Abstract
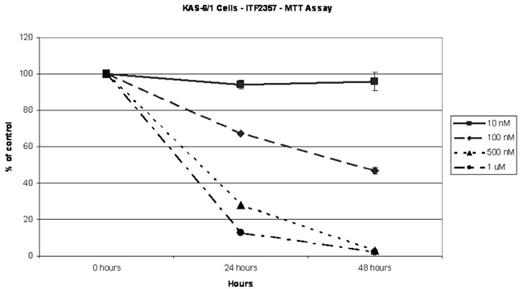
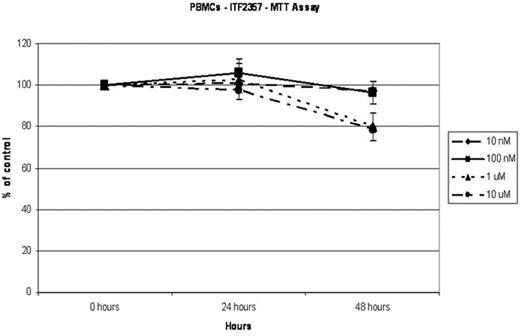
We have evaluated the efficacy of a novel hydroxamic acid-derived histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, ITF2357, to promote cell death in multiple myeloma (MM) cells. HDAC inhibitors, which promote histone hyperacetylation and increase gene expression, have been evaluated as candidate agents for combating malignancies because they impact the expression of genes related to proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Exposure of MM cell lines to 1 micromolar ITF2357 led to dramatically increased levels of histone acetylation at 4 hours and 8 hours by Western analysis. Sub-micromolar concentrations of ITF2357 promoted time- and concentration-dependent cell death in MM cell lines. Using 500 nM ITF2357, a concentration potentially achievable in vivo, viability of KAS-6/1 IL-6 dependent myeloma cells was reduced to 28% of control at 24 hrs and 2% of control at 48 hours (Figure 1). In contrast, viability of normal PBMCs was 100% at 24 hours and 80% at 48 hours (Figure 2). U266 and 8226 myeloma cells were found to be sensitive to ITF-2357 in a similar fashion with U266 being least sensitive. Cell death proceeded via apoptosis as measured using Annexin V/propidium iodide staining. ITF 2357 was superior to suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) at inhibition of stromal cell IL-6 production. IL-1beta (10 pg/ml) was used to stimulate bone marrow stromal cell IL-6 production (105 ng/ml) after 48 hours. Concentration of ITF2357:Stromal Cell IL-6 production after 48 hours were as follows - 10 nM: 78 ng/ml; 100 nM: 79 ng/ml; 1000 nM; 32 ng/ml. SAHA at similar concentrations showed no significant decrease in stromal cell IL-6 production compared with the no drug control. In summary, ITF2357 induces significant myeloma cell apoptosis and can inhibit stromal cell IL-6 production. It represents an attractive therapeutic candidate for MM clinical trials.
Author notes
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.