Abstract
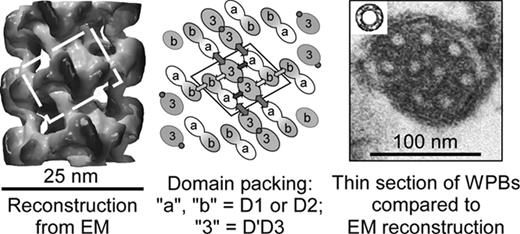
Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs) are elongated secretory granules of endothelial cells that are packed with tubules composed of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a multimeric protein required for hemostasis. Disruption of tubular packing prevents the orderly secretion of VWF multimers and blocks the subsequent binding of platelets. The cigar-like shape and tubular cross section of WPBs are conserved in all vertebrates, but little is known about how VWF specifies this packing arrangement. Starting from recombinant 82 kDa VWF propeptide (domains D1D2) and 114 kDa disulfide-bonded D’D3 dimer, we now have assembled tubules reversibly in vitro with the same dimensions as VWF tubules in WPBs. Assembly was induced at pH 6.2, reversed at pH 7.4, and required Ca2+. Recombinant D’D3 dimers did not self-associate at pH 7.4 or pH 6.2, with or without Ca2+. Without Ca2+, VWF propeptide did not bind to D’D3 dimers. At pH 7.4, with Ca2+, VWF propeptide formed noncovalent 160 kDa dimers and, when mixed with D’D3 dimers, assembled a 280 kDa complex of two propeptides and one D’D3 dimer as shown by gel filtration chromatography and multi-angle light scattering. Lowering the pH to 6.2 caused the formation of >3 MDa aggregates with the same stoichiometry, which dissociated upon adding EDTA or raising the pH to 7.4. Quick-freeze deep-etch EM showed that the large aggregates are hollow right-handed tubular helices. The iterative helical real space reconstruction method was used to make 3D reconstructions of the tubules at 22 Å resolution from negative stain EM images (Figure, left). Tubules consist of a right-handed helix with axial rise of 26.2 Å and twist of 85.6 degrees per subunit, or 4.2 subunits per 11 nm turn. The dimensions (outside diameter 25 nm, inside diameter 12 nm) are similar to those of tubules in WPBs in thin sections of endothelial cells by transmission EM (Figure, right and its insert). Each subunit contains one D’D3 dimer flanked by two D1D2 propeptides (Figure, center). Each D’D3 dimer makes a total of six contacts with D1D2 domains. Each D1D2 propeptide makes three contacts with D’D3 and just one end-to-end homotypic contact. The spatial arrangement of these building blocks and inter-domain contacts in tubules suggest a model by which decreasing pH along the secretory pathway coordinates the formation of intersubunit disulfide bonds with the tubular packaging of VWF multimers. Within the WPB, Ca2+-dependent and pH-dependent binding of D1D2 to D’D3 domains stabilizes the packing of VWF multimers into tubules, which behave as constrained springs. Upon secretion, the increased pH weakens these constraints and permits the helical tubules to unfurl into flowing blood without tangling.
Author notes
Disclosure:Consultancy: J.E.S. is a consultant for Baxter BioSciences.