Abstract
Background: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) has a high morbidity and mortality rate despite current standard therapy comprising plasma exchange (PEX). Aim of this prospective clinical trial was to test the safety and efficacy of the anti von Willebrand Factor aptamer ARC1779 in patients with relapsing TTP, and to find possible proof of concept.
Methods: Three patients with relapsing TTP (with detectable anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies) received bolus primed continuous intravenous infusions of ARC1779 (0.002 mg/kg/min) on top of standard PEX therapy until remission of TTP was induced, or for 14 days whatever came first. ARC1779 concentrations were quantified by a highperformance liquid chromatography/ultraviolet assay, the inhibitory effect of ARC1779 on vWF activity was evaluated with an ELISA kit (READDS vWF Activity ELISA Test Kit, Corgenix, Inc, Westminster, Colo), and platelet function was assessed with the platelet function analyzer (PFA-100).
Results: ARC1779 was well tolerated without any evidence for bleeding in these patients. Median ARC1779 concentrations of approximately 10μg/mL in plasma were reached under steady state, and inhibited the collagen binding site of the vWF A1 domain by >95%. While plasma exchange (PEX) removed some 50% of the drug from the blood, ARC1779 concentrations could be restored by subsequent mini boluses.
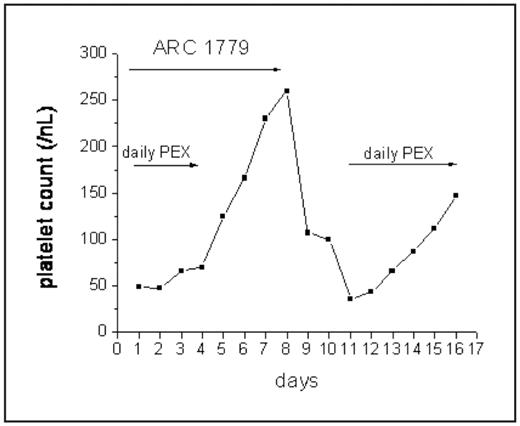
Platelet counts in all patients normalized with concurrent ARC1779 and PEX: 2 days after initiation of ARC1779 in two patients, and after 6 days in the third. In the third, the time course of response (see Figure) provides support for the concept that ARC1779 can restore platelet counts, and thus interferes with the disease process. While PEX was stopped when platelet counts reached 125/nL, 4 more days of therapy with ARC1779 increased platelet counts to 260/nL. Discontinuation of the ARC1779 infusion was associated with an immediate drop in platelet counts, so that PEX had to be restarted after 2 days (Figure).
Conclusion: These data indicate that ARC1779 effectively inhibits VWF and thereby increases platelet counts in TTP patients. Addition of ARC1779 to PEX may have the potential to accelerate recovery from organ dysfunction in TTP and thereby decrease morbidity/mortality.
Disclosures: Jilma:Archemix, Baxter and others: Research Funding. Gilbert:Archemix Corp.: Employment. Hutabarat:Archemix. Corp.: Employment. Wagner:Archemix Corp.: Employment.
Author notes
Corresponding author