Abstract
Pain during vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC) in sickle cell disease (SCD) is commonly treated with continuous intravenous infusion (CI) of morphine. During CI the treating physician titrates the dose of morphine until adequate relief of pain has been established. Patient controlled analgesia (PCA) allows the patient to self-administer doses of morphine for the relief of pain and has shown to be equianalgesic in post surgical patients with lower morphine consumption than with CI of morphine. Morphine has many dose-related side-effects and high plasma levels of morphine are associated with serious complications. Therefore, we conducted the first randomized controlled trial to compare the administration of morphine with PCA versus CI in sickle cell patients with VOC. 26 consecutive episodes of VOC in 21 patients with SCD were included. Patients were randomized between PCA and CI of morphine within 24 hours after hospital admission. Endpoints of the study were: the mean and cumulative morphine dose, pain intensity and quality of life (QoL). Pain intensity was measured daily using a ten-point-scale verbal pain score. Reduction of pain intensity was measured by subtracting a pain score on a ten point visual analogue scale (VAS) before randomization from the same measurement two days after randomization. QoL was measured using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short Form Healthy Survey (SF36).
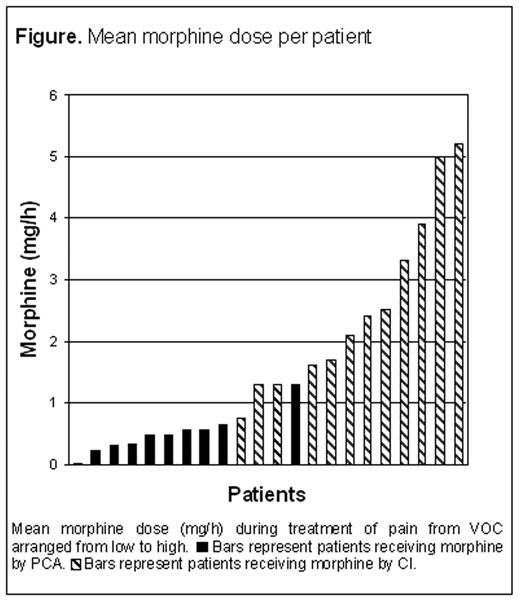
Patients with PCA demonstrated to have significant lower morphine consumption as compared to patients randomized to CI. The mean and total cumulative morphine dose was 0.5 mg/h and 33 mg in the PCA-group versus 2.3 mg/h and 275 mg in the CI-group, respectively (p=0.02 and p<0.001). The pain intensity was not different between the groups. The mean daily ten-point-scale verbal pain score was 5.1 in the PCA group versus 5.3 in the CI-group (p=0.20). Reduction in pain intensity (VAS) two days after randomization was −2.4 in the PCA-group versus −3.8 in the CI-group (p=1.00). Also no difference in QoL was found.
We conclude that the use of PCA in sickle cell patients with VOC results in adequate pain relief at a significant lower morphine dose as compared to morphine administration by continuous infusion.
Author notes
Corresponding author