Abstract
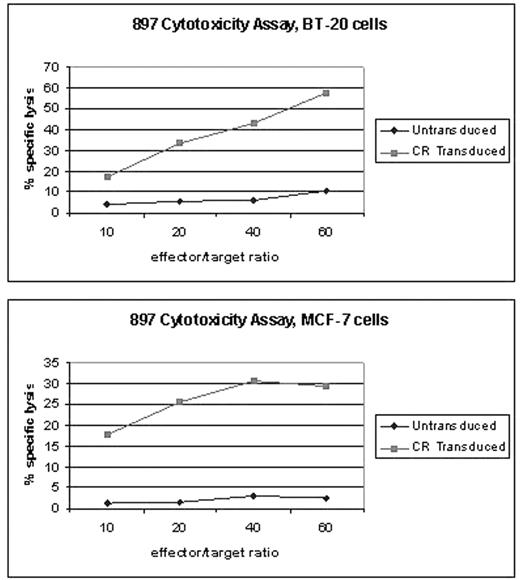
Mucin1 (Muc1), a tumor-associated antigen, is overexpressed in many adenocarcinomas including breast, pancreas, ovary, prostate, colon, and in multiple myeloma. Therefore, tumor associated Muc1 is an attractive target for immunotherapy. Several types of immunotherapeutic approaches targeting Muc1 are currently being tested in preclinical and clinical settings. A major limitation of vaccination strategies involving tumor antigens is the lack of induction of sufficient number of antigen-specific effector T cells systemically to achieve objective clinical response. In an effort to redirect activated T cells towards tumor cells, we constructed lentiviral vectors expressing chimeric receptors consisting of a novel single chain variable domain (scFv) of a monoclonal antibody against Muc1 combined with various cytoplasmic signaling domains such as CD3 Zeta, CD28 and OX40. Human peripheral blood T cells were lentivirally transduced with chimeric immune receptors in order to redirect them towards Muc1 positive tumor cells. A sufficiently high level of transduction (>80) was achieved without any positive selection. Transduced T cells were stimulated and expanded over a period of 10–15 days in the presence of IL-2. Gene-modified T cells efficiently recognized Muc1 expressing tumor target cells in an MHC-independent manner as demonstrated by antigen-specific tumor cell cytolysis. Furthermore, transduced T cells showed antigen-specific proliferation and secreted interferon gamma upon ligation with Muc1 on tumor cells. These results indicate that generation of large numbers of antigen specific T cells for clinical application is possible through the use of this chimeric immune receptor gene transfer strategy. This approach might be an attractive strategy in a minimal residual disease setting complementing traditional therapies based on surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy. Therefore, present study suggests a promising new strategy for cancer immunotherapy using gene-modified T cells.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author