Abstract
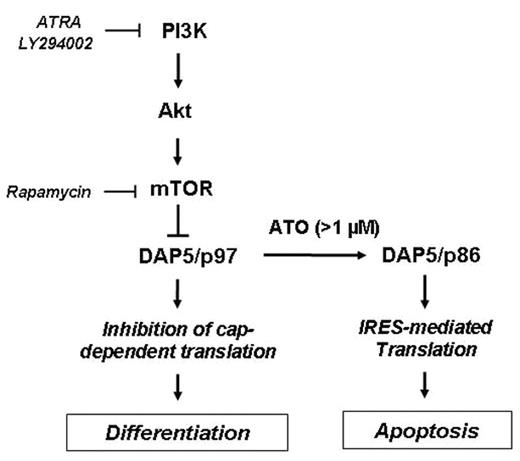
All-trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA) is a naturally occurring metabolite of retinol (vitamin A)and acts as a potent inducer of cellular differentiation and growth arrest in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), a type of acute myeloid leukemia (M3-AML). APL is characterized by translocation t(15;17), fusing PML (promyelocytic leukemia) and RARα (retinoic acid receptor) genes, leding to expression of PML/RARα receptor protein and differentiation block. Arsenic trioxide (ATO) induces (<0.5 μM) differentiation at low doses and apoptosis at high doses (>1 μM) in APL cells. Currently, both ATRA and ATO are successfully used in the treatment of APL in the clinic. However, the molecular mechanisms of myeloid differentiation and apoptosis induced by these agents are not fully understood. We previously reported that ATRA inhibits the translation initiation through multiple mechanisms, including upregulation of translation initiation inhibitors, DAP5/p97 and PDCD4 tumor suppressor protein. Here we investigated the role and regulation of death associated protein-5 (DAP5/p97/NAT1), a novel inhibitor of translational initiation, in myeloid (granulocytic and monocytic) cell differentiation and apoptosis. We found that ATRA (1 μM) induced a marked DAP5/p97 protein and mRNA expression during granulocytic differentiation of NB4 and HL60 cells but not in differentiation-resistant cells, which express very low levels of DAP5/p97. DAP5/p97 was translocated into nucleus during the differentiation of NB4 cells induced ATRA. At differentiation inducing doses, ATO, dimethysulfoxide, 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin-D3, and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate also induced a significant DAP5/p97 expression in NB4 cells. However, ATO at apoptotic doses, but not ATRA, induced DAP5/p86, a proapoptotic form of DAP5/p97. ATRA and ATO -induced expression of DAP5/p97 was associated with inhibition of phosphaditylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, which is known to stimulate cap-dependent translation of mRNAs. To show direct link between PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and DAP5 expression, we treated cell with PI3K and mTOR inhibitors LY294002 and by rapamycin, respectively. We found that inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway upregulated DAP5/p97 expression in NB4 cells. Finally, knockdown of DAP5/p97 expression by small interfering RNA significantly inhibited ATRA-induced granulocytic differentiation detected by expression of CD11b and ATO-induced apoptosis in NB4 cells detected by Annexin V assay (p<0.05). In conclusion, our data suggest that DAP5/p97 plays a role in ATRA-induced differentiation and ATO-induced apoptosis in APL cells. Our data demonstrated for the first time that DAP5/p97 is constitutively suppressed by of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, and ATRA and ATO-induced expression of DAP5 is mediated by the inhibition of this survival pathway, suggesting a novel mechanism of DAP5 regulation and a role of translational control in induction of differentiation and apoptosis.
Author notes
Disclosure:Off Label Use: PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and mTOR inhibitor are commercially available products used for research purposes.