Abstract
Widespread microvascular injury followed by vessel obstruction may lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). We describe a murine model wherein leukocytes interacting with inflamed microvessels in vivo are activated by antibodies. Treatment of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)–primed mice with anti–Ly-6G antibodies reproduced many of the features of septic or traumatic shock including microvessel obstruction and coagulation, severe vasculitis, respiratory difficulties, and vascular leakage. Mice lacking either E-selectin or P-selectin were protected from this reaction as were animals treated with a combination of either selectin-blocking antibodies and heparin or a selectin antagonist plus heparin. Combined blockade of leukocyte/platelet adhesion and coagulation may provide convincing protection in DIC.
Introduction
In sepsis and severe trauma a misdirected or overly vigorous host response can throw the innate immune system into chaos. Severe cases and poor outcomes are associated with diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).1,2 That the acronym DIC is often interpreted as “Death Is Coming” underscores the deficiency of current treatments and the need for deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying this condition. Although primary therapy is appropriately aimed at treatment of the underlying disorder, there is widespread belief that anticoagulant strategies will provide additional benefit.1 A recent clinical trial demonstrating only modestly reduced mortality in patients with severe sepsis treated with the anticoagulant molecule activated protein C3 suggests that additional strategies should also be considered. Obstruction of the microvasculature by inflammatory cells is an event that may contribute to DIC and could be targeted for therapy.
To reach an injured tissue, circulating leukocytes first attach to and then roll along vascular endothelium. This initial interaction is primarily mediated by the selectin family of adhesion molecules and their ligands.4 Subsequent steps are supported by further adhesion molecules including integrins and members of the immunoglobulin superfamily.5 As leukocytes roll they integrate signals from chemoattractants presented by endothelial cells until they receive sufficient stimulation to enter the next phase of the inflammatory response.5 After rolling, leukocytes firmly adhere, transmigrate, and infiltrate injured areas. Complex arrays of chemoattractants and adhesion molecules are presented to leukocytes in logical order, directing them out of vessels.5,6 End-target chemoattractants dominate over intermediate signals6 ensuring that, under normal conditions, leukocytes reach their targets without distraction.
In severe inflammatory conditions, significant tissue activation may be coupled with the presence of blood-borne neutrophil activators including chemokines, complement, and bacterial cell wall products. Intravascular neutrophil activation by such agents has the potential to seriously upset the usually ordered recruitment system. Without clear signals directing them out of vessels, activated neutrophils may obstruct and injure the microvasculature, a situation that will be worsened by pre-existing tissue inflammation.7-9
During intravital microscopy experiments using antibodies against Ly-6G (a glycosylphosphatidylinositol [GPI]–linked cell surface protein found on granulocytes), we observed that tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)–primed mice suffered an extreme and unexpected reaction. Features of this reaction, including intravascular aggregation of leukocytes and platelets, plasma leakage, and microvascular hemorrhagic injury, can be related to sequelae associated with severe shock and DIC. Interestingly, strategies to inhibit both coagulation and leukocyte adhesion are required to prevent the response to Ly-6G ligation in mice primed with TNF-α.
Materials and methods
Materials
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were all purchased from Pharmingen (Oxford, United Kingdom) with the exception of the E-selectin–blocking antibody 10E6, which was a kind gift from Dr B. Wolitzky (Hoffman- La Roche, Nutley, NJ). Polyclonal rabbit antimouse polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) antiserum was purchased from Accurate Chemical & Scientific Corporation (Westbury, NY). Recombinant murine TNF-α (270 000 U/μg) was purchased from R & D Systems (Oxon, United Kingdom). P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 fused to Ig (rPSGL-Ig) was a kind gift from Dr R. Schaub (Genetics Institute, Andover, MA). Fluorescent microspheres were purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR; www.probes.com). Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–albumin was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Poole, United Kingdom).
Anti–Ly-6G antibodies
Ly-6G (previously known as the myeloid differentiation antigen Gr-1) is a 21- to 25-kDa, GPI-anchored protein expressed preferentially on granulocytes in murine bone marrow and on neutrophils and eosinophils in the periphery.10-13 We have used 2 antibodies that recognize Ly-6G. RB6-8C5 is a mAb (isotype IgG2b) raised against Ly-6G that also cross-reacts with Ly-6C. Ly-6C is expressed on neutrophils, monocytes, about 50% of CD8+ T cells,10,14 and endothelial cells15,16 and its expression can be up-regulated by interferon α/β (IFN-α/β) and IFN-γ. RB6-8C5 has been used extensively to deplete granulocytes from the peripheral circulation of mice.13,17 18 Similar to RB6-8C5, 1A8 is a mAb (isotype IgG2a) raised against Ly-6G. Unlike RB6-8C5, however, 1A8 does not cross-react with Ly-6C. RB6-8C5 and 1A8 were purchased from Pharmingen. RB6-8C5 was certified no azide and low endotoxin, having less than 0.01 ng endotoxin/μg protein. We also used Fab and F(ab′)2 fragments of RB6-8C5 in some experiments, which were generated by Cymbus Biotechnology (Hampshire, United Kingdom).
Animals
C57BL/6 and C3/HeJOlaHsd-Lpsd(lipopolysaccharide [LPS]–resistant) mice were purchased from Harlan (Oxon, United Kingdom) or from Hilltop Lab Animals (Scottdale, PA). Colonies of P-selectin knockout,19E-selectin knockout,20 and E/P-selectin double-knockout mice21 were bred in-house. With the exception of C3/HeJOlaHsd-Lpsd mice, all animals used in this study were backcrossed into the C57BL/6 background for at least 6 generations. Male mice weighing between 25 and 35 g were used in these experiments. All procedures performed in the United Kingdom were approved by the University of Sheffield ethics committee and performed in accordance with the Home Office Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1985 of the United Kingdom. All procedures conducted at the University of Virginia were performed under a protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow was harvested from donor mice and transplanted into irradiated recipient mice as described.22 Briefly, recipient mice were lethally irradiated with 2 doses of 6 Gy, each approximately 4 hours apart. Donor mice were killed and bone marrow cells harvested under sterile conditions. Bones were flushed with RPMI 1640 medium and approximately 50 million nucleated cells obtained from each donor mouse. After washing cells and lysing erythrocytes, approximately 1 to 2 million unfractionated bone marrow cells were injected intravenously into recipient mice. Mice were housed in a barrier facility (individually ventilated cages, high-efficiency particulate air filter) under pathogen-free conditions before and after bone marrow transplantation. After transplantation, mice received antibiotics and autoclaved food and water. This procedure routinely produces mice with more than 95% platelets of the donor phenotype 4 to 5 weeks after transplantation.23 Transplantation of P-selectin–deficient bone marrow into wild-type recipients produced mice with P-selectin–positive endothelium and P-selectin–negative platelets. Transplantation of wild-type bone marrow into P-selectin–deficient recipients produced mice with P-selectin–positive platelets and P-selectin–negative endothelium. Wild-type mice also received transplants of wild-type bone marrow as a control.
TNF-α/RB6-8C5–induced microvascular arrest and death
Cremaster inflammation was induced in mice by an intrascrotal injection of TNF-α (20-500 ng in 200 μL saline). The cremaster was prepared for intravital microscopy 3 to 4 hours later as described.17 Briefly, mice were anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine, xylazine, and atropine; cannulations of the trachea, jugular vein, and carotid artery were performed, and the cremaster muscle was exposed and spread over a specialized viewing platform. Temperature was controlled using a thermistor regulated heating pad (PDTronics, Sheffield, United Kingdom) and the cremaster was superfused with thermocontrolled (36°C) bicarbonate-buffered saline.
Microscopic observations were made using an upright microscope (Nikon eclipse E600-FN, Nikon UK, Kingston upon Thames, United Kingdom) equipped for bright field and fluorescence microscopy and with a water immersion objective (40 ×/0.80 W). Images were recorded using a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera (Dage MTI DC-330; DAGE MTI, Michigan City, IN) onto sVHS videocassettes. Single, unbranched venules (20-50 μm diameter) were typically selected and observed for the entire experimental period. Center-line blood flow velocity (VCL) was measured in vessels of interest either using a commercially available velocimeter (Circusoft, Hockessin, DE) or by tracking fluorescent microspheres through vessels.24Vessels with VCL between 1 and 5 mm/s were selected for these studies. Antibody RB6-8C5 or controls (10 μg in 200 μL saline) were injected into the jugular vein 4 to 4.5 hours after TNF-α injection and reactions observed for up to 1 hour. Blood samples were drawn from the carotid at key times (before and after treatments) during the experiment and analyzed for total and differential leukocyte concentrations. Intravital microscopy continued for up to 1 hour unless mice died before this time.
Survival time
To permit assessment of a large number of treatments some mice were not exposed to intravital microscopic procedures. Four hours after TNF-α treatment (20-500 ng, intrascrotally) mice were anesthetized as described and cannulae inserted into their left jugular veins. RB6-8C6 (10 μg) was then injected and time to death or survival at 1 hour recorded. Heparin, where indicated, was given at a dose of 50 U/mouse. Treatments applied prior to TNF-α were given intraperitoneally, whereas treatments applied prior to RB6-8C5 were given intravenously.
Neutrophil depletion studies
In some experiments circulating neutrophils were depleted 48 hours prior to TNF-α stimulation by intraperitoneal injection of 250 μL antineutrophil antiserum (Accurate Chemical and Scientific Corporation). This procedure removed 82% ± 9% of PMN cells from the peripheral circulation of mice without significant effect on mononuclear cells.
Histology
Animals received an intrascrotal injection of TNF-α and were anesthetized 4 hours later as described. A jugular vein was then cannulated and RB6-8C5 (10 μg) injected. After a further 15 minutes (sufficient time for an intense reaction to develop), mice were killed by cervical dislocation and fixatives injected into the scrotum to preserve the cremaster muscle. Cremasters and lungs were then removed and stored in fixative until processed. Tissues were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin prior to hematoxylin and eosin staining and in 3% glutaraldehyde prior to processing for transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
For light microscopy, tissues were embedded flat in paraffin blocks and 4- to 5-μm longitudinal sections cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin according to standard methods. Sections were viewed using the intravital microscopy setup, replacing water-immersion objectives with nonimmersion objectives. Images were captured using Lucia32 G software supplied by Nikon UK. For TEM, sections (0.5 μm) were cut and stained with toluidine blue for identification of areas of interest. Thinner (0.1 μm) sections were then cut and viewed by TEM (Philips 400T; Philips, Eindhoven, Holland).
Flow cytometry
Mice were stimulated for 4 hours with either saline or TNF-α (500 ng intrascrotally). Mice were then anesthetized and anticoagulated with heparin (50 U). Blood (1 mL) was collected by cardiac puncture using a heparinized syringe. Blood samples were incubated with either RB6-8C5 (4 μg/mL final concentration) or phorbol myristate acetate (PMA; 10−7 M final concentration) for 10 minutes at 37°C. FITC-conjugated antibodies against CD11b (M1/70; Pharmingen) or isotype control (A95-1) were then added and CD11b expression of neutrophils analyzed by flow cytometry of appropriately gated cell populations.
Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software (www.graphpad.com). Circulating leukocyte counts before and after application of RB6-8C5 were compared by paired t test. Survival statistics were analyzed using the log-rank test. Points of interest on blood flow plots were compared using unpaired ttest or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Neuman-Keuls procedure for multiple comparisons.
Online supplemental material
A selection of QuickTime movie files is included on theBlood website; see the Supplemental Videos link at the top of the online article. Movies were digitized from video archives,24 and prepared for online viewing using Adobe Premiere version 5.1 (www.adobe.com/premiere) and QuickTime Pro version 5 (www.apple.com/quicktime). Movies run at 1 to 20 times normal speed depending on the duration of the footage.
Results
Tissue activation by TNF-α combined with anti–Ly-6G antibodies: a 2-hit model of DIC
The mAb RB6-8C5 has been extensively used to deplete granulocytes from the peripheral circulation of mice.13 17 In unstimulated mice, RB6-8C5 selectively removed PMN leukocytes from the circulation within 2 minutes of injection (Table1). Interestingly, RB6-8C5 showed less specificity when applied to mice stimulated for 4 hours with 500 ng TNF-α, in which case both PMN and mononuclear cells were depleted (Table 1).
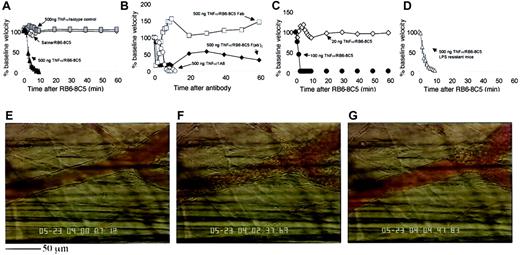
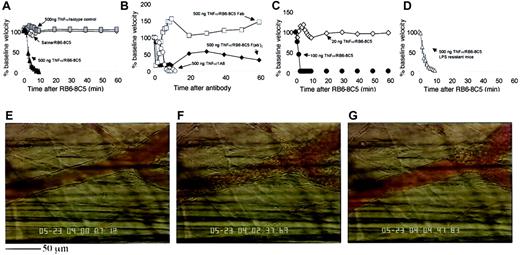
Application of RB6-8C5 to TNF-α–primed mice also revealed a more dramatic effect in the microcirculation than that seen in unstimulated animals. In cremaster venules of mice stimulated with 500 ng TNF-α, we measured a profound reduction of blood flow within minutes of RB6-8C5 (Figure 1). After interruption of normal flow (Figure 1E), red blood cells (RBCs) became densely packed (Figure 1F) and affected vessels eventually clotted (Figure 1G). This response was highly reproducible and all mice treated with RB6-8C5 4 hours after intrascrotal TNF-α (500 ng) eventually died. Injection of isotype control antibody (A95-1) into 500 ng TNF-α–treated mice caused no such reaction and application of RB6-8C5 to unstimulated mice caused only a minor transient disturbance to the microcirculation (Figure 1A).
TNF-α stimulation followed by anti–Ly-6G antibody induces microvascular arrest and coagulation in the mouse cremaster muscle.
(A) Change in venular center-line blood flow velocity induced by RB6-8C5 mAb in unstimulated (⋄) and TNF-α–stimulated (▴) mice and by control IgG (░) in TNF-α–stimulated mice. Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 6 venules from 6 mice. (B) Change in venular center-line blood flow velocity induced by mAb 1A8 (○) against Ly-6G and by Fab (■) and F(ab′)2 (♦) fragments of antibody RB6-8C5. Data shown are representative of 3 or 4 mice per treatment. (C) Effect of RB6-8C5 in mice treated for 4 hours with 100 ng (●) or 20 ng (⋄) TNF-α. Data shown are representative of 3 or 4 mice per treatment. (D) Effect of RB6-8C5 in C3H/HeJOlaHsd-LPSd(LPS-resistant) mice stimulated for 4 hours with TNF-α (500 ng, intrascrotal injection). Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 6 venules from 6 mice. (E) Appearance of a typical venule 4 hours after TNF-α. The same vessel 2 to 3 minutes after RB6-8C5 (F) and 5 minutes after RB6-8C5 (G). The scale bar below panel E measures 50 μm and applies to all three images. A time-lapse movie (Video 1) of panels E to G is included with the online version of the manuscript.
TNF-α stimulation followed by anti–Ly-6G antibody induces microvascular arrest and coagulation in the mouse cremaster muscle.
(A) Change in venular center-line blood flow velocity induced by RB6-8C5 mAb in unstimulated (⋄) and TNF-α–stimulated (▴) mice and by control IgG (░) in TNF-α–stimulated mice. Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 6 venules from 6 mice. (B) Change in venular center-line blood flow velocity induced by mAb 1A8 (○) against Ly-6G and by Fab (■) and F(ab′)2 (♦) fragments of antibody RB6-8C5. Data shown are representative of 3 or 4 mice per treatment. (C) Effect of RB6-8C5 in mice treated for 4 hours with 100 ng (●) or 20 ng (⋄) TNF-α. Data shown are representative of 3 or 4 mice per treatment. (D) Effect of RB6-8C5 in C3H/HeJOlaHsd-LPSd(LPS-resistant) mice stimulated for 4 hours with TNF-α (500 ng, intrascrotal injection). Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 6 venules from 6 mice. (E) Appearance of a typical venule 4 hours after TNF-α. The same vessel 2 to 3 minutes after RB6-8C5 (F) and 5 minutes after RB6-8C5 (G). The scale bar below panel E measures 50 μm and applies to all three images. A time-lapse movie (Video 1) of panels E to G is included with the online version of the manuscript.
Antibody 1A8, which specifically recognizes Ly-6G, caused a reaction that was essentially the same as that induced by RB6-8C5 (Figure 1B) although 1 of 4 mice treated with 1A8 survived the 1-hour observation period after an initial fall in blood flow. Fab and F(ab′)2fragments of RB6-8C5 also reduced flow in TNF-α–primed mice although higher doses (100 μg/mouse) were required and effects were less intense (Figure 1B). Fab of RB6-8C5 only transiently interrupted flow but to a much greater degree than control antibody. F(ab′)2fragments caused a more sustained flow disturbance. All mice treated with Fab or F(ab′)2 fragments of RB6-8C5 survived the 1-hour experimental period.
Mice treated with 100 ng TNF-α followed by RB6-8C5 also showed a marked and sustained fall in blood flow (Figure 1C) similar to that seen in mice treated with 500 ng TNF-α and 50% of these animals died within 1 hour of RB6-8C5 injection (Table2). Mice treated with 20 ng TNF-α showed only a brief disturbance of blood flow (Figure 1C) and all survived the 1-hour observation period (Table 2). Like mice stimulated with 500 ng TNF-α, those treated with 100 ng had clear evidence of an inflammatory response (firmly adherent and transmigrated leukocytes, slow leukocyte rolling in venules, and substantial arteriolar rolling). Mice receiving 20 ng TNF-α had less evidence of inflammation, although rolling in venules was slower than would be expected in an unstimulated mouse, suggesting some E-selectin up-regulation.
LPS-resistant (C3H/HeJOlaHsd-Lpsd) mice treated with 500 ng TNF-α followed 4 hours later with 10 μg RB6-8C5 suffered a marked and sustained fall in cremasteric blood flow (Figure 1D) and all died within 20 minutes of RB6-8C5 injection (Table 2). Thus, it is extremely unlikely that the reaction we describe is a consequence of LPS contamination of either antibody or TNF-α preparations.
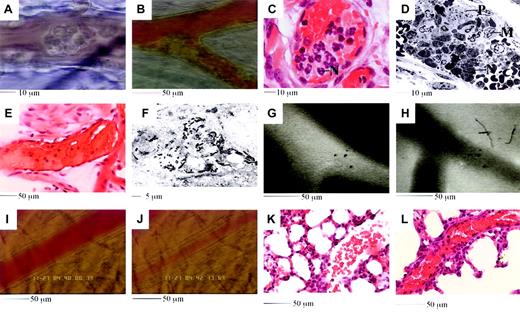
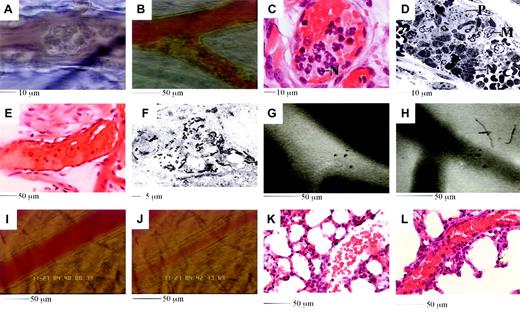
Because 500 ng TNF-α followed by 10 μg RB6-8C5 produced the most dramatic and reliable responses, further studies were performed with these treatments. Following RB6-8C5 application to 500 ng TNF-α–stimulated mice, leukocytes aggregated on the walls of both venules and arterioles (Figure 2A-B). Some aggregates embolized, whereas others were more stable, grew, and often appeared to breach or block vessels. Histologic and electron microscopic examination revealed aggregates to be comprised of a mixture of neutrophils, monocytes, and platelets (Figure 2C-D).
Aggregates often continued to grow beyond the time when most leukocytes had been removed from the circulation. This growth was regularly accompanied by a change in appearance from a form in which individual leukocytes could be easily identified to a more homogenous mass. Rapid formation of leukocyte aggregates followed by a more gradual incorporation of platelets may be responsible for this change in appearance. Significant platelet deposition in the microcirculation was also suggested by depletion of these bodies from the systemic circulation (not shown). After slowing of flow, blood often appeared viscous or clotted (Figure 2E, pale pink areas suggest platelet and fibrin deposition) and electron microscopy revealed fibrin deposition in certain vessels (Figure 2F).
Features of the reaction induced by 4 hours of TNF-α followed by RB6-8C5.
(A-B) Leukocytes adhere and form aggregates in venules (A) and arterioles (B). (C-D) Aggregates are comprised of neutrophils (marked N in panels C and D), platelets (marked P in panel D), and monocytes (marked M in panel D). (E) Plasma clots develop in obstructed vessels; pale pink areas suggest platelets and fibrin. (F) Intravascular fibrin deposition. Black electron dense fibrin strands are clearly evident. Section runs through a compartment that also contains RBCs (not shown). (G-H) Injected fluorescent albumin remains vessel bound after TNF-α (G), but rapidly leaks into tissues if RB6-8C5 is applied (H). (I-J) Arteriolar vasoconstriction is detected soon after RB6-8C5. Panel K shows a lung section from a mouse stimulated with TNFα (50 ng, intrascrotal). Alveolar capillaries appear congested and contain inflammatory cells, but the large vessel to the right remains open. Panel L shows a lung section from a TNFα-stimulated mouse subsequently treated with RB6-8C5. The large vessel running diagonally across the image is extremely congested.
Features of the reaction induced by 4 hours of TNF-α followed by RB6-8C5.
(A-B) Leukocytes adhere and form aggregates in venules (A) and arterioles (B). (C-D) Aggregates are comprised of neutrophils (marked N in panels C and D), platelets (marked P in panel D), and monocytes (marked M in panel D). (E) Plasma clots develop in obstructed vessels; pale pink areas suggest platelets and fibrin. (F) Intravascular fibrin deposition. Black electron dense fibrin strands are clearly evident. Section runs through a compartment that also contains RBCs (not shown). (G-H) Injected fluorescent albumin remains vessel bound after TNF-α (G), but rapidly leaks into tissues if RB6-8C5 is applied (H). (I-J) Arteriolar vasoconstriction is detected soon after RB6-8C5. Panel K shows a lung section from a mouse stimulated with TNFα (50 ng, intrascrotal). Alveolar capillaries appear congested and contain inflammatory cells, but the large vessel to the right remains open. Panel L shows a lung section from a TNFα-stimulated mouse subsequently treated with RB6-8C5. The large vessel running diagonally across the image is extremely congested.
In experiments with fluorescent albumin, we detected plasma leakage from observed vessels into surrounding tissues following RB6-8C5 application (Figure 2G-H). When attention was focused on arterioles we regularly noticed a reduced hematocrit and vasoconstriction following RB6-8C5 (Figure 2I-J). Histologic examination of lung sections revealed features similar to those seen in the cremaster (Figure 2K-L). All of the above features may be implicated in the pathogenesis of conditions associated with DIC.
A role for selectins in reactions induced by TNF-α/RB6-8C5
One of the early events in the reaction was formation of aggregates in arterioles and venules. The selectin family of adhesion molecules mediates many of the initial contacts between leukocytes, endothelial cells, and platelets and may contribute to the reaction described. We used selectin-deficient mice, selectin-blocking antibodies, and a pharmacologic selectin inhibitor to investigate this contribution.
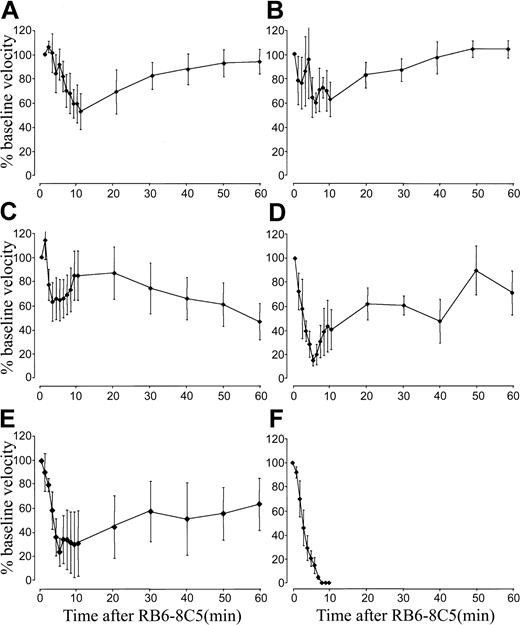
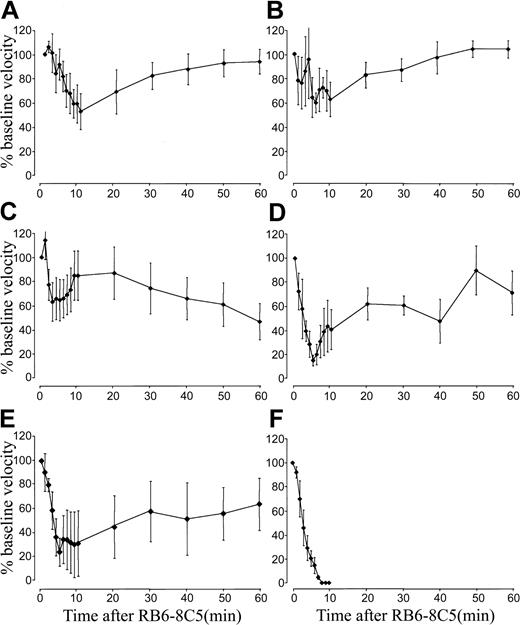
When compared with wild-type mice (Figure 1A), mice deficient in E-selectin or P-selectin suffered only slight reductions in blood flow following 500 ng TNF-α/RB6-8C5 treatment (Figure 3A-B). Blood flow did not fall below 40% of baseline in either E-selectin or P-selectin–deficient mice and in both cases blood flow returned to baseline within 1 hour. Mice lacking both E-selectin and P-selectin were also protected from the reaction induced by 500 ng TNF-α/RB6-8C5 (Figure 3C). All selectin-deficient mice survived for more than 1 hour.
Selectin deficiency protects mice from microvascular arrest induced by TNF-α and RB6-8C5.
(A-C) TNF-α/RB6-8C5–induced blood flow changes in P-selectin–deficient (A), E-selectin–deficient (B), and E-selectin/P-selectin double-deficient (C) mice. (D-F) TNF-α/RB6-8C5–induced changes in bone marrow transplantation experiments; wild-type mice given transplants of P-selectin–deficient bone marrow (D), P-selectin–deficient mice given transplants of wild-type bone marrow (E), wild-type mice given transplants of wild-type bone marrow (F). Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 1 to 3 vessels from 4 to 6 mice per group.
Selectin deficiency protects mice from microvascular arrest induced by TNF-α and RB6-8C5.
(A-C) TNF-α/RB6-8C5–induced blood flow changes in P-selectin–deficient (A), E-selectin–deficient (B), and E-selectin/P-selectin double-deficient (C) mice. (D-F) TNF-α/RB6-8C5–induced changes in bone marrow transplantation experiments; wild-type mice given transplants of P-selectin–deficient bone marrow (D), P-selectin–deficient mice given transplants of wild-type bone marrow (E), wild-type mice given transplants of wild-type bone marrow (F). Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 1 to 3 vessels from 4 to 6 mice per group.
We performed bone marrow transplantation experiments to further explore the contribution of P-selectin to the reaction induced by 500 ng TNF-α/RB6-8C5. Mice lacking either platelet (Figure 3D) or endothelial cell (Figure 3E) P-selectin were protected albeit to a lesser degree than mice devoid of P-selectin. This suggests an important function for P-selectin from both potential cellular sources. Reactions in wild-type mice given transplants of wild-type bone marrow were identical to those in mice that did not receive transplants (Figure 3F).
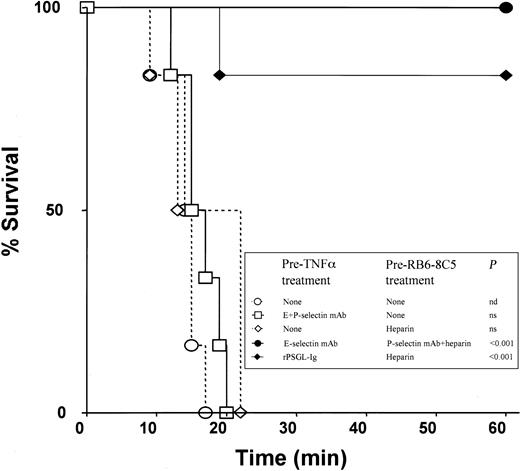
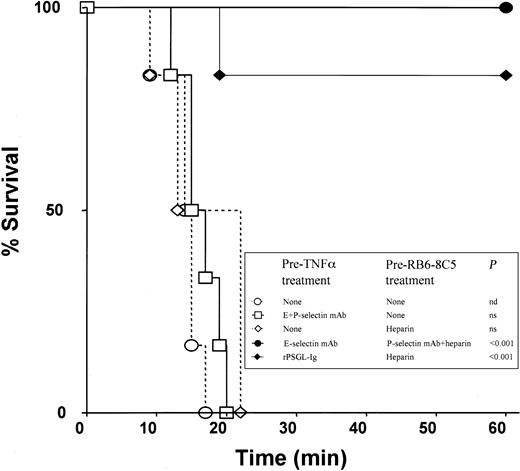
In experiments on survival time, all wild-type animals that received 500 ng TNF-α plus RB6-8C5 died within 20 minutes (Figure4). Similar times to death were recorded in intravital microscopy experiments (not shown). Neutrophil depletion (about 90%) with a polyclonal anti-PMN antiserum protected most mice from death (Table 2), adding further support to the hypothesis that the effects of anti-Ly6G antibodies are mediated through their actions on neutrophils. In surprising contrast to experiments with selectin-deficient mice, a combination of antibodies against E-selectin (10E6, 30 μg intraperitoneally) and P-selectin (RB40.34, 30 μg intraperitoneally) failed to protect against microvascular arrest and death induced by 500 ng TNF-α and RB6-8C5 (Figure 4). Scrutiny of videorecordings revealed that blood in venules of mice treated with both antibodies appeared to simultaneously clot and stop following RB6-8C5 treatment, contrasting with mice without these antibodies wherein blood stopped and then gradually clotted. This observation led us to hypothesize that an anticoagulant applied in combination with E-selectin and P-selectin antibodies might provide protection.
Survival rates in differently treated mice.
All mice received 500 ng TNF-α at −4 hours and RB6-8C5 at 0 minute.P values represent difference from mice treated with TNF-α and RB6-8C5 alone; n = 6 mice per group. Further survival data are shown in Table 2.
Survival rates in differently treated mice.
All mice received 500 ng TNF-α at −4 hours and RB6-8C5 at 0 minute.P values represent difference from mice treated with TNF-α and RB6-8C5 alone; n = 6 mice per group. Further survival data are shown in Table 2.
Heparin combined with antibodies against E-selectin and P-selectin protected mice from death induced by 500 ng TNF-α and RB6-8C5 (Table 2; Figure 4) with the strongest protection seen when E-selectin antibody was applied prior to TNF-α injection and P-selectin antibody plus heparin were applied prior to injection of RB6-8C5 (Figure 4). Heparin prior to TNF-α, anti–E-selectin plus heparin or anti–P-selectin plus heparin were either less or not protective (Table 2), suggesting that coagulation and both E-selectin and P-selectin need to be targeted for prevention of the reaction under investigation.
A selectin inhibitor (rPSGL-Ig) has been developed that can inhibit leukocyte rolling via all 3 selectins in vivo if given at appropriate doses.25 rPSGL-Ig prevented death induced by 500 ng TNF-α and RB6-8C5 in 5 of 6 mice if given prior to TNF-α and if heparin was also applied (Figure 4). Intravital microscopy experiments revealed that these mice were also protected from microvascular arrest (not shown). No protection was seen if rPSGL-Ig was given before TNF-α without later heparin treatment or if it was given in combination with heparin after 4 hours of TNF-α stimulation (Table 2).
Treatments and genetic deletions that provided protection did not prevent disappearance of leukocytes from the circulation in response to TNF-α/RB68-C5 (Table 1, most protective treatment shown). This suggests that, rather than inhibiting the fundamental response stimulated by RB6-8C5, antiselectin/anticoagulant treatment prevents downstream consequences of this response. None of the inhibitor-treated mice or selectin-deficient mice were entirely protected from the inflammatory consequences of TNF-α/RB6-8C5. Leukocyte endothelial cell interaction was detectable 4 hours after TNF-α in all intravital microscopy experiments. Mice deficient in E-selectin or mice treated with anti–E-selectin antibody had faster leukocyte rolling as expected, and E/P-selectin double-deficient, double antibody–treated or rPSGL-Ig–treated mice had reduced but detectable leukocyte rolling. Aggregate formation was detectable in all groups following RB6-8C5 treatment, possibly explaining the fall in blood flow seen in selectin-deficient mice. Embolization of aggregates seemed more prevalent in selectin-deficient and inhibitor-treated-mice. We were unable to reliably quantify aggregate formation or embolization because detection depended on coincidence between our point of observation (selected prior to RB6-8C5) and the location of aggregate formation. Based on these qualitative observations we believe that altered size and stability of formed aggregates may underlie the protective consequences of antiselectin strategies and suggest that subtle differences in these parameters might explain the discrepancy between results with selectin-deficient and inhibitor-treated mice.
Potential mechanisms by which RB6-8C5 induces microvascular arrest in mice stimulated with TNF-α
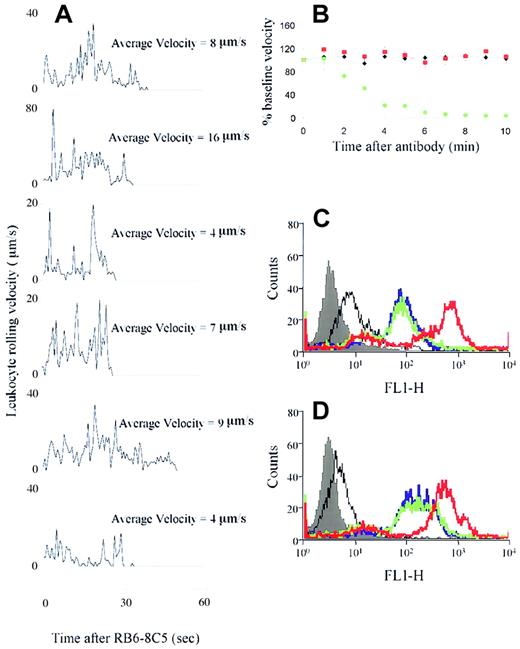
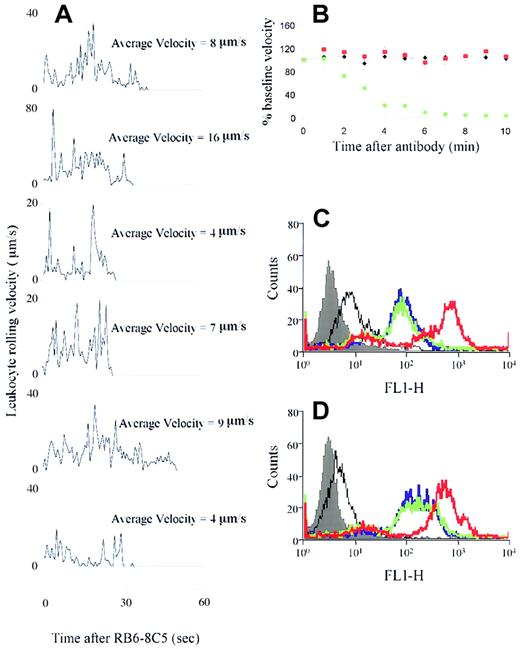
To investigate whether injection of RB6-8C5 caused leukocyte activation, we tracked rolling leukocytes through venules of mice that had been stimulated for 4 hours with TNF-α and had just received RB6-8C5. Rolling velocities of 6 leukocytes in a typical venule are shown in Figure 5A. All of the tracked leukocytes arrested (velocity = 0) within 40 seconds of RB6-8C5, indicating rapid activation of these cells on exposure to the antibody (which takes about 30 seconds to reach the cremaster). This rapid effect is in keeping with the time course of the measured changes in blood flow and the rapid depletion of leukocytes from the circulation following RB6-8C5. Without TNF-α pretreatment, RB6-8C5 injection caused rolling leukocytes to detach from the endothelium with a similar time course to the firm adhesion response previously described.
RB6-8C5 activation of leukocytes/neutrophils in vivo but not in vitro.
(A) Positional changes of rolling leukocytes were determined every 40 video frames commencing at the time of RB6-8C5 application and continuing for 1 minute. Velocity = 0 indicates arrest of the cells. (B) Changes in blood flow induced by control treatments. Black diamonds represent mice receiving anti–L-selectin mAb (Mel-14) in place of RB6-8C5; red squares represent mice receiving anti–PSGL-1 mAb 2PH1 in place of RB6-8C5. Green circles represent mice receiving anti–Fcγ receptor II/III antibody 100 μg intravenously) followed 5 minutes later by RB6-8C5. Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 4 to 6 mice per group. (C-D) Effect of RB6-8C5 on CD11b expression of neutrophils from saline (C) and TNF-α–stimulated (D) mice. Filled histogram indicates autofluorescence, black line, isotype control for CD11b mAb; blue line, basal CD11b expression; green line, CD11b expression after RB6-8C5 treatment; red line, CD11b expression after PMA (positive control) treatment. Figures are representative of data obtained in 3 separate experiments.
RB6-8C5 activation of leukocytes/neutrophils in vivo but not in vitro.
(A) Positional changes of rolling leukocytes were determined every 40 video frames commencing at the time of RB6-8C5 application and continuing for 1 minute. Velocity = 0 indicates arrest of the cells. (B) Changes in blood flow induced by control treatments. Black diamonds represent mice receiving anti–L-selectin mAb (Mel-14) in place of RB6-8C5; red squares represent mice receiving anti–PSGL-1 mAb 2PH1 in place of RB6-8C5. Green circles represent mice receiving anti–Fcγ receptor II/III antibody 100 μg intravenously) followed 5 minutes later by RB6-8C5. Data are shown as means ± SEMs of 4 to 6 mice per group. (C-D) Effect of RB6-8C5 on CD11b expression of neutrophils from saline (C) and TNF-α–stimulated (D) mice. Filled histogram indicates autofluorescence, black line, isotype control for CD11b mAb; blue line, basal CD11b expression; green line, CD11b expression after RB6-8C5 treatment; red line, CD11b expression after PMA (positive control) treatment. Figures are representative of data obtained in 3 separate experiments.
The reaction we describe could be a nonspecific consequence of ligating Ly-6G or may be directly related to its function. We studied a range of controls to investigate this question. Nonbinding isotype control antibody did not alter blood flow in TNF-α–stimulated mice (Figure1). We have also studied the effects of antibodies against molecules that are known to be expressed on the surface of neutrophils and have been implicated in neutrophil activation. Antibodies against L-selectin and against PSGL-1 did not alter blood flow in TNF-α–stimulated mice (Figure 5B) and showed no sign of initiating leukocyte aggregate formation at the vessel wall.
Although Fab and F(ab′)2 fragments of RB6-8C5 showed activity, the possibility that cross-linking Fcγ receptors contributed to the more pronounced effects of whole antibodies remained. Others have described arrest of rolling neutrophils in vitro in response to antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and an in vivo shock reaction induced by antibodies against glycoprotein IIb/IIIa on platelets that are both Fcγ receptor dependent.26,27 In contrast to the above, our reaction was not Fcγ receptor dependent (Figure 5B). Antibody 2.4G2, at a dose which blocks Fcγ receptors II and III,27 failed to protect mice from RB6-8C5–induced microvascular arrest and death (Figure 5B) or to prevent leukocyte depletion by RB6-8C5 (not shown). These data in combination with the positive effects of antibody fragments suggest that the striking effects of RB6-8C5 are not mediated by Fc.
We used flow cytometry to determine the effect of RB6-8C5 on neutrophils in vitro. Although 4 hours of in vivo TNF-α stimulation increased CD11b expression on murine neutrophils (compare Figure 5C with 5D), no further change was seen on addition of RB6-8C5 at a concentration equivalent to that given in vivo. This suggests that an, as yet, unidentified “in vivo factor” is required for the actions of RB6-8C5.
Discussion
The tendency of blood to clot increases if endothelium is injured, blood flow is interrupted, or coagulability of the blood is increased. Although TNF-α has many procoagulant effects,28 500 ng TNF-α did not induce generalized coagulation of the cremaster muscle after 4 hours in our model. We propose that 4 hours after TNF-α, the microcirculation of the cremaster (and other activated tissues) is in a primed state wherein anticoagulant mechanisms prevail. Application of anti–Ly-6G antibodies upsets the equilibrium somehow, tipping the balance toward coagulation. Anti–Ly-6G antibodies cause neutrophil adhesion and aggregation (perturbing blood flow), may cause neutrophil activation (injuring endothelium), and recruit monocytes and platelets (bringing in additional procoagulant effectors). These effects will favor widespread intravascular coagulation if multiple vascular beds are affected.
Inspection of the cremaster microcirculation following RB6-8C5 application to 500 ng TNF-α–stimulated mice reveals a multitude of features that may be causes or consequences of the measured microvascular arrest and eventual death of the mouse. These features (platelet and leukocyte aggregation, microvascular obstruction, intravascular fibrin deposition, vascular leakage, respiratory problems) are also common in patients with sepsis or traumatic shock.1,28 Less dramatic effects are seen in mice receiving lower doses of TNF-α, which is consistent with previously described effects of this agent on inflammatory responses in the microcirculation.29
Gene-targeted mice lacking either E-selectin or P-selectin were convincingly protected from the reaction induced by RB6-8C5. Protection was also seen in mice lacking both and E-selectin and P-selectin and, to a lesser extent, in mice lacking just platelet P-selectin or just endothelial cell P-selectin. Presented with these clear data, it is tempting to form the simple hypothesis that neutrophils rolling on E-selectin and P-selectin are activated in response to Ly-6G ligation and that they then aggregate and recruit platelets and monocytes (perhaps through platelet P-selectin). Although experiments with selectin-blocking antibodies upset this hypothesis (eg, a combination of E-selectin plus P-selectin antibodies is not protective), data may be reconciled by 2 possible explanations: (1) either gene targeting produces effects that cannot be reproduced by acute antibody treatment, or (2) antibody treatment has consequences that are not encountered with gene-targeted mice.
Interestingly, a combination of selectin-blocking antibodies plus heparin provided convincing protection against RB6-8C5–induced microvascular arrest and death. The discrepancy between knockout mouse and antibody data may relate to reduced coagulation (or enhanced anticoagulation) in mice lacking either E-selectin or P-selectin or to a procoagulant effect of selectin-blocking antibodies. Published data exist supporting both of these possibilities. Mice with a mutation in the cytoplasmic tail of P-selectin have elevated soluble P-selectin and a procoagulant phenotype,30 suggesting the possibility that mice lacking selectins have less propensity toward coagulation. Alternatively, antibodies against platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa induce thrombocytopenia, hypothermia, and acute lung injury via an Fcγ receptor–mediated reaction.27 It is possible that antibodies against E-selectin and P-selectin produce unwarranted effects on endothelial cells or platelets counteracting the protective effects they also have. Our data with rPSGL-Ig, which lacks Fc binding, tend to support the former explanation.
Why these antibodies induce such an intense reaction in TNF-α–primed mice is not clear. RB6-8C5 binds to Ly-6G, which is preferentially expressed on granulocytes in the peripheral circulation,10-13 and Ly-6C, which is expressed on a variety of other cells including monocytes,10CD8+ T cells,10 and endothelial cells.15 16 Although it could be argued that targeting Ly-6C on monocytes is more likely to induce coagulation (monocytes being an abundant source of tissue factor), our data with 1A8 antibody and with neutrophil-depleting antiserum implicate neutrophils as the initial target for activation. Neutrophil aggregates in small blood vessels may impair blood flow, favoring coagulation. Secondary recruitment of monocytes and platelets is likely to ensure that coagulation occurs in TNF-α–primed mice.
Little is known regarding the function of the Ly-6 family. A signaling role has been suggested, based largely on observations of cell activation following antibody ligation of some family members including Ly-6C.16,31 A ligand (Ly-6d-L) for one member of the Ly-6 family has also been identified.32 Particularly interesting possibilities arise from the phenotype of mice lacking Ly-6A, T cells of which exhibit prolonged proliferative responses to antigen stimulation.33 This suggests a down-regulatory function of Ly-6A. If a similar role for Ly-6G is hypothesized then it is tempting to imagine that antibody ligation of Ly-6G might remove an important negative regulator of neutrophil function, resulting in activation and the responses we have described. Rigorous investigation of this hypothesis will require identification of the in vivo factor required for neutrophil activation in response to Ly-6G.
Patients with sepsis or trauma-induced DIC do not typically have circulating antineutrophil antibodies and DIC develops more gradually than events occurring in response to TNF-α/RB6-8C5. Blood-borne agents (chemokines, complement, bacterial cell wall products) capable of activating neutrophils and other leukocytes are likely to have untoward effects especially within blood vessels that are already activated. Patients' organs and tissues may be successively or continuously exposed to events similar to those induced by TNF-α/RB6-8C5, resulting in progressive vessel and organ injury, consumption of hemostatic factors, and gradual deterioration of the patient.
We propose neutrophil activation on a background of preexisting tissue inflammation as a fundamental mechanism in DIC associated with sepsis and major trauma. Investigating the effects of neutrophil-activating agents within primed tissues may reveal much about the pathogenesis of these conditions. Furthermore, results with selectin inhibitors and knockout mice suggest that heparin combined with appropriate adhesion molecule blockade may have clinical benefit.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, September 19, 2002; DOI 10.1182/blood-2001-12-0190.
Supported by a Career Establishment Grant from the Medical Research Council and grants 061305 and 057108 from the Wellcome Trust. M.J.C. is supported by a studentship (FS99040) from the British Heart Foundation.
The online version of the article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Keith Norman, Cardiovascular Research Group, Clinical Sciences Centre, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield S5 7AU, United Kingdom; e-mail: k.norman@shef.ac.uk.