Abstract
Donor cell leukemia (DCL) is a rare complication of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Its incidence has been reported between 0.12% and 5%, although the majority of cases are anecdotal. The mechanisms of leukemogenesis in DCL may be distinct from other types of leukemia. Possible causes of DCL include oncogenic alteration or premature aging of transplanted donor cells in an immunosuppressed person. Although many studies have recently better characterized leukemic stem cells, it is important to also consider that both intrinsic cell factors and external signals from the hematopoietic microenvironment govern the developmental fate of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Therefore, in cases of DCL, alteration of the microenvironment after HCT may increase the likelihood that some progeny of normal HSCs become leukemic. This complex intercommunication between cells, growth factors, and cytokines in the hematopoietic microenvironment are critical to balance HSC self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation. However, this homeostasis is likely perturbed in the development of DCL, allowing unique insight into the stimuli that regulate normal and potentially abnormal hematopoietic development. In this article, we discuss the possible pathogenesis of DCL, its association with stem cells, and its likely dependence on a less-supportive stem cell niche.
Introduction
Donor cell leukemia (DCL), a rare although well-recognized disease entity following hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), occurs as the result of oncogenic transformation of apparently normal donor hematopoietic cells in the transplant recipient. DCL was first described in 1971,1 and, since then, descriptions of more than 50 cases have been published.2-6 DCL is less common after HCT than leukemic recurrence or relapse of the patient's original malignancy. In addition to de novo leukemia, there are cases documenting the occult transfer of malignant cells from donors during HCT.7 Notably, transfer of malignant cells can also occur with solid-organ transplantation.8-10 Defining the true incidence of DCL is difficult because of vagaries in its recognition and in reporting; therefore, the majority of evidence in the literature is anecdotal. In 1982 Boyd et al11 reported an incidence as high as 5%, and a recent large survey by the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) reported 14 cases from 10 489 transplantations performed during a 21-year period.12 The diagnosis of DCL is dependant on the ability to accurately identify the donor origin of the leukemic cells. With steady improvements in the molecular analysis of donor-host chimerism, the stage is set for improved and more accurate detection. A variety of methods to diagnose DCL have been used, including karyotype analysis, chimerism analyses, and, more recently, short tandem repeat analyses and variable number of tandem repeats, but in some of the earlier cases the diagnosis was based on differences in morphology alone.3 DCL can occur within 4 months after HCT, and the median time reported is 17 months after HCT. Therefore, it is scientifically interesting and potentially informative to speculate on the target cell for leukemogenesis among the apparently healthy donor cells, as well as what occurs during the earliest steps in what may be a unique neoplastic process.
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), a more extensively studied disease, may provide clues to the pathogenesis of DCL.13-15 PTLDs have a reported cumulative incidence of 1% to 2% after HCT and most occur within the first 6 months after HCT. The majority of PTLDs after HCT are donor in origin, although host-derived PTLDs after HCT are described. The recipient or donor origin of the PTLD after HCT appears to depend on the status of engraftment.16 In contrast, PTLDs following solid-organ transplantation are predominantly host derived.17 Epstein-Barr virus plays a pivotal role and is almost always associated with PTLD. Other risk factors include ex vivo T-cell depletion of the graft, in vivo T-cell therapy during transplantation, and histocompatibility between donor and host. Host-derived PTLDs suggest impaired tumor surveillance secondary to T-cell dysfunction after HCT allows an uncontrolled proliferation of transformed B cells. Although immunoregulatory dysfunction likely has a role to play in donor-derived PTLDs and DCL, additional mechanisms are also speculated. In DCL, the host environment in which the original malignancy developed might trigger a similar oncogenic process in donor cells favored by the immunocompromised status after transplantation. The correlation of engraftment status and origin of the PTLD suggests that either the recipient or donor cell population that is present can become transformed. This would support the theory that the environment in which the cell is placed has a role in its fate. Alternatively, chronic antigenic stimulation by minor histocompatibility differences between the donor cells and the host may trigger leukemogenesis in a setting of impaired tumor surveillance.1,18 Perturbations within the host bone marrow microenvironment following multiple rounds of chemotherapy may contribute.19 In some cases, as described later, premature aging of the donor cells and the associated chromosomal instability, as a consequence of the replicative stress ensuing from the effort to repopulate the recipient's marrow after transplantation, may also play a role.20,21 Certainly, combinations of these processes, or alternative mechanisms, are also feasible contributions to the development of lymphoid and myeloid malignancies after HCT.22,23
Cellular changes after HCT
Following HCT, there are vigorous proliferative demands on the transplanted cells. A rapid proliferative rate often correlates with a higher likelihood of replication error or mutation. A preleukemic mutation may occur, and, with ensuing immunosuppression and impaired immune surveillance, this may more readily result in leukemia. Even unselected umbilical cord blood (UCB) units (a cell source becoming more common for HCT) have been shown to harbor preleukemic clones.24 These clones may be associated with an increased risk of leukemia when combined with the proliferative stress after HCT, although this remains to be formally proven.25 Studies of telomere length in HSCs from donors and recipients of bone marrow (BM) and peripheral blood (PB) HC transplants show an accelerated rate of shortening equivalent to approximately 15 years of aging after transplantation, compared with age-matched controls.20 Shortened telomeres are associated with premature replicative senescence and genomic instability, factors that could contribute to development of DCL. It is unlikely that telomere shortening after HCT is sufficient by itself to cause hematologic dysfunction, although it may be additive or synergistic to other changes in the bone marrow environment.26 There has been no consistent correlation between age of the donor or recipient, nor the type and extent of pre-HCT therapy, with after-HCT changes in telomere length.27 Interestingly, mononuclear cells of HC transplant UCB recipients have significantly longer telomeres compared with allogeneic PB HC transplant recipients, and it has been hypothesized that UCB transplants may provide patients with replicative “reserve” potential and a delay in the onset of hematologic disorders.28 Also the telomere dynamics of mesenchymal stem cells were shown to be unaffected by HCT, suggesting a distinct role of the microenvironment as a homeostatic regulator.29
Stem cell source for development of DCL
Differences in the ontogenic source of stem cells may also account for some of the variation in the incidence and timing of DCL. Until 2005, reports of DCL were exclusively in allogeneic bone marrow HC transplant recipients; however, there have now been at least 4 cases reported in PB HC transplant recipients.7,12 The first report in an UCB transplant recipient was in 200530 and was quickly followed by 2 additional cases reports.31,32 The predominance of DCL in allogeneic BM HCTs compared with both PB and UCB may simply be a result of the longer historical use of this cell source.
However, there are functional differences between the different ontogenic sources.33 Repopulation capacity differs between these cell sources, and the response of transplanted stem cells to replicative stresses may differ accordingly. These differences may reflect the frequency of HSCs in the cell source, although to date there has been a lack of correlation between the number of infused cells and changes in telomere length. UCB HC transplant recipients receive a lower total cell dose compared with other cell sources; the biologic differences in stem cell repopulation may have an impact on the replicative stresses on engrafting stem cells. These differences may be particularly relevant to UCB as a stem cell source, with the incidence of preleukemic mutations reported.24,25 However, on the basis of the information from the EBMT survey with prolonged follow-up of donors,12 donors from whom DCL develops are not typically destined to develop leukemia themselves. Future analysis of DCL, its clonal origin, and stem cell source may yield more information.
Leukemic and cancer stem cells
Leukemic stem cells (LSCs) were first described in 1994.34 The studies of cancer stem cells have since been extended to other tissue types, including breast cancer,35 brain tumors,36 prostate cancer,37 melanoma,38 and lung cancer.39 The recognition that malignancies may develop from a population of “cancer stem cells” has caused both scientists and clinicians to consider the important implications such a cell population and developmental process could have on cancer pathogenesis and therapeutics.
The characterization of cancer stem cells, in particular LSCs, has led to several proposed models of leukemogenesis.40 The paradigm of cancer stem cells considers leukemia a hierarchical disease process whose growth is sustained by a rare population of LSCs.41 Two factors suggest the stem cell as the target: (1) self-renewal machinery is already active and (2) quiescence that allows greater opportunity for the accumulation of mutations. LSCs maintain the capacity to self-renew and give rise to malignant progeny with extensive proliferative potential. The precise cell of origin and the mechanism of transformation is unknown in the majority of cases. It is speculated that the transformation involves at least a 2-step process, one mutation blocking differentiation and another event conferring its progeny with a proliferative advantage. Myeloid leukemia has been shown to originate from a primitive hematopoietic cell.42,43 Other LSCs may result from dedifferentiation of more committed progenitors that reacquire the ability to self-renew prior to accumulating transforming mutations.44 In BCR-ABL–associated leukemias, the transformation occurs at the stem cell and progenitor cell level depending on the phenotype and fusion transcript isoform.45 Several other exceptions exist, including PML-RARα,46 MLL-ENL,47 and MOZ-TIF2,48 whereby leukemia is promoted by fusion oncogenes, and self-renewal characteristics are imposed on more committed progenitors in the hematopoietic hierarchy. These models suggest an intrinsic cellular mechanism for leukemogenesis. However, it is evident that the fate of normal HSCs and LSCs is also determined by cell-independent mechanisms, including regulatory cues from their microenvironment.49,50
Donor cell leukemia and stem cells
The shared intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms governing HSCs and LSCs may shed light on the unique pathogenesis of DCL whereby transplanted “apparently healthy” donor cells become leukemogenic over a short time. In most cases, specific mechanisms that result in the development of DCL are unknown. No consistent pattern of cytogenetic abnormality is apparent among the reported cases of DCL; almost half are associated with a normal karyotype. The remainder includes a heterogeneous mix of complex karyotypes, deletion, and fusion oncogenes.
We speculate that DCL is an illustration that leukemia development is not entirely cell autonomous. The important influence of the microenvironment must be considered. Studies of cancer stem cells have never made external factors irrelevant to tumorigenesis, but these aspects are often overlooked. Clearly distinct cell niches, including the endothelium and vasculature and other cell types, have an impact on tumor cell development.51 A better understanding of DCL may shift the emphasis from the stem cell toward the external homeostatic influence of the bone marrow microenvironment on the HSC. If the niche becomes dysregulated, the homeostatic balance may be disturbed, leading to changes in hematopoietic developmental pathways. These critical regulatory processes, both positive and negative, that govern HSC development are undoubtedly strained and potentially more prone to abnormalities at times of replicative stress, such as those that exist when donor HSCs repopulate the recipient marrow after HCT.
Seed and soil hypothesis as applied to DCL
The seminal “seed and soil hypothesis” of cancer development was published by Paget in 1889 and can be used as a model for DCL.52,53 Paget was struck by the discrepancy between the relative blood supply and frequency of cancer metastasis in certain organs. He proposed that the “seed” (cancer cell) will only grow if it falls on congenial “soil,” and he used this hypothesis to explain the nonrandom pattern of cancer metastasis to visceral organs and bones. Some parallels can be drawn with the original seed and soil hypothesis and the relationship between the newly engrafted HSCs (seeds) and the complex bone marrow niche (soil) in which they arrive after HCT. Optimal development of HSCs occurs when the seed and the soil are in equilibrium. The soil plays an essential role in the maintenance and development of the seed. It regulates the quiescence, self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation of the stem cells.50,54,55 Niche structures have the potential to determine stem cell fate, and the niche can become damaged after HCT. Important insight for this process comes from other developmental models, such as development of Drosophila germ cells in which nonstem cells can acquire either a more proliferative phenotype or frankly revert to a less-differentiated stem cell-like state when transplanted into certain permissive microenvironments.56,57 This finding suggests that the niche may actively impose stem cell characteristics on more differentiated cells. Other studies have also shown that a vacant viable niche can engage other cell types and cause a phenotypic change by providing “stem cell-like” features to more mature cells.54
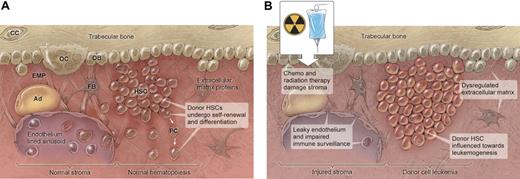
Following HCT, HSCs engraft into a complex stromal environment composed of endosteal bone, osteoblasts, endothelial-lined sinuses, blood vessels, adipocytes, insoluble extracellular matrix proteins, and soluble peptides (chemokines and cytokines)58 (Figure 1A). All the molecular events that govern HSC decisions and its associated stroma are not known. In addition, after HCT, the effects of endogenous and pharmacologic cytokines on the stromal equilibrium are not well understood. Physical interaction between the HSC and trabecular bone via N-cadherin is known to help anchor the HSC at this interface.59,60 Osteoblasts under the influence of bone morphogenic signaling and parathyroid hormone (PTH) or PTH-related protein receptor also represent a regulatory element for the HSC.59,61 Osteoclasts may have a role in the localization and regulation of HSCs within the niche.62 Notch receptors have a role in HSC self-renewal,63 and interactions between angiopoietin-1 on bone and Tie-2 on stem cells seem to maintain quiescence.60 Disturbances in the cross talk between these cytokine and cellular stimuli and the HSC could contribute to leukemogenesis.
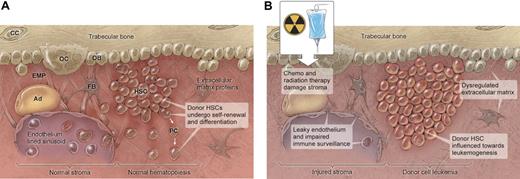
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and hematopoietic progenitor cells reside in the bone marrow in tissue composed of trabecular bone adjacent to endothelial lined sinuses and surrounded by various stromal cells that include osteoblasts (OB), osteoclasts (OC), chrondrocytes (CC), adipocytes (Ad), and fibroblasts (FB). This tissue also contains a complex environment of extracellular matrix proteins (EMP) and soluble cytokines. The interaction and homeostasis of these stromal components with the HSCs may determine its normal or neoplastic fate after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Figure 1A illustrates the normal HSC niche in which donor HSCs undergo self-renewal and differentiation to donor progenitor cells (PCs). Figure 1B illustrates the altered environment after HCT in which changes in the balance of extrinsic signals because of chemotherapy and radiation therapy may influence normal donor HSC development toward donor cell leukemia (DCL). These changes after HCT include injured stroma, leaky endothelium, impaired tumor surveillance, and a dysregulated extracellular matrix. Illustration by Kenneth Probst.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and hematopoietic progenitor cells reside in the bone marrow in tissue composed of trabecular bone adjacent to endothelial lined sinuses and surrounded by various stromal cells that include osteoblasts (OB), osteoclasts (OC), chrondrocytes (CC), adipocytes (Ad), and fibroblasts (FB). This tissue also contains a complex environment of extracellular matrix proteins (EMP) and soluble cytokines. The interaction and homeostasis of these stromal components with the HSCs may determine its normal or neoplastic fate after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Figure 1A illustrates the normal HSC niche in which donor HSCs undergo self-renewal and differentiation to donor progenitor cells (PCs). Figure 1B illustrates the altered environment after HCT in which changes in the balance of extrinsic signals because of chemotherapy and radiation therapy may influence normal donor HSC development toward donor cell leukemia (DCL). These changes after HCT include injured stroma, leaky endothelium, impaired tumor surveillance, and a dysregulated extracellular matrix. Illustration by Kenneth Probst.
This normally supportive bone marrow environment is markedly changed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy that precedes HCT (Figure 1B). Patients are exposed to these agents both as a part of the treatment for the underlying malignancy and as a part of the conditioning prior to HCT. Ionizing radiation exposure during total body irradiation has direct effects on irradiated cells and the microenvironment.64 Radiation-induced injury can also contribute to secondary cell damage in the microenvironment as a consequence of an inflammatory-type response.65 Transplantation of growth factor–dependant cells into syngeneic mice produces leukemia from donor cells in higher numbers and at a faster rate in irradiated compared with nonirradiated recipients.66 These findings may reflect dysregulation of the stroma and alteration of the growth and phenotypic characteristics of stem cells.67 Chemotherapeutic drugs such as cyclophosphamide also cause endothelial injury and allow cells, proteins, and cytokines to move between the vascular space and the bone marrow niche.68
Almost all cases of DCL are acute myeloid leukemia. The original diseases included chronic myeloid leukemia and acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukemias2,4,5,12,32 ; there have been 3 case reports with aplastic anemia and single cases with several other diseases (chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Langerhans histiocytosis, thalassasemia, renal cell carcinoma, and adult T-cell lymphoma). The stem cell niche likely has a role in de novo leukemogenesis and DCL; it appears to impact early hematopoietic development, as mature cellular malignancies are rarely seen. The association of DCL with myeloid disease suggests that the equilibrium between lymphoid and myeloid differentiation may be altered after HCT.
DCL and implications for donors
Prolonged follow-up, as already mentioned, has shown that donors from whom DCL develops are not destined to develop leukemia.12 Until recently, in most cases described the donors were siblings; however, there are recent reports of cases in unrelated donors, including UCB donors30,31 which brings a new set of issues. The question of whether to inform an unrelated donor about the development of leukemia from his or her cells in a recipient, and the potential consequences for the donor, represents a significant ethical and medical challenge.
Conclusion
DCL is a unique disease entity, although there is undoubtedly some mechanistic overlap between the development of DCL and other forms of leukemia. In the pathogenesis of DCL, it is important to consider that its cause is multifactorial in nature. Factors intrinsic to the cell and external signaling cues from the niche determine a normal versus neoplastic fate for the transplanted donor cells. Continued research to characterize DCL will help to understand better the dynamic equilibrium between both normal and leukemic stem cells and the hematopoietic microenvironment.
Authorship
Contribution: C.M.F. wrote and edited the manuscript; and D.S.K. wrote and edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Dan S. Kaufman, Stem Cell Institute, Translational Research Facility, 2001 6th St SE, Mail Code 2873, Minneapolis, MN 55455; e-mail: kaufm020@umn.edu.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Daniel Weisdorf and Dr Catherine Verfaillie for critically reviewing the paper.