Abstract
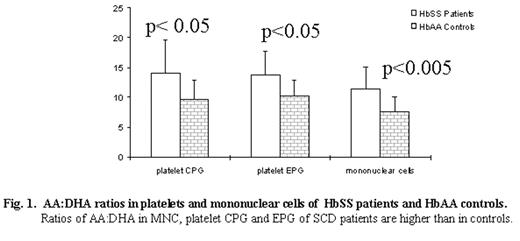
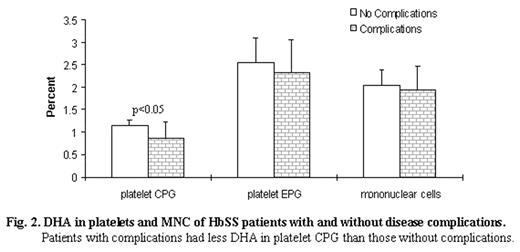
Leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium contributes to vaso-occlusion and widespread organ damage in sickle cell disease (SCD). Previously, we found high expression of the adhesion molecules αMβ2 integrin and L-selectin in HbSS individuals with severe disease. The n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (FA) are vital structural and functional components of cell and sub-cellular membranes. They modulate cell adhesion, inflammation, aggregation and vascular tone. We investigated the FA composition of mononuclear cells (MNC) and platelets of HbSS patients in steady-state (n = 28); and racially matched, healthy HbAA controls (n = 13). MNC phospholipids of the patients had low levels of docosahexanoic acid (DHA, p<0.01), n-3 metabolites (p<0.05) and total n-3 polyunsaturated FA (p<0.05); table 1. In contrast, arachidonic (AA, p<0.005), AA:DHA ratio (p<0.005, fig 1) and total n-6 metabolites (p<0.05) were increased in the patients. Similarly, platelets from HbSS patients had low levels of eicosapentanoic acid (EPA, p<0.05), and raised AA (p<0.05) in choline phosphoglycerides (CPG); with reduced linoleic acid (LA, p<0.005) and DHA (p<0.05) in ethanolamine phosphoglycerides. Platelet CPG had lower DHA levels in HbSS individuals with complications of SCD compared to those who had no complications (p<0.05, fig.2). Reduced EPA and DHA relative to AA favours the production of aggregatory and pro-inflmmatory eicosanoids that activate leukocytes and platelets. This may lead to enhanced inflammation, leukocyte adhesion, platelet aggregation and vaso-occlusion in SCD.
Table 1: Fatty Acid Composition of MNC Total Phospholipids in HbSS Patients and HbAA Controls
| Fatty Acids . | HbSS Patients . | HbAA Controls . |
|---|---|---|
| Values are Means [SD}. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ****p<0.001 | ||
| 24:0 | 0.71 [0.30]*** | 1.3 [0.4] |
| saturates ∑ | 38.2 [3.6] | 39.1 [1.7] |
| 16:1 | 0.69 [0.45] | 0.56 [0.11] |
| 18:1 | 14.4 [1.8]* | 12.9 [1.9] |
| 24:1 | 1.2 [0.3] | 1.1 [0.4] |
| ∑monoenes | 16.2 [2.1]** | 14.3 [1.4] |
| 18:2n-6 | 6.1 [0.9] | 7.0 [1.4] |
| 18:3n-6 | 0.11 [0.04]* | 0.23 [0.17] |
| 20:2n-6 | 0.56 [0.18]** | 0.83 [0.32] |
| 20:3n-6 (DHGLA) | 1.2 [0.2]* | 1.4 [0.2] |
| 20:4n-6 | 20.2 [1.7]*** | 18.1 [1.8] |
| 22:4n-6 | 1.7 [0.4] | 1.6 [0.4] |
| 22:5n-6 | 0.3 [0.21] | 0.24 [0.14] |
| n-6 metabolites ∑ | 24.1 [1.9]* | 22.6 [1.7] |
| n-6 ∑ | 30.2 [2.0] | 29.7 [2.2] |
| 20:5n-3 (EPA) | 0.43 [0.16] | 0.61 [0.35] |
| 22:6n-3 (DHA) | 1.9 [0.4]** | 2.5 [0.6] |
| ∑n-3metabolites | 4.3 [0.9]* | 4.8 [0.4] |
| n-3 ∑ | 4.5 [0.9]* | 5.0 [0.4] |
| DHGLA:AA ratio | 0.06 [0.01]**** | 0.08 [0.01] |
| AA:EPA ratio | 52.4 [20.9] | 38.6 [18.4] |
| Fatty Acids . | HbSS Patients . | HbAA Controls . |
|---|---|---|
| Values are Means [SD}. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ****p<0.001 | ||
| 24:0 | 0.71 [0.30]*** | 1.3 [0.4] |
| saturates ∑ | 38.2 [3.6] | 39.1 [1.7] |
| 16:1 | 0.69 [0.45] | 0.56 [0.11] |
| 18:1 | 14.4 [1.8]* | 12.9 [1.9] |
| 24:1 | 1.2 [0.3] | 1.1 [0.4] |
| ∑monoenes | 16.2 [2.1]** | 14.3 [1.4] |
| 18:2n-6 | 6.1 [0.9] | 7.0 [1.4] |
| 18:3n-6 | 0.11 [0.04]* | 0.23 [0.17] |
| 20:2n-6 | 0.56 [0.18]** | 0.83 [0.32] |
| 20:3n-6 (DHGLA) | 1.2 [0.2]* | 1.4 [0.2] |
| 20:4n-6 | 20.2 [1.7]*** | 18.1 [1.8] |
| 22:4n-6 | 1.7 [0.4] | 1.6 [0.4] |
| 22:5n-6 | 0.3 [0.21] | 0.24 [0.14] |
| n-6 metabolites ∑ | 24.1 [1.9]* | 22.6 [1.7] |
| n-6 ∑ | 30.2 [2.0] | 29.7 [2.2] |
| 20:5n-3 (EPA) | 0.43 [0.16] | 0.61 [0.35] |
| 22:6n-3 (DHA) | 1.9 [0.4]** | 2.5 [0.6] |
| ∑n-3metabolites | 4.3 [0.9]* | 4.8 [0.4] |
| n-3 ∑ | 4.5 [0.9]* | 5.0 [0.4] |
| DHGLA:AA ratio | 0.06 [0.01]**** | 0.08 [0.01] |
| AA:EPA ratio | 52.4 [20.9] | 38.6 [18.4] |
Author notes
Corresponding author