Abstract
Tumor growth is associated with aberrant myelopoiesis, including the accumulation of CD11b+Gr-1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) that have the potential to promote tumor growth. However, the identity, growth, and migration of tumor-associated MDSCs remain undefined. We demonstrate herein that MDSCs at tumor site were composed primarily of bone marrow-derived CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils and CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi macrophages. Unexpectedly, in vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling and parabiosis experiments revealed that tumor-infiltrating macrophages were replenished more rapidly than neutrophils. CCR2 deficiency caused striking conversion of infiltrating cellular dominance from macrophages to neutrophils in the tumor with the excessive production of CXCR2 ligands and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in the tumor without affecting tumor growth. Overall, our data established the identity and dynamics of MDSCs in a tumor-bearing host mediated by chemokines and elucidated unexpected effects of the paucity of macrophages on tumor development.
Introduction
Tumor tissue consists not only of malignant cells but also of stromal cells and infiltrating leukocytes.1,2 It is thought that tumor-infiltrating inflammatory cells play an important role in regulating tumor progression through immune responses, angiogenesis, and tissue remodeling.1,3 Evidence from clinical as well as experimental studies indicate that a high frequency of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) correlates with favorable prognosis,4,5 whereas that of myeloid cells is associated with poor prognosis through increased angiogenesis, tissue remodeling and suppression of antitumor immune responses.3,6 Tumor growth often induces aberrant myelopoiesis. However, the cellular heterogeneity within the tumor-associated CD11b+Gr-1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) has generated confusion regarding their identity versus conventional myeloid-lineage cells (ie, macrophages and neutrophils).
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which are considered to be recruited by chemokines such as CCL2, are the predominant leukocytes infiltrating solid tumors,3,7 and their frequency is usually associated with poor prognosis.8 Lin et al9 have reported that in a spontaneous breast cancer model, null mutation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) gene caused a reduction of TAMs and an inhibition of tumor progression and metastasis. Several clinical and experimental data suggest that TAMs promote angiogenesis and tissue remodeling through the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9).10,11 TAMs also can have an inhibitory role in the development of antitumor T-cell responses through the production of immune suppressive cytokines transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS), and reactive oxygen species (ROS).12-14
Neutrophils can also infiltrate tumors, and, in some cases, tumor progression is also associated with the neutrophilia.1,15,16 During inflammatory responses, neutrophils are the first-recruited effector cells and produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines necessary for after inflammatory cascade.17,18 Although neutrophils can secrete cytotoxic mediators (such as ROS), proteases, cytokines (such as TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and interferons (IFNs),19 most studies suggested that they promote tumor growth through the secretion of VEGF and MMP9.20 Pekarek et al21 reported that neutrophil depletion by anti-Gr-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) inhibited tumor growth. However, anti-Gr-1 mAb administration also affects monocytes, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs), and a subset of effector/memory T cells and MDSCs.22
In addition to conventional myeloid lineage cells, CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs have stimulated scientific interest as a therapeutic target as a result of their ability to suppress T-cell immune responses.23,24 MDSCs are thought to be a heterogeneous cellular population containing macrophages, granulocytes, immature DCs, and early myeloid precursors. Although most myeloid lineage cells are bone marrow (BM)-derived under steady-state conditions, several studies have suggested that MDSCs could also undergo extramedullary proliferation in response to tumor-derived growth factors.25,26 From a functional perspective, they suppress T-cell responses in vitro through direct cell-cell contact or by producing arginase 1 (ARG1) and iNOS.27 In addition, Nagaraj et al28 recently reported that MDSCs induce antigen-specific CD8 T-cell tolerance through the nitration of TCR-CD8 complex by producing ROS and peroxynitrite. Furthermore, MDSCs directly promote angiogenesis and tissue remodeling via MMP9 and VEGF.29
Although accumulating evidence suggests that there are phenotypic and functional overlap between MDSCs and conventional myeloid cells, information about the cell lineage and tumor-promoting roles of MDSC subpopulations in vivo is limited. Moreover, their growth and migration dynamics regulated by chemokine system has not been established. Based on the immunophenotype, cytomorphology, and cytochemistry, we describe herein a growth dynamics of CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs in tumor-bearing wild-type (WT) or chemokine receptor-deficient mice. In addition, in vivo BrdU labeling and parabiosis were used to examine their site(s) of proliferation and turnover in the tumor-bearing host.
Methods
Mice and cell lines
C57BL/6 (CD45.2) and BALB/c mice were purchased from CLEA Japan Inc. (Shizuoka, Japan). Congenic B6.SJL (CD45.1), CCR2−/−, CX3CR1gfp/gfp, and CCR1−/−30 were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) or Taconic Farms (Tarrytown, NY). CCR5−/− mice were generated as described previously.31 Congenic and chemokine receptor deficient mice were back-crossed for 8 to 10 generations on the C57BL/6 background and housed in a pathogen-free environment. All animal procedures described in this study were performed according to the guidelines for animal experiments of the University of Tokyo. Tumor cell lines 3LL (Lewis lung carcinoma), B16, and Meth A were provided by Dr Abe (Nipponkayaku, Tokyo, Japan) and Cell Resource Center for Biomedical Research, Tohoku University (Sendai, Japan).
Tumor challenge
WT and chemokine receptor-deficient mice received subcutaneous (s.c.) injections of 5 or 105 major histocompatibility complex matched tumor cell lines in the flank. Tumor dimensions were assessed using calipers, and the tumor volume was determined using the formula for a prolated sphere: volume = [length × (width)2] × 0.5.
Cell preparation
Tumors, spleens, and draining axillary lymph nodes (LNs) were cut into small fragments and digested for 45 minutes at 37°C with 0.1% collagenase D (Roche Diagnostics, Penzberg, Germany). The cells were then subjected to 40%/70% Percoll (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) gradient and leukocytes were recovered from the interphase. BM cells and peripheral blood (PB) leukocytes were prepared by standard method.
Flow cytometry, in vivo BrdU labeling, and cell sorting
Purified and fluorescein isothiocyanate-, phycoerythrin-, allophycocyanin-, PerCP-Cy5.5-, PC7-, or biotin-conjugated anti–mouse mAbs to FcγR (2.4G2), CD4 (RM4-5), CD8α (53-6.7), CD11a (M17/4), CD11b (M1/70), CD11c (HL3), CD24 (M1-69), CD29 (Ha2/5), CD43 (S7), CD45 (30-F11), CD45.1 (A20), CD45.2,(104) CD62L (MEL-14), CD86 (GL1), CXCR4 (2B11/CXCR4), CCR5 (C34-3448), NK1.1 (PK136), as well as subclass-matched control antibody and fluorescent dye-conjugated streptavidin were purchased from BD Pharmingen (San Diego, CA). Anti–mouse mAbs to CD80 (16-10A1), CD115 (AFS98), F4/80 (BM8), Foxp3 (FJK-16s), and anti–mouse/rat Foxp3 staining set were purchased from eBioscience (San Diego, CA). Anti–mouse mAbs to CXCR2 (242216) and MMP9 (116103) were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). For IFN-γ detection, cells were stimulated with 5 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and 0.5 μg/mL ionomycin for 5 hours in the presence of 10 μg/mL brefeldin A followed by intracellular staining using Cytofix/Cytoperm Kit (BD Pharmingen). Intracellular staining for MMP9 was also performed using Cytofix/Cytoperm Kit. For BrdU labeling experiments, after the initial intraperitoneal injection of BrdU (2 mg per mouse), mice were maintained on drinking water containing 0.8 mg/mL of BrdU, and the BrdU incorporated cells were stained with BrdU Staining kit with DNase (BD Pharmingen). Flow cytometry and cell sorting were performed by an EPICS ALTRA cell sorter with EXPO32 software (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA) and analyzed with FlowJo software (version 8.5.2; TreeStar, Ashland, OR). Dead cells were excluded on the basis of forward and side scatter profiles and propidium iodide staining. For the cytochemical and reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis, CD11b+ cells were magnetically enriched by positive selection using a magnetic cell sorting system (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) and then CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi macrophages and CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils were sorted using the EPICS ALTRA. The purity of sorted cells was routinely more than 98%.
RT-PCR analysis
For quantitative RT-PCR, total RNA was isolated from sorted cells or tumors using TRIzol solution (Invitrogen Life Technologies) and reverse-transcribed with a High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Real-time PCR was performed on Applied Biosystems PRISM 7500 sequence detection system using a TaqMan probes, SYBR green incorporation with TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix, or Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (all from Applied Biosystems). Gene specific primes and probes are given in Table S1 (available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). The quantity of target mRNA was normalized by the level of GAPDH in each samples.
Cytochemical analysis
Sorted cells were cytospun onto slides and were stained with Diff-Quik (Baxter Diagnostics, McGraw Park, IL). Detection of macrophage-specific esterase/α-naphthyl acetate esterase and myeloid-cell specific esterase/Naphthol AS-D chloroacetate esterase was performed using esterase staining kit and esterase AS-D staining kit (Muto Pure Chemicals, Tokyo, Japan).
Histologic analysis
Fresh frozen sections were stained as described previously.32 In brief, cryosections were fixed in ice-cold acetone and preincubated in Block Ace (Dainippon Pharmaceutical, Tokyo, Japan). Subsequently, samples were incubated with primary antibodies or appropriate control antibodies, followed by appropriate Alexa Fluor-labeled secondary reagents (Invitrogen Japan K.K., Tokyo, Japan). The samples were then analyzed using an Olympus IX-70 confocal laser-scanning microscope (Olympus Optical, Tokyo, Japan). To calculate the ratio of the area stained with anti-CD31 or Type IV collagen (LSL, Tokyo, Japan), digitized pictures were analyzed with WinRoof image processing software (version 3.6.1; Mitani, Tokyo, Japan). To calculate the ratio of necrotic area, hematoxylin and eosin staining images of the tumors were analyzed by a WinRoof image processing software.
Parabiosis
Parabiosis and separation were performed with body weight–matched C57BL/6 (CD45.2) and B6.SJL (CD45.1) mice as described previously.33,34 In brief, the skin and fascia of anesthetized mice were longitudinally incised, and the pair of fascia and skin was joined. Chimerism of PB leukocytes was confirmed 14 days after surgery and the tumor cells were inoculated subcutaneously at the opposite side of surgery on day 40. In some experiments, established parabionts were surgically separated 7 days after tumor inoculation. For each pair of joined mice, average chimerism was calculated as follows: (percentage CD45.1+ cells in CD45.2 mouse ± percentage CD45.2+ cells in CD45.1 mouse)/2.
Competitive migration assay
Competitive migration assays were performed as described previously.35 In brief, an equal number (2 × 107 cells) of CCR2+/+CD45.1+CD45.2+ and CCR2−/−CD45.1−CD45.2+ BM cells were intravenously injected into CCR2+/+CD45.1+CD45.2−-recipient mice, which had been subcutaneously inoculated with tumor cells 7 days before transfer. Twenty-four hours later, mice were perfused with 50 mL phosphate-buffered saline, and leukocytes were collected from the tumor, spleen, blood, and BM were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as means with standard deviation. Statistical comparisons between groups were made using the Student t test. P values less than .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs are composed primarily of macrophages and neutrophils
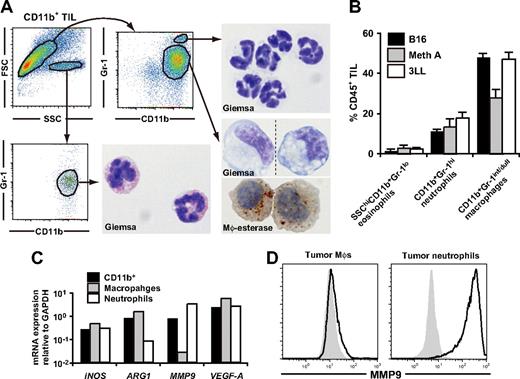
Because not only MDSCs but also macrophages and neutrophils express CD11b and Gr-1, we examined the possible overlaps between these populations. We first examined subcutaneous C57BL/6-derived 3LL tumors (H2b) with diameter of 6-10 mm. Based on forward scatter versus side scatter and the CD11b versus Gr-1 profile, we identified three distinct populations in tumor-infiltrating CD11b+ cells: SSChiCD11b+Gr-1−/int cells with eosinophil-like morphology (2.3 ± 0.7%), SSCloCD11b+Gr-1hi cells with neutrophil-like morphology (17.8 ± 3.0%), and SSCloCD11b+Gr-1int/dull cells (47.1 ± 3.4%) (Figure 1A,B). CD11b+Gr-1int/dull cells were morphologically heterogeneous in size and nuclear shape, but most of the cells had nonspecific esterase activity and expressed CD80, CD86, CD115, F4/80, and Ly-6C, indicating that these cells have similar characteristics to inflammation-associated macrophages (Figure 1A; Table 1). Therefore, we hereafter considered CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint cells as tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi cells as macrophages.36 It is noteworthy that these tumor-associated leukocyte subpopulations were also detected in subcutaneous B16 melanoma (H2b) and Meth A fibrosarcoma (H2d) tumors as the primarily infiltrating leukocytic population (Figure 1B).
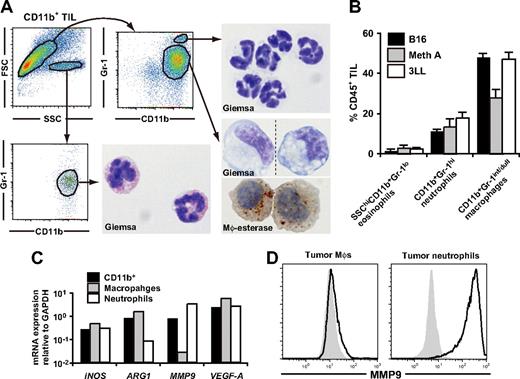
Characterization of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs. CD11b+ cells were enriched from subcutaneous 3LL tumors when tumor grew to 6-10 mm in diameter, and the subpopulations were subsequently sorted by a cell sorter. (A) The sorted cells were subjected to Giemsa or macrophage-specific esterase staining. Dotted line in the bottom right image indicates that different parts of the same slide were grouped to show the cells with representative morphology. Original magnification, ×1200. (B) The percentage of MDSC subpopulations in tumor-infiltrating CD45+ leukocytes in various tumor models. B16 melanoma, Meth A fibrosarcoma, and 3LL were used. (C) mRNA expression of iNOS, ARG1, VEGF-A, and MMP9 in tumor-infiltrating CD11b+ cells, CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi macrophages, and CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cdull neutrophils were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (D) Expression of intracellular MMP9 was analyzed by a flow cytometry. Solid lines indicate staining with anti-MMP9 mAb, shaded histograms indicates isotype control. In panels A, C, and D, cells were collected from tumor of 5-8 mice. In B, graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3 mice. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.
Characterization of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs. CD11b+ cells were enriched from subcutaneous 3LL tumors when tumor grew to 6-10 mm in diameter, and the subpopulations were subsequently sorted by a cell sorter. (A) The sorted cells were subjected to Giemsa or macrophage-specific esterase staining. Dotted line in the bottom right image indicates that different parts of the same slide were grouped to show the cells with representative morphology. Original magnification, ×1200. (B) The percentage of MDSC subpopulations in tumor-infiltrating CD45+ leukocytes in various tumor models. B16 melanoma, Meth A fibrosarcoma, and 3LL were used. (C) mRNA expression of iNOS, ARG1, VEGF-A, and MMP9 in tumor-infiltrating CD11b+ cells, CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi macrophages, and CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cdull neutrophils were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (D) Expression of intracellular MMP9 was analyzed by a flow cytometry. Solid lines indicate staining with anti-MMP9 mAb, shaded histograms indicates isotype control. In panels A, C, and D, cells were collected from tumor of 5-8 mice. In B, graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3 mice. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.
We also analyzed the functional characteristics and intratumoral distribution of neutrophils and macrophages. Flow cytometric and real-time RT-PCR analysis revealed that expression of MMP9 was enriched in neutrophils among CD11b+ cells at both mRNA and protein levels; whereas ARG1 was enriched in macrophages, suggesting that the tumor-promoting function of MDSCs might be a mixed function of macrophages and neutrophils (Figure 1C,D). In the tumor tissue, CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages were diffusely distributed throughout the tumor, whereas CD11b+F4/80− neutrophils were accumulated near the center of the tumor, and the MMP9 expression were mainly detected in this neutrophil clusters (Figure S1A-C).
It is noteworthy that neutrophils and macrophages constituted less than 0.1% of the draining LN cells up to day 21 after tumor induction (data not shown), suggesting that they play only a minor role in the regulation of antitumor T-cell responses in the draining LNs. We also found that CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Cint immature myeloid cells containing promyelocytes and myelocytes were increased in the BM and spleen of tumor-bearing mice only when the tumor grew to more than 10% of body weight. However, these cells were not observed in the tumor until day 40 (Figure S2A,B).
Origin and dynamics of tumor-infiltrating MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice
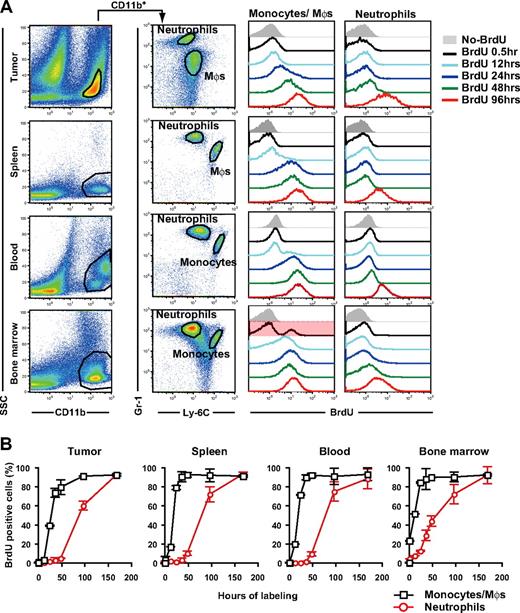
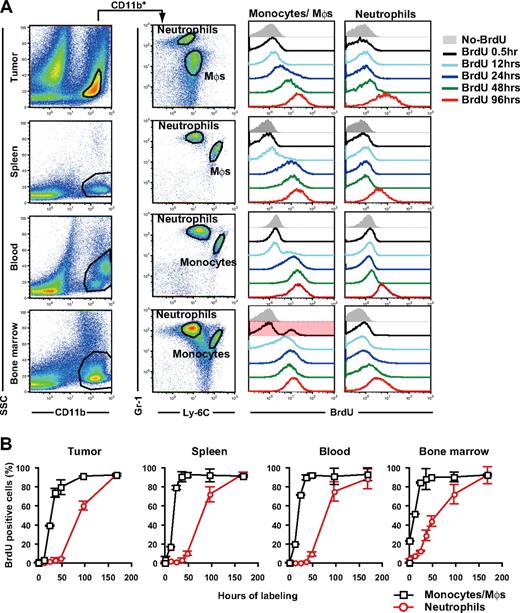
It has been suggested that tumor growth stimulates extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen.25,26 To address the origin and dynamics of tumor-infiltrating MDSCs, we examined the turnover of CD11b+Gr-1+ cell subpopulations in several compartments by BrdU incorporation analysis. After 30 minutes of in vivo cellular labeling, 4.0% and 23.3% of neutrophils and monocytes in the BM were labeled with BrdU, but less than 0.5% of those in blood, spleen, and tumor (Figure 2A,B). This suggests that macrophages and neutrophils in peripheral tissues extravasate at these sites after expansion and mobilization from the BM rather than proliferate in the peripheral tissues in situ. In the tumor, 39.3% and 1.9% of macrophages and neutrophils, respectively, were labeled with BrdU within 24 hours, whereas 60.4% of tumor-infiltrating neutrophils were labeled with BrdU within 96 hours of labeling (Figure 2A,B). Thus, macrophage progenitors proliferate more rapidly than neutrophil progenitors in the tumor-bearing mice.
Turnover of tumor-infiltrating MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with BrdU for various time periods before cell preparation on day 14 of tumor inoculation, and the BrdU uptake by neutrophils and monocytes/monocyte-derived macrophages were analyzed by a flow cytometry. (A) Representative Gr-1 and Ly-6C profiles in CD11b+ cells from tumor, spleen, blood, and BM and the longitudinal BrdU incorporation by monocytes/macrophages (Mφs) and neutrophils. (B) BrdU labeling kinetics of neutrophils (red circles) and monocytes/ Mφs (black squares) in tumor-bearing mice. Each time point represents the mean (± SD) of 3 mice.
Turnover of tumor-infiltrating MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with BrdU for various time periods before cell preparation on day 14 of tumor inoculation, and the BrdU uptake by neutrophils and monocytes/monocyte-derived macrophages were analyzed by a flow cytometry. (A) Representative Gr-1 and Ly-6C profiles in CD11b+ cells from tumor, spleen, blood, and BM and the longitudinal BrdU incorporation by monocytes/macrophages (Mφs) and neutrophils. (B) BrdU labeling kinetics of neutrophils (red circles) and monocytes/ Mφs (black squares) in tumor-bearing mice. Each time point represents the mean (± SD) of 3 mice.
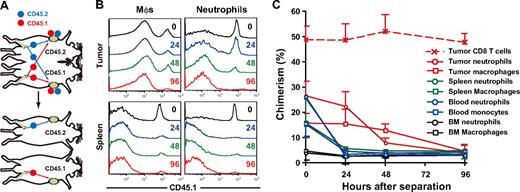
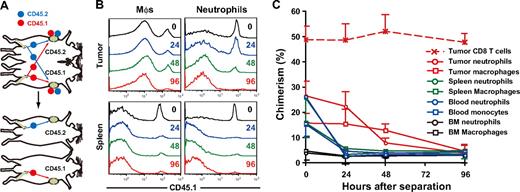
To determine the residence time of MDSCs within peripheral tissues, we established tumor-bearing parabiotic mice using CD45.1/CD45.2 congenic mice and thereafter surgically separated them (Figure 3A). Within 14 days after parabiosis, chimerism of CD4 and CD8 T cells in the blood reached a plateau at 40% to 48%, whereas that of neutrophils and macrophages reached a plateau at 25% to 28%, and 15% to 17%, respectively (data not shown). Unequal exchange of monocytes and neutrophils suggests that neutrophils and macrophages are rapidly removed from the circulation.33 After surgical separation of tumor-bearing parabiotic mice, monocyte and neutrophil chimerism in the blood and spleen rapidly dropped, such that they returned to background levels by 24 hours. It is noteworthy that both macrophages and neutrophils in the tumor were retained longer than in the spleen (tumor, 48-96 hours; spleen, 24 hours), suggesting that the tumor microenvironment may not only recruit macrophages and neutrophils but also support their survival in situ (Figure 3B,C).
Residence time of MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice. (A) Parabiotic mice were established between C57BL/6 (CD45.2) and congenic B6. SJL (CD45.1) mice, and 3LL tumors were subcutaneously inoculated to each parabiont 40 days after surgery. Seven days after tumor inoculation, parabionts were surgically separated, and then the chimerism of neutrophils and monocytes was analyzed at various times after separation. (B) Representative CD45.1 profiles in macrophages and neutrophils in the tumor and spleen after separation. (C) Chimerism of neutrophils (circles) and monocytes/ Mφs (square) in tumor (red), spleen (green), blood (blue), and bone marrow (black) at various time points after surgical separation. Each time point represents the mean (± SD) of 3 mice.
Residence time of MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice. (A) Parabiotic mice were established between C57BL/6 (CD45.2) and congenic B6. SJL (CD45.1) mice, and 3LL tumors were subcutaneously inoculated to each parabiont 40 days after surgery. Seven days after tumor inoculation, parabionts were surgically separated, and then the chimerism of neutrophils and monocytes was analyzed at various times after separation. (B) Representative CD45.1 profiles in macrophages and neutrophils in the tumor and spleen after separation. (C) Chimerism of neutrophils (circles) and monocytes/ Mφs (square) in tumor (red), spleen (green), blood (blue), and bone marrow (black) at various time points after surgical separation. Each time point represents the mean (± SD) of 3 mice.
Chemoattraction of MDSC subpopulations to the tumor through chemokine receptors
Because macrophage- and neutrophil-lineage cells do not appear to proliferate at extramedullary sites, we hypothesized that the inhibition of tumor recruitment of MDSCs by regulating chemokine system would reduce tumor infiltration by MDSCs. To this end, we next analyzed the chemokine receptor expression of tumor-infiltrating MDSC subpopulations. Flow cytometric and real-time RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that neutrophils expressed chemokine receptors CXCR2 and CXCR4, whereas macrophages expressed CCR2, CCR5, CXCR4, and CX3CR1 (Figure S3A,B).
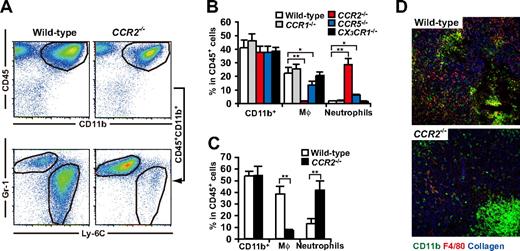
It has been reported that CCR2 plays a pivotal role in the tissue recruitment of monocytes in several inflammatory conditions.37-39 In addition, Huang et al40 recently reported that CCR2 mediated the migration or facilitated the arrest of adoptively transferred CD115+Gr-1+ MDSCs to tumors. As expected, studies on chemokine receptor-deficient mice revealed that macrophages strikingly decreased in the 3LL tumors established in CCR2−/− mice, and also significantly decreased in CCR5−/− mice but were unchanged in CCR1−/− or CX3CR1−/− mice. It is noteworthy that tumor infiltration by CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils was significantly increased in CCR2−/− mice resulting in a conservation of the total number of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+Gr-1+ “MDSCs” (Figure 4A,B). Similar results were obtained in a B16 melanoma subcutaneous tumor model (Figure 4C). Histologic analysis further confirmed that tumor-infiltrating F4/80+ macrophages markedly decreased, whereas neutrophil clusters increased within necrotic areas in CCR2−/− mice (Figure 4D). We next analyzed the CCR2 ligands mRNA expression in the tumors of WT and CCR2−/− mice. CCR2 ligands CCL2 and CCL7 play a pivotal role in the recruitment of monocytes to inflammatory sites.39 As expected, CCL2 and CCL7 mRNA were highly expressed in the 3LL tumors of WT mice, and comparable expression levels were detected in the tumor of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 5A).
Chemokine receptor usage for accumulation of MDSCs in tumor. 3LL tumors were subcutaneously inoculated to WT, CCR1−/−, CCR2−/−, CCR5−/−, or CX3CR1−/− mice. Seven days after tumor inoculation, when tumor grew to 6-10 mm in diameter, tumor-infiltrating leukocytes were analyzed by a flow cytometry. (A) Representative flow cytometric profiles of tumor-infiltrating CD45+CD11b+ cells in WT and CCR2−/− mice. (B) Percentage of CD11b+ cells, macrophages, and neutrophils in CD45+ leukocytes from tumors of WT or chemokine receptor-deficient mice. (C) Percentage of CD11b+ cells, macrophages, and neutrophils in CD45+ leukocytes from B16 tumor of WT or CCR2−/− mice. (D) Cryosections of tumors from CCR2+/+ and CCR2−/− mice were subjected to immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to CD11b (green), F4/80 (red), type IV collagen (blue). Representative image of 3 mice for each group. (B,C) Graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3-5 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01.
Chemokine receptor usage for accumulation of MDSCs in tumor. 3LL tumors were subcutaneously inoculated to WT, CCR1−/−, CCR2−/−, CCR5−/−, or CX3CR1−/− mice. Seven days after tumor inoculation, when tumor grew to 6-10 mm in diameter, tumor-infiltrating leukocytes were analyzed by a flow cytometry. (A) Representative flow cytometric profiles of tumor-infiltrating CD45+CD11b+ cells in WT and CCR2−/− mice. (B) Percentage of CD11b+ cells, macrophages, and neutrophils in CD45+ leukocytes from tumors of WT or chemokine receptor-deficient mice. (C) Percentage of CD11b+ cells, macrophages, and neutrophils in CD45+ leukocytes from B16 tumor of WT or CCR2−/− mice. (D) Cryosections of tumors from CCR2+/+ and CCR2−/− mice were subjected to immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to CD11b (green), F4/80 (red), type IV collagen (blue). Representative image of 3 mice for each group. (B,C) Graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3-5 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01.
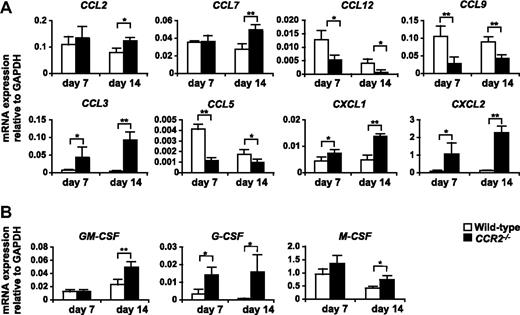
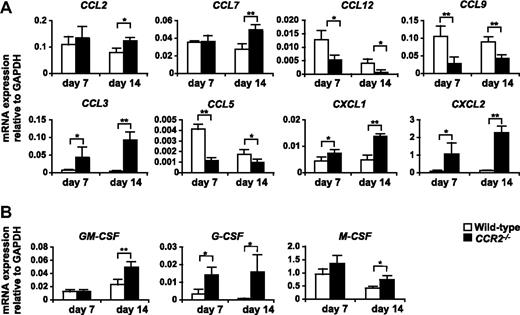
Expression of mRNA for chemokines and myeloid colony stimulation factors in the tumor of WT and CCR2−/− mice. 3LL tumors were resected from WT or CCR2−/− mice on days 7 and 14 after tumor inoculation, and the expression of mRNA for chemokines (A) and myeloid colony stimulation factors (B) was analyzed by RT-PCR. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of four mice. *P < .05; **P < .01. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.
Expression of mRNA for chemokines and myeloid colony stimulation factors in the tumor of WT and CCR2−/− mice. 3LL tumors were resected from WT or CCR2−/− mice on days 7 and 14 after tumor inoculation, and the expression of mRNA for chemokines (A) and myeloid colony stimulation factors (B) was analyzed by RT-PCR. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of four mice. *P < .05; **P < .01. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.
We next addressed the molecular mechanism that underlies the aberrant excessive accumulation of neutrophils in the tumor of CCR2−/− mice. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the expression of mRNA for CXCR2 ligands CXCL1 and CXCL2, which mediate both the mobilization and tissue infiltration of neutrophils,41 was significantly up-regulated in the tumors of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 5A). In addition, we also found that granulocyte–colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), the pivotal growth factor for neutrophil development, was markedly up-regulated in the tumors of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 5B).
Regulation of the dynamics of MDSC subpopulations by CCR2
Accumulating evidence indicates that CCR2 mediates the mobilization of monocytes from the BM to blood. However, conflicting data exist regarding the role of CCR2 in the extravasation of monocytes from the blood into inflammatory site during adoptive transfer experiments in thioglycollate-induced peritonitis.38,39 To determine how CCR2 expression regulates the dynamics of MDSC subpopulations in tumor-bearing mice, we analyzed the kinetics of monocytic cells and neutrophils in BM, blood, spleen, and tumor. In CCR2−/− mice, the frequencies of monocytic cells in blood, spleen, and tumor was significantly decreased, whereas monocytes accumulated in the BM, suggesting impairment in the mobilization of monocytes from the BM to the blood as one aspect of the reduction of CCR2−/− macrophages in the tumors (Figure S4A). Tumor progression is also associated with neutrophilia15,16 As expected, the frequency of blood neutrophils gradually increased in both WT and CCR2−/− mice with the tumor progression, but compared with WT mice, neutrophil expansion was accelerated in CCR2−/− mice (Figure S4B), which may be due to excessive production of G-CSF in the tumor of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 5B). These data suggest that intervention of the migration of monocytes by CCR2 blockage is closely associated with the enhanced tumor infiltration by neutrophils and the sequestration of monocytes in the BM.
To determine whether CCR2 is required for the migration of monocytes from the blood into tumors, we undertook adop-tive transfer studies. A mixture of equal numbers of CD45.1+CD45.2+CCR2+/+ and CD45.1−CD45.2+CCR2−/− BM cells were intravenously injected into CD45.1+ CD45.2+ tumor-bearing mice. Twenty-four hours after the transfer, the CCR2−/−/CCR2+/+ cell ratio decreased in spleen and blood (37% and 57% reduction, respectively) but increased 190% in the BM, suggesting the marginalization of circulating CCR2−/− monocytes into the BM. In the draining and nondraining LNs, no donor-derived CD11b+Gr-1+ cells could be detected (data not shown). It is noteworthy that the CCR2−/−/CCR2+/+ ratio was most severely reduced within the tumors (88% reduction), suggesting that CCR2 is also required for the migration of monocytes from the blood into tumors, in addition to mobilization from the BM to the blood (Figure S4C-E).
T-cell responses are not enhanced in the absence of tumor-infiltrating macrophages
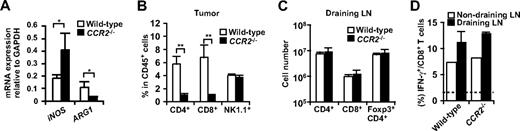
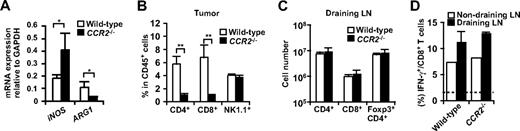
Several studies have suggested that monocytic cells rather than neutrophils are responsible for the suppressive function of CD11b+Gr-1+ “MDSC” through iNOS and ARG1.23 Consistent with our findings that ARG1 was mainly expressed in macrophages, ARG1 mRNA expression was severely decreased in the tumors from CCR2−/− mice (Figure 6A). Unexpectedly, despite the reduction in tumor-infiltrating macrophages and ARG1 expression in CCR2−/− mice, CD4 and CD8 T cells were significantly reduced in the tumors of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 6B). This was not due to an impairment in the induction of antitumor CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, because the absolute numbers of CD4+ T cells, Foxp3+CD4+ T cells, CD8 T cells, and IFN-γ+ cells in CD8 T cells were not significantly changed in the draining LNs of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 6C,D). These results suggest that a reduction of tumor-infiltrating macrophages is not sufficient to augment T-cell responses against a tumor.
T cell responses in CCR2−/− mice. (A) mRNA expression of iNOS and ARG1 in the tumor of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by RT-PCR. (B) Percentage of CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells, and NK1.1+ cells in CD45+ leukocytes from tumors of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Number of CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells, and Foxp3+CD4+ cells in the draining LNs of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Ex vivo IFN-γ production of CD8 T cells from tumor-draining LNs and nondraining LNs of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. Dotted line indicates no-stimulation background. Graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3 to 5 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01. Representative of 2 independent experiments.
T cell responses in CCR2−/− mice. (A) mRNA expression of iNOS and ARG1 in the tumor of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by RT-PCR. (B) Percentage of CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells, and NK1.1+ cells in CD45+ leukocytes from tumors of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Number of CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells, and Foxp3+CD4+ cells in the draining LNs of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Ex vivo IFN-γ production of CD8 T cells from tumor-draining LNs and nondraining LNs of WT or CCR2−/− mice was analyzed by flow cytometry. Dotted line indicates no-stimulation background. Graphs represent the mean (± SD) of 3 to 5 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01. Representative of 2 independent experiments.
Tumor development in chemokine receptor-deficient mice
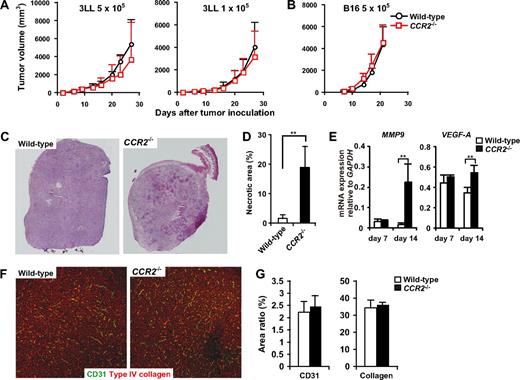
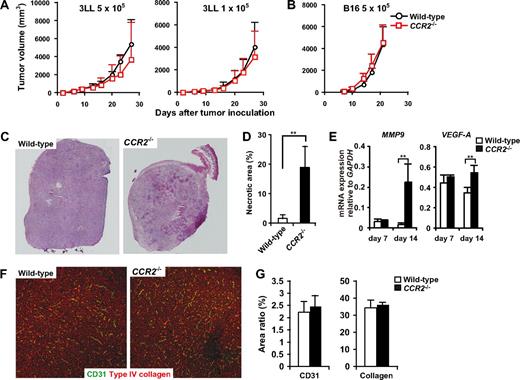
We next examined whether the aberrant mobilization and migration of monocytes and neutrophils in CCR2−/− mice would affect the tumor development. Unexpectedly, we found that tumor growth was not significantly changed in CCR2−/− mice in both 3LL and B16 s.c. models (Figure 7A,B), although we found an expansion of the necrotic areas within tumors in CCR2−/− mice (Figure 7C,D). Although tumor-infiltrating macrophages have been reported to promote tumor angiogenesis and tissue remodeling, the densities of CD31+ endothelial cells and collagen fibers were not significantly different between WT and CCR2−/− mice in the non-necrotic areas of the tumors (Figure 7F,G). Moreover, MMP9 and VEGF mRNA expression was increased in the tumors of CCR2−/− mice (Figure 7E). These results corresponded to our finding that MMP9 was mainly expressed in neutrophils.
Tumor development and angiogenesis in CCR2−/− mice. (A) WT (n = 8) and CCR2−/− (n = 7) mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 or 1 × 105 3LL cells. (B) WT (n = 8) and CCR2−/− (n = 9) were inoculated with 5 × 105 B16 cells. Each time point represents the mean (± SD). (C) Cryosections of 8- to 10-mm tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining. Representative image from 5 mice for each group. Original magnification, ×50. Whole tumor images were reconstituted with Adobe Photoshop (Adobe Systems, Mountain View, CA). (D) Percentage of necrotic area in the tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 5 mice. (E) mRNA expressions of MMP9 and VEGF in the tumor of WT and CCR2−/− mice. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 4 mice. (F) Cryosections of 8- to 10-mm tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice were stained with antibodies to CD31 (green) and type IV collagen (red). Representative images of non-necrotic area. Original magnification, ×100. (G) Percentage of CD31- or Type IV collagen-positive areas in non-necrotic area. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 5 mice.
Tumor development and angiogenesis in CCR2−/− mice. (A) WT (n = 8) and CCR2−/− (n = 7) mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 or 1 × 105 3LL cells. (B) WT (n = 8) and CCR2−/− (n = 9) were inoculated with 5 × 105 B16 cells. Each time point represents the mean (± SD). (C) Cryosections of 8- to 10-mm tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining. Representative image from 5 mice for each group. Original magnification, ×50. Whole tumor images were reconstituted with Adobe Photoshop (Adobe Systems, Mountain View, CA). (D) Percentage of necrotic area in the tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 5 mice. (E) mRNA expressions of MMP9 and VEGF in the tumor of WT and CCR2−/− mice. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 4 mice. (F) Cryosections of 8- to 10-mm tumors from CCR2+/+ or CCR2−/− mice were stained with antibodies to CD31 (green) and type IV collagen (red). Representative images of non-necrotic area. Original magnification, ×100. (G) Percentage of CD31- or Type IV collagen-positive areas in non-necrotic area. Graph represents the mean (± SD) of 5 mice.
Discussion
Tumor growth is associated with abnormal myelopoiesis as a result of tumor secretion of colony stimulation factors.25,26 Our results show that tumor-associated CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs primarily consist of CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils and CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi blood monocyte-derived macrophages. Furthermore, with tumor growth, CD11b+Gr-1low-negaLy-6Cint immature myeloid cells increased in the BM, blood, and spleen but not in the tumors, suggesting that large tumors augment myelopoiesis and mobilization of immature myeloid cells from BM to the circulation, but still these immature cells failed to infiltrate into the tumors. We consider only mature neutrophils and monocytes with appropriate homing receptors to have been able to infiltrate into the tumors. Our observations suggest that not only tumor types but also tumor stage affect the distribution and number of CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSC subpopulations. We suggest that precise identification of specific changes in the CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSC subpopulations and their distribution during tumor development is required for an improved understanding of the roles of MDSCs in tumor pathogenesis.
Kusmartsev et al42 have reported that splenic CD11b+Gr-1+ cells from tumor-bearing mice showed early myeloid progenitor-like properties, such that they could differentiate into mature macrophages, DCs, and granulocytes in the presence of appropriate growth factors. However, there is a possibility that G-CSF and granulocyte-macrophage–colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) simply maintain the survival of terminally differentiated neutrophils and macrophages, respectively, which results in the enrichment of mature neutrophils or macrophages. Furthermore, it has been reported that mouse monocytes can differentiate into dendritic cells in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-4,43 and that monocyte-derived macrophages themselves express DC markers such as CD11c, MHC class II, and CD86 after activation.44 Together with our results showing that CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs in the peripheral tissues of tumor-bearing mice were composed primarily of short-lived, nonproliferating macrophages and neutrophils, it seems more likely that the differentiation of myeloid lineage cells, except for the conventional DCs, were primarily occurred in the BM but not spleen even in the tumor-bearing state.
BrdU incorporation studies and parabiosis experiments suggested that both neutrophils and monocytic cells proliferate primarily in the BM and not in peripheral tissues, even in tumor-bearing mice. The absence of peripheral proliferation by MDSC subpopulations indicates that the inhibition of MDSCs mobilization from the BM to the blood or migration from the blood to tumors by targeting chemokine system would provide a potentially important therapeutic approach for the depletion of MDSCs from tumor tissues. Furthermore, the BrdU labeling kinetics revealed the unexpected results that tumor-infiltrating macrophages were replenished more rapidly than neutrophils. In the BM, 23.3% of CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi monocyte precursors were labeled with BrdU within 30 minutes of labeling, suggesting that monocyte precursors were vigorously proliferating in the BM and can be rapidly mobilized into circulation. This result is essentially consistent with an observation by Van Furth et al45 that [3H]thymidine-labeled BM monocyte precursors could be detected within 2 hours and peaked at 24 hours of labeling. Although we did not address the labeling kinetics of monocytic cells in steady-state conditions, proliferation of monocyte precursors may be accelerated by inflammatory conditions such as those that occur in tumor-bearing mice.46,47 Compared with monocytes, CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils had relatively slower BrdU incorporation kinetics, suggesting that neutrophil precursors require a longer time than monocyte precursors for proliferation and maturation in the BM. In the steady-state condition, postmitotic neutrophils were released from BM within 4 to 6 days, and administration of G-CSF shortened the time to 1 to 2 days.48 Our results showing that BrdU+ neutrophils were detected within 48 hours of labeling suggest that tumor-derived factors such as G-CSF accelerate the proliferation and release of neutrophil (precursors) in tumor-bearing mice.
Parabiosis experiments revealed that the residence time of partner-derived macrophages and neutrophils in the tumors was relatively longer than that in spleens and blood. Gregory et al49 reported that apoptosis of neutrophils was accelerated in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa–infected lungs in G-CSFR−/− mice. Therefore, the production of G-CSF in the tumor microenvironment may promote the maintenance of tumor infiltrating neutrophils, in addition to accelerating the neutrophil production in the BM.
Although CCR2 has been thought of as the most important chemokine receptor in the regulation of the monocytic migration in both steady-state and inflammatory conditions, involvement of CX3CR1 and CCR5 has been also suggested.50,51 Our results suggest that in the tumor-bearing mice, CCR2 has a major role in controlling both the mobilization of monocytes from the BM to the blood and the migration from the blood to tumor. However, tumor-infiltrating macrophages are also marginally reduced in CCR5−/− mice, but not in CX3CR1−/− mice. Our flow cytometric analysis showed that CCR5 was expressed on tumor-infiltrating macrophages but not on blood monocytes (Figure S3A and data not shown). Furthermore, we saw no significant difference in the efficiency of infiltration into tumors by adoptively transferred CCR5+/+ and CCR5−/− BM monocytes. Tyner et al52 reported that CCL5-CCR5 interaction provides antiapoptotic signals for macrophages during viral infection. Thus, CCR5 may not contribute to monocyte migration from blood to tumor but may be involved in the survival of tumor-infiltrating macrophages. In this context, whether chemokine system might affect the function of MDSC subpopulations at the cellular level independent of the migration remains to be elucidated.
Kitamura et al53 have recently demonstrated that CCL9-CCR1 interactions mediated the marginalization of CD11b+CD34+ “immature myeloid cells” to the invasion front of colorectal cancer and promoted tumor invasion. However, we did not detect distinct population expressing CD11b+CD34+ in our s.c. tumor model, and neither the number of tumor infiltrating CD11b+ cells nor tumor growth was changed in CCR1−/− mice, which may be due to differences among the tumor models. Moreover, it is important to keep in mind that transplanted tumors may differ from spontaneous tumors in inflammatory conditions, including chemokine and cytokine microenvironments, which may affect the patterns of infiltrating cells. Further study is therefore needed to elucidate the differences and similarities in the regulation of myeloid cell dynamics between transplanted and spontaneous tumors.
The reduction of macrophages was associated with the aberrant excessive accumulation of neutrophils in the tumor of CCR2−/− mice. This observation suggests that there might be an inverse relationship between macrophage and neutrophil infiltration in tumors. Likewise, an inverse relationship has been observed in the op/op mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes, in which the recruitment of blood monocytes to inflamed tissues was significantly reduced but neutrophils aberrantly accumulated.54 G-CSF is not only the pivotal growth factor for neutrophil development but also mediates mobilization of neutrophils from the BM to the circulation through disrupting neutrophil retention by CXCL12–CXCR4 interaction.41 Therefore, excessive production of CXCR2 ligands and G-CSF at tumor site in CCR2−/− mice might synergistically induce the aberrant accumulation of neutrophils in the tumors of CCR2−/− mice. Further studies are needed to elucidate the mechanisms that induce excessive local production of CXCR2 ligands and G-CSF at tumor sites in the absence of macrophages in CCR2−/− mice.
It is generally accepted that monocytic cells are responsible for the suppressive function of MDSCs, and our results demonstrating that ARG1 was highly expressed by macrophages support this hypothesis. However, the significant reduction in blood monocytes in CCR2−/− mice did not augment IFN-γ+ effector CD8 T cells in the draining LNs but resulted rather in the reduction of tumor-infiltrating T cells. Because monocytic cells and neutrophils are rarely detected in draining LNs even in WT mice, and the number of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells was not changed in the draining LNs of CCR2−/− mice, MDSCs may not be directly involved in the induction of antitumor effector T cells. It is possible that the reduction of TILs in CCR2−/− mice may be due to the aberrant neutrophil accumulation, because they produce proapoptotic factors, including ROS and neutrophil serine proteases.18 Furthermore, neither vascularity nor tumor growth was significantly different between WT and CCR2−/− mice. Several studies have suggested that BM-derived CD11b+ myeloid cells play a pivotal role in angiogenesis via MMP9.53,55 Therefore, even though macrophages may have an important role in angiogenesis by producing angiogenic factors, other accessory cells such as neutrophils could also support angiogenesis in tumor.
In conclusion, we report that tumor-associated CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs were composed primarily of BM-derived CD11b+Gr-1hiLy-6Cint neutrophils and CD11b+Gr-1int/dullLy-6Chi macrophages. However, CD11b+Gr-1low-negaLy-6Cint immature myeloid cells were increased in the BM, blood, and spleen but not in the tumors of morbid mice, unless the tumor burden exceeded 10% of body weight. In vivo BrdU labeling and parabiosis experiments revealed that tumor-infiltrating macrophages were replenished more rapidly than neutrophils. In tumor-bearing mice, the dynamic turnover of tumor-infiltrating monocytes was mediated by CCR2, and CCR2 deficiency caused striking conversion of infiltrating cellular dominance from macrophages to neutrophils in the tumor with the excessive production of CXCR2 ligands and G-CSF in the tumor without affecting tumor growth. Simultaneous blockage of the migration of macrophages and neutrophils will further reveal the role of tumor-infiltrating macrophages and neutrophils in tumor growth and development and may provide a novel strategy for therapeutic intervention.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Drs S. Hashimoto, K. Kimura, and S. Ishikawa for scientific discussions; to K. Stites for special proofreading; and to S. Fujita, S. Aoki, Y. Harukawa, S. Takao, J. Kurachi, Y. Lee, K. Ogoshi, M. Ogawa, Y. Hosono, S. Iwashita, and S. Shawkat for their kind assistance.
This work was supported in part by Solution Oriented Research for Science and Technology (SORST), by the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST), and a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Authorship
Contribution: Y. Sawanobori performed research and analyzed data; S.U. designed and performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; M. Kurachi, J.A., Y. Shono, M. Kitabatake, K.K., and N.M. analyzed data; J.E.T. analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; and K. Matsushima designed research and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Kouji Matsushima, Department of Molecular Preventive Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan; e-mail: koujim@m.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
References
Author notes
*Y. Sawanobori and S.U. contributed equally to this work.