Abstract
Background: As a series of our previous investigation (Haematologica, 2005. 90: 939–48) identifying poor prognostic factors (lymphocytopenia and visceral involvement) at the onset of acute GVHD (aGVHD) in patients with a history of aGVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT), we tried to identify variables that could predict the development of chronic GVHD of progressive or quiescent type (pq cGVHD) and patients’ outcome after the diagnosis of cGVHD in cohort of 99 patients who experienced aGVHD after allogeneic SCT.
Patients and Methods: We evaluated the risk factors for cGVHD of pq cGVHD with various clinical parameters in patient group with a history of aGVHD and also the prognostic significance of various clinical parameters at diagnosis of cGVHD to determine the prognostic factor for GVHD-specific survival (GSS) in patients with pq cGVHD.
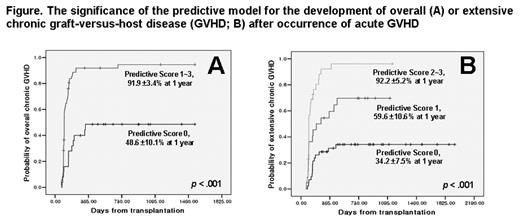
Results: From 118 patient experienced aGVHD of any degree, 99 patients were evaluated for cGVHD. The cumulative incidence of overall and extensive pq cGVHD at 2 years was estimated as 84.4% and 63.1%, respectively. In univariate analyses for risk factors of pq cGVHD, severe grade 3,4 aGVHD, primary treatment failure (PTF), lymphocytopenia (≤100/μl), elevated ALP (>160IU/l), visceral involvement, hepatic or gut involvement were identified. Especially, severe aGVHD (p=0.022 and <0.001), PTF (p=0.009 and 0.010) for overall and extensive pq cGVHD, lymphocytopenia (p=0.031) for extensive pq cGVHD, and elevated ALP (p=0.001) for overall pq cGVHD were independent risk factors. The prediction model of subsequent pq cGVHD validated these risk factors with respect to the incidences of overall pq cGVHD (48.6% versus 91.9% for no risk factor versus 1~3 risk factor(s)) and of extensive pq cGVHD (34.2% versus 59.6% versus 92.2% for no / 1 / 2~3 risk factors). HLA-disparity and stem cell source did not influence on the development of pq cGVHD in this cohort. The GSS and probability of systemic immunosuppressive treatment at 2 year after diagnosis of cGVHD was estimated as 55.9% and 51.9%. The GSS was significantly associated with the performance status (p=0.004) and lymphocytopenia (≤ 1,000/μl, p=0.022) at diagnosis of cGVHD by Cox’s proportional hazard model.
Conclusion: Severe aGVHD, PTF, lymphocytopenia and elevated ALP may be useful predictive factors for the development of pq cGVHD in a cohort of patients who experienced a GVHD after allogeneic SCT.
The significance of the predictive model for the development of overall (A) or extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD; B) after occurence of acute GVHD
The significance of the predictive model for the development of overall (A) or extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD; B) after occurence of acute GVHD
Author notes
Corresponding author