Abstract
BACKGROUND: The use of hematopoetic growth factors after conventional induction chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains controversial. Yet from former studies with sequential high dose AraC (S-HAM) in relapsed and refractory AML it was shown that the use of G-CSF reduced the early death rate significantly in this clinical setting. Pegylated filgrastim (NEULASTA©, Amgen) has shown to have a sustained-duration effect compared to conventional filgrastim due to decreased renal clearance. This analysis focuses on pegfilgrastim pharmacokinetics and effect on neutrophil recovery in AML.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: The ongoing AML CG pilot trial uses sequential high dose AraC as accelerated dose dense induction therapy in AML. It comprises 66 % of the established HAM-HAM double induction regimen (HAM: AraC 3 g/m2 bid for 3 days and mitoxantron 10 mg/m2 for 3 days) given within 2 weeks instead of four. 6 mg of Neulasta© was applied subcutaneously to all patients with complete blast clearance on day 18 after start of S-HAM. Blood samples for measurement of Neulasta plasma levels were obtained before application and afterwards daily up to day 21. Plasma concentrations of pegfilgrastim were measured by ELISA technique. Leukocyte count was obtained daily.
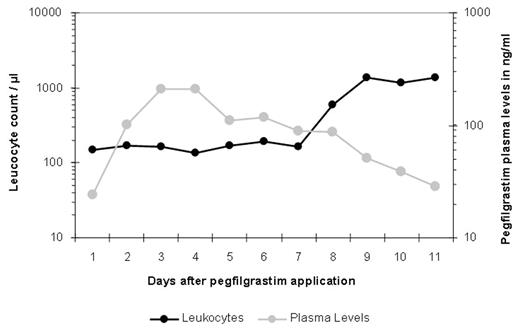
RESULTS: Analyses were performed in 19 patients at two institutions. After injection, peak plasma levels with a mean of 174 ng/ml were achieved within 48 hours after injection and t ½ was 6 days. 7 of these patients received a second injection of Neulasta 10 – 15 days later due to insufficient neutropenic recovery. Here plasma levels of > 200 ng/ml were achieved. Effective plasma levels of Neulasta (> 2.0 ng/ml) were observed up to 14 days after injection. In those patients who remained neutropenic, Neulasta plasma levels were observed even longer (t ½ > 6 days).
Pegfilgrastim clearance was significantly correlated to neutrophil recovery (r=−0.91, p=0.001). Median time to leukocyte recovery of > 1 G/l was 9 days after injection of the first dose in all evaluable patients.
CONCLUSION: In our study, time to neutrophil recovery in primary AML was shortened to 26 days by use of an accelerated, dose dense regimen plus pegfilgrastim application as compared historically to standard double induction therapy (median time to neutrophil recovery 45 days).
Disclosures: AMGEN research grant.
Author notes
Corresponding author