular cytokines using FCM. The upper panels are representative flow plots for IL-2 and TNFa expression, and the lower panels are pooled data from 3 experiments with 3 donors. The numbers in each column indicate the percentage of IL-2 TNF-a positive populations. Dots and bars represent individual data from each donor and SEM, respectively. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ns, not significant (vs CD19-CAR T group) using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
CCR4-CAR T cells eradicate tumor cells in NSG mice
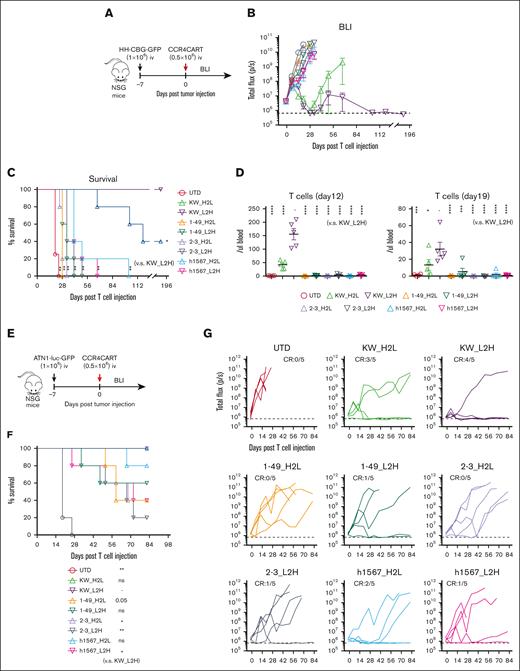
To compare the antitumor efficacy of CCR4-CARs in vivo, we treated HH cell xenografts with a low dose (0.5 × 106) of CAR-positive T cells or control UTD T cells to reveal any differences in effectiveness (Figure 4A). The tumor burden was followed by BLI for over 6 months to assess long-term remission. CAR T cells with KW-H2L and L2H scFv formats showed robust antitumor efficacy (Figure 4B), but only CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells led to 100% survival in the long term (Figure 4C). Superior antitumor efficacy was associated with better T-cell engraftment, as anti-CCR4(KW_H2L/L2H)-CAR T cells induced the highest level of T-cell expansion and persistence (Figure 4D). In addition, we noted that CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR T cells exhibited only minor antitumor efficacy. Off-tumor–related toxicity, including graft-versus-host disease and body weight loss, was not observed (supplemental Figure 7). We further tested the antitumor efficacy of CAR T cells against another cell-line (ATN-1)–derived xenograft model (Figure 4E). Although 1 mouse in the CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T-cell group relapsed, we confirmed a similar trend, where KW_L2H induced a significant survival benefit and tumor suppression (Figure 4F and G). Based on these results, we selected CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T and CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR T cells for further evaluation.
CCR4-CAR (KW_L2H) cures ATN-1 and HH cell xenograft mice and induces superior T-cell engraftment. (A) Schematic representation of the experiment. NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 HH cells expressing the click beetle luciferase (HH-CGB-GFP). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 0.5 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or untransduced T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (B) Overall kinetics of tumor burden by BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. Dots and bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 4 for the UTD group and n = 5 for the other groups). (C) Survival curve obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ns, not significant (vs KW_L2H group) using the log-rank test. (D) T-cell count of peripheral blood on days 12 and 19 by FCM. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (E) Schematic representation of the experiment. The NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 ATN-1 cells expressing firefly luciferase (ATN1-luc-GFP). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 0.5 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or untransduced T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (F) Survival curve using the Kaplan-Meier method. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ns, not significant (vs KW_L2H group) using the log-rank test. (G) Kinetics of tumor burden using BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. The lines indicate the individual data from each mouse.
CCR4-CAR (KW_L2H) cures ATN-1 and HH cell xenograft mice and induces superior T-cell engraftment. (A) Schematic representation of the experiment. NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 HH cells expressing the click beetle luciferase (HH-CGB-GFP). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 0.5 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or untransduced T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (B) Overall kinetics of tumor burden by BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. Dots and bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 4 for the UTD group and n = 5 for the other groups). (C) Survival curve obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ns, not significant (vs KW_L2H group) using the log-rank test. (D) T-cell count of peripheral blood on days 12 and 19 by FCM. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (E) Schematic representation of the experiment. The NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 ATN-1 cells expressing firefly luciferase (ATN1-luc-GFP). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 0.5 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or untransduced T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (F) Survival curve using the Kaplan-Meier method. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ns, not significant (vs KW_L2H group) using the log-rank test. (G) Kinetics of tumor burden using BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. The lines indicate the individual data from each mouse.
Antitumor efficacy and T-cell engraftment of CCR4-CAR T cells are superior to those of CD19-CAR T cells
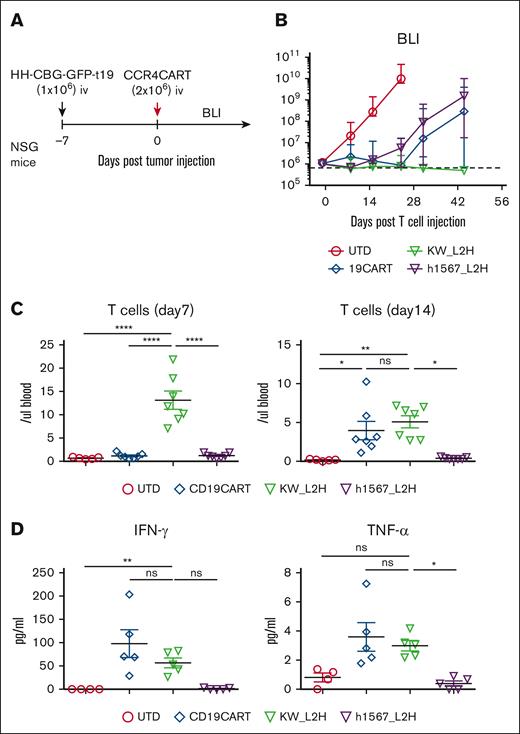
To further evaluate the in vivo efficacy of CCR4-CAR T cells and compare it to the gold standard of CD19-CAR T cells, we used CCR4+ HH cells engineered to express CD19 (HH-CBG-GFP-t19) (supplemental Figure 8A). NSG mice were inoculated with 1 × 106 HH-CBG-GFP-t19 cells and treated with 2 × 106 CAR-positive T cells or UTD cells on day 7 after tumor inoculation (Figure 5A). CD19-CAR T cells and CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR T cells showed similar antitumor efficacy against CCR4- and CD19-expressing tumors, whereas CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells induced a higher rate of complete remission (Figure 5B). In addition, CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells showed higher levels of T-cell engraftment than CD19-CAR T cells in the early phase (day 7), and showed comparable T-cell engraftment at later time points (day 14; Figure 5C; supplemental Figure 8B). Very few T cells were detectable in peripheral blood on day 28, with the exception of 1 mouse from the CD19-CAR T-cell group that developed graft-versus-host disease and showed a rapid increase in T cells in peripheral blood (supplemental Figure 5B). CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells and CD19-CAR T cells produced comparable levels of IFN-γ and TNFα, whereas CCR4(h1567_L2H)-CAR T cells secreted lower levels of cytokines (Figure 5C). Together, these results establish the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of lead CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells against CCR4-expressing tumor lines.
CCR4-CAR (KW_L2H) induces comparable antitumor efficacy to CD19-CAR in NSG mice engrafted with HH expressing CD19 (HH-CBG-GFP-t19). (A) Schematic representation of the experiment. NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 HH cells expressing luciferase and truncated CD19 (HH-CGB-GFP-t19). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 2 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or UTD T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (B) Overall kinetics of the tumor burden by BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. Dots and bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 5 for the UTD group and n = 7 for the other groups). The data are representative of 2 experiments from 2 donors. (C) T-cell counts in peripheral blood on days 7 and 14. Peripheral blood was analyzed for T-cell counts on days 7 and 14 by FCM using counting beads. Bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 5 for the UTD group and n = 7 for the other groups). The data are representative of 2 experiments from 2 donors. (D) Cytokine levels of serum on day 6. Serum was collected from mouse whole blood at day 6 using the same experimental schedule as described in panels A-C. Cytokines were analyzed using high-sensitivity LUMINEX assay. Bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 4 for the UTD group and n = 5 for the other groups). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. ns, not significant.
CCR4-CAR (KW_L2H) induces comparable antitumor efficacy to CD19-CAR in NSG mice engrafted with HH expressing CD19 (HH-CBG-GFP-t19). (A) Schematic representation of the experiment. NSG mice were intravenously inoculated with 1 × 106 HH cells expressing luciferase and truncated CD19 (HH-CGB-GFP-t19). Engrafted tumors were intravenously treated with either 2 × 106 CCR4-CAR–positive T cells or UTD T cells 7 days after tumor cell inoculation. (B) Overall kinetics of the tumor burden by BLI. The dashed line represents the background level of photons determined by imaging tumor-free mice. Dots and bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 5 for the UTD group and n = 7 for the other groups). The data are representative of 2 experiments from 2 donors. (C) T-cell counts in peripheral blood on days 7 and 14. Peripheral blood was analyzed for T-cell counts on days 7 and 14 by FCM using counting beads. Bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 5 for the UTD group and n = 7 for the other groups). The data are representative of 2 experiments from 2 donors. (D) Cytokine levels of serum on day 6. Serum was collected from mouse whole blood at day 6 using the same experimental schedule as described in panels A-C. Cytokines were analyzed using high-sensitivity LUMINEX assay. Bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 4 for the UTD group and n = 5 for the other groups). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. ns, not significant.
CCR4-CAR T cells respond to and lyse primary CTCL cells
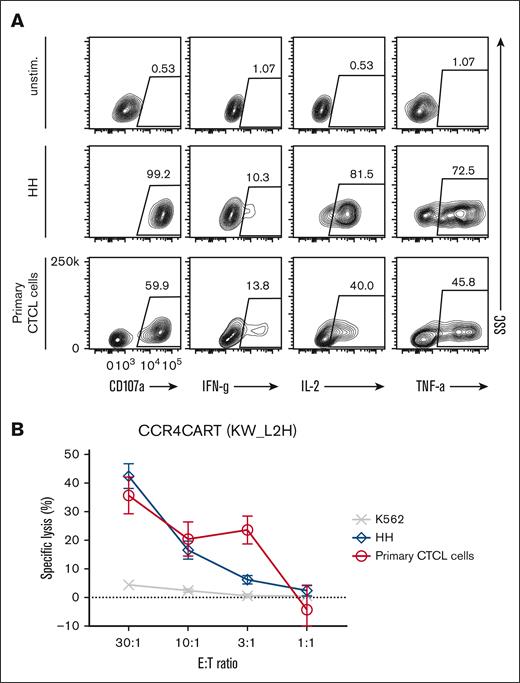
To validate whether CCR4(KW_L2H) CAR T cells can target and kill the samples from patients with T-cell lymphoma, we tested their lytic activity against patient–derived primary CTCL cells. Initially, we confirmed that isolated tumor cells expressed phenotypic markers characteristic of CTCL: CD4+, CCR4+, CD7–, CD25–, and CD157–, and also expressed CCR4 by flow cytometry40 (supplemental Figure 9A). In addition, we confirmed that the patient sample contained a low frequency of normal blood (<5%; supplemental Figure 9A). Upon coculture using samples from patients with the CTCL, CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells were activated, as demonstrated by CD107a upregulation and secretion of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNFα cytokines (Figure 6A). Importantly, CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells specifically and effectively lysed primary tumor cells from patients with CTCL (Figure 6B). We also tested the cytotoxicity of CCR4(KW_L2H)-CAR T cells against another primary T-cell lymphoma that expressed CCR4 in a peripherally circulating CD4 T-cell population (supplemental Figure 9A). CCR4-CAR T cells effectively lysed target cells whereas control CD19-CAR T cells did not lyse target cells, indicating specific cytotoxicity (supplemental Figure 9B).
CCR4-CAR T cells can lyse and respond to patient–derived primary CTCL cells. (A) Cytokine production by CCR4-CAR T cells upon stimulation with primary CTCL cells. Cytokine production of CAR T cells at 6 hours after stimulation was analyzed by intracellular staining and FCM. The gates represent a positive population of the indicated cytokines in CAR-positive cells. (B) Lytic activity of CCR4-CAR T cells against primary CTCL cells. The killing activity of CAR T cells against each cell at 4 hours of coculture was analyzed by a 51Cr release assay. Dots and bars represent the mean and standard deviation from a single donor experiment (technical triplicate).
CCR4-CAR T cells can lyse and respond to patient–derived primary CTCL cells. (A) Cytokine production by CCR4-CAR T cells upon stimulation with primary CTCL cells. Cytokine production of CAR T cells at 6 hours after stimulation was analyzed by intracellular staining and FCM. The gates represent a positive population of the indicated cytokines in CAR-positive cells. (B) Lytic activity of CCR4-CAR T cells against primary CTCL cells. The killing activity of CAR T cells against each cell at 4 hours of coculture was analyzed by a 51Cr release assay. Dots and bars represent the mean and standard deviation from a single donor experiment (technical triplicate).
Discussion
Mature T-cell lymphomas, including CTCL, ATLL, and PTCL, are generally associated with poor prognosis.8 Although new therapies such as the anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody mogamulizumab can delay tumor progression, long-term complete remissions are rarely achieved.9 Here, we demonstrate that mogamulizumab-derived CCR4-CAR T cells can effectively target both CCR4+ tumor cell lines and primary CTCL cells and eradicate established tumors in preclinical models. Mogamulizumab-derived CCR4-CAR T cells were superior to other CCR4-CART cells derived from the h1567 and mAb2-3 antibodies that were previously used to generate anti-CCR4 CAR T cells by another group.28 We also demonstrated mechanisms of fratricide in CCR4-CAR T cells and demonstrated its relevance to CAR T cell functions. Indeed, the superior antitumor efficacy of CCR4-CAR T cells was associated with the rapid and complete depletion of CCR4-positive T cells. In addition, the data revealed that the degree of fratricide is scFv-dependent, influencing the degree to which CCR4-CAR can mask target CCR4 in cis. CARs derived from KW-0761 only partially bound CCR4 in cis, permitting unhindered fratricide; however, CARs derived from h1567 and its derivatives almost completely blocked the epitope in cis allowing CCR4-CAR-positive cells to persist. This observation is compatible with a previous report showing that when a CD19-CAR is unintentionally introduced into a leukemic B cell, it can induce leukemia resistance because of binding of the CAR19 to CD19 epitope on the surface of leukemic cells, masking it from recognition by CD19-CAR T cells.35 It was unexpected that the high-affinity CAR (KW_H2L/L2H) did not cross block the epitope completely, whereas the lower affinity CARs did. This may be explained by the location of epitopes; KW-0761 recognizes the N-terminus of CCR4 (distal epitope), whereas h1567 and its derivatives recognize the loops (proximal epitope) of CCR4. Further analysis, including 3D structure and CAR affinity, is required to completely understand the biophysical differences of the CARs.
With regard to our functional analysis, the only large in vitro difference between the 8 types of CAR T cells, was the degree of target-cell–independent continuous degranulation; CCR4CARs derived from h1567 and its derivatives induced continuous ligand-independent degranulation of CAR T cells, but CARs derived from KW did not induce this, which was associated with residual CCR4 levels. Higher baseline degranulation was associated with decreased polyfunctional cytokine production upon encountering the CCR4+ target cells. This is similar to previous reports where CARs that can induce ligand-independent tonic signaling induced CAR T-cell dysfunction.39 We also observed better antitumor efficacy of the KW_L2H version than that of the KW_H2L version in a xenograft model. The difference in orientation could potentially affect the 3D structure that can affect the affinity of CAR, expression levels, or signal transduction, but we could not determine the precise mechanism in this study. Currently, we and others practically test both the L2H and H2L orientation for new CAR or Bispecific T-cell Engager designs.41,42 Application of computational prediction of scFv structure including the VH/VL orientation would be useful for future CAR design.43 Many promising CAR T cells has been developed to target different antigens for T-cell malignancies, including CD4,44 CD5,20 CD7,21 and TRBC1/2.45 Among them, CCR4 CAR T cells are exceptional, where T cells specifically deplete immune suppressive T cells, such as Treg cells, in addition to tumor cells. We found that CCR4-CAR T cells produced a Th1 dominant CAR T-cell product relative to Th2 and Tregs, a feature that may enhance the antitumor activity of CAR T cells, as Th1 subsets play central roles in anticancer immunity, whereas, Th2 and Tregs possibly counteract this effect. Furthermore, CD19-CAR T cells also displayed improved characteristics during CAR T-cell manufacturing when mixed with a small number of CCR4 CAR T cells, suggesting that CCR4-CAR T cells can be utilized as a tool to change the characteristics of other CAR T cell products. This result also suggests that host normal CCR4-positive T cells can be depleted in vivo by CCR4-CAR T cells, as reported after mogamulizumab treatment.46 Th2-mediated inflammation often supports tumor growth and cancer immune evasion, and higher Th2 infiltration is associated with poor treatment outcome.47,48 We demonstrated that CCR4-CAR T cells specifically depleted effector Treg cells in normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Tregs also have an important role for tumor growth and immune evasion. Tregs can suppress effector T cell–mediated tumor killing and high Treg infiltration of the tumor microenvironment is associated with poor outcome of many types of tumors including colorectal,49 breast,50 ovarian,51 renal,52 non-small cell lung,53 melanoma,54 lymphoma,55 and hepatocellular56 cancers. Even transient depletion of Tregs can enhance the efficacy of tumor vaccine therapy in animal models.57,58 Therefore, depletion of CCR4-positive Treg and Th2 by CCR4-CAR T cells has the potential to augment antitumor immunity in addition to directly killing CCR4-positive tumor cells. Indeed, mogamulizumab has been tested as a Treg-depleting therapy in patients with solid tumor. A significant reduction in CCR4-positive T cells, immune responses to cancer/testis antigens, and an autoantibody response to thyroid peroxidase was observed following mogamulizumab treatment in some patients.59
Further investigation is required to determine whether systemic CCR4 cell depletion induces autoimmune disease and/or on-target off-tumor toxicity. A case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome with dermal infiltration of CD8+ T cells after mogamulizumab therapy may be associated with Treg depletion.60 CCR4 expression in normal organs are reported in RNA expression levels including kidney, lung, and pancreas in some databases32 including the human protein atlas (https://www.proteinatlas.org/), but fortunately its expression levels are low and severe organ specific adverse effects other than a manageable thrombocytopenia are not reported in the clinical studies of mogamulizumab.12-15 Nonetheless, enhanced activity of the CCR4-CAR T-cell therapy may induce such toxicity. Therefore, modulation of CCR4-CAR activity via a suicide system,61,62 strategies of chemotherapeutic or antibiotic depletion of CAR T cells,63,64 or inducible expression of CAR65 may be warranted in cases of toxicity. In addition, therapeutics for autoimmune diseases, including abatacept (CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein) might be useful for the toxicity. Another limitation of our study is that we tested CART cell production using healthy donor–derived T cells. It is likely T cells from patients with T-cell malignancies are dysfunctional because of the disease itself and repeated chemotherapy. In summary, we identified highly active CCR4-CAR T cells derived from the KW-0761(mogamulizumab) antibody. Its efficacy was associated with fratricidal depletion of Th2, Treg, and Th17 subsets while sparing Th1 cells. Numerous states of immunopathology have been described because of excessive Th2 and Th17 cells.66,67 The optimized anti-CCR4 CAR T cells identified in this study could be beneficial for the treatment of patients with T-cell lymphoma, as well as for Th2 and Treg-depleting therapy in conditions of immune dysregulation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Michael C. Milone and Selene Nunez-Cruz for their help with 51Cr release assay; Joseph A. Fraietta for gift of Nalm6; Carolyn Shaw, Caroline Sands, and Yuki Ishige for technical support; and Philipp Rommel and Jesse Rodriguez for providing materials and help with experiments. Animal experiments were performed in Stem Cell and Xenograft core; flow cytometric analysis and cell sorting were performed with support from the Flowcytometry core; the LUMINEX assay was performed using the Human Immunology Core; and T cells were obtained from the Human Immunology Core at the University of Pennsylvania. Financial support for this work was provided, in part, by grants from the National Cancer Institute (P01 CA214278 [C.H.J.] and R01 CA226983 [C.H.J.]), Tmunity Therapeutics (C.H.J.), and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (JP20ck0106570 [K.W.]). M.R. was supported by the Lymphoma Research Foundation, Gilead Research Scholars Award, Gabrielle’s Angel Foundation, Laffey-McHugh Foundation; Emerson Collective Award, Laffey-McHugh Foundation, Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Berman and Maguire Funds for Lymphoma Research at Penn, NCI (grants 1K99CA212302 and R00CA212302).
Authorship
Contribution: K.W. designed and performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; M.S. designed experiments, performed experiments, and analyzed data; T.D., D.S., A.M.G., and A.R. performed experiments; S.K. and S.A. designed and performed experiments; A.H.R. and P.L.H. provided critical materials; A.D.P. designed experiments and provided critical materials; J.S. and M.R. designed experiments; R.M.Y. supervised the project, designed experiments, and wrote the manuscript; and C.H.J. conceptualized and supervised the project, designed experiments, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.W., J.S., R.M.Y., and C.H.J. have filed a patent on this work. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Carl H. June, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, 3400 Civic Center Blvd, 8th floor, Room 8-123, Philadelphia, PA 19104-5156; e-mail: cjune@upenn.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are available upon request from the corresponding author, Carl H. June (cjune@upenn.edu).
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.