Abstract
Gene expression profiling has yielded a new molecular taxonomy of DLBCL in which 3 subtypes are distinguished; germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtype, derived from a germinal center B-cell; activated B-cell (ABC) subtype, derived from a post-germinal center B-cell; and primary mediastinal B-cell (PMBL) subtype, likely derived from a “thymic” B-cell. To define the effect of pathobiology on treatment outcome, immunophenotype has been used as an “approximate surrogate” biomarker for molecular taxonomy. Recent studies suggest that rituximab (R) benefit is primarily in BCL-6− (
Biomarker Distribution
| Biomarker . | Number . | Percent . |
|---|---|---|
| BCL-6 Neg | 14 | 24 |
| BCL-6 Pos | 44 | 76 |
| BCL-2 Neg | 24 | 41 |
| BCL-2 Pos | 35 | 59 |
| GCB | 34 | 67 |
| ABC | 17 | 33 |
| MIB-1 < 80% | 13 | 33 |
| MIB-1 > 80% | 39 | 67 |
| CD10 Neg | 36 | 63 |
| CD10 Pos | 21 | 37 |
| Mum-1 Neg | 30 | 64 |
| Mum-1 Pos | 17 | 36 |
| Biomarker . | Number . | Percent . |
|---|---|---|
| BCL-6 Neg | 14 | 24 |
| BCL-6 Pos | 44 | 76 |
| BCL-2 Neg | 24 | 41 |
| BCL-2 Pos | 35 | 59 |
| GCB | 34 | 67 |
| ABC | 17 | 33 |
| MIB-1 < 80% | 13 | 33 |
| MIB-1 > 80% | 39 | 67 |
| CD10 Neg | 36 | 63 |
| CD10 Pos | 21 | 37 |
| Mum-1 Neg | 30 | 64 |
| Mum-1 Pos | 17 | 36 |
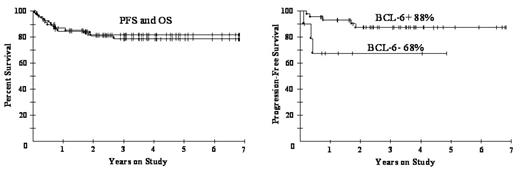
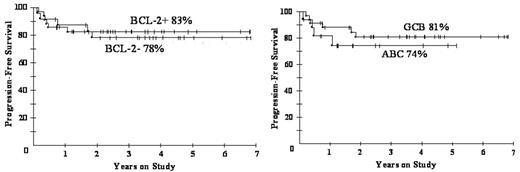
In conclusion, DA-EPOCH-R appears equally effective among all biomarker subgroups. Of note, DA-EPOCH-R is highly effective in BCL-6+ DLBCL, in which R does not appear to be very useful, suggesting the DA-EPOCH regimen itself may be highly effective in this group. The CALGB has initiated a Phase III randomized study of R-CHOP vr. DA-EPOCH-R to determine if DA-EPOCH-R represents a treatment advance. Gene expression profiling will be performed to assess the effect of the new molecular taxonomy and tumor biology on outcome.
Disclosures: Not all agents in the DA-EPOCH-R regimen are approved for the upfront treatment of DLBCL.
Author notes
Corresponding author