Abstract
Vaso-occlusion is the major cause of morbidity and mortality in sickle cell disease. The tendency of red blood cells (RBCs) to adhere to extracellular matrix molecules and the vascular endothelium is believed to be a significant contributor to the vaso-occlusive process. Some published studies have shown that hydroxyurea decreases sickle (SS) RBC adhesion to some ligands, although the mechanism by which this occurs is not completely understood. SS RBCs demonstrate increased expression of several adhesion molecules, especially BCAM/LU, and also conserve functional signaling pathways that are associated with upregulation of adhesion. BCAM/LU mediates adhesion to the extracellular matrix protein laminin. We hypothesized that patients responsive to hydroxyurea (HU) therapy would exhibit reduced adhesion to laminin as well as a decrease in adhesion molecule expression. Our subjects included patients with Hb SS between the ages of 5 to 18. They were divided into three groups:
children not receiving HU therapy (n = 3);
children receiving HU therapy for over 6 months (n = 5), and
children initially not receiving HU but who were initiating therapy at the time of study enrollment (n = 5).
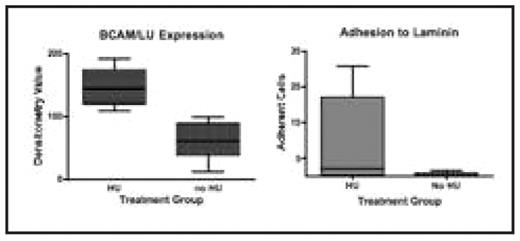
Adhesion to laminin was examined using a graduated height flow chamber to quantitate the adhesion of SS RBCs. Expression of adhesion molecules was analyzed by western blot and densitometry, using monoclonal antibody to BCAM/LU. We found that HU therapy was associated with significantly increased expression of BCAM/LU (HU: 145.8 ± 14.0 SEM; no HU: 60.8 ± 11.0 SEM densitometry units, p = .0014). This somewhat unexpected finding confirms results published earlier this year by Odievre et al. (2008). Adhesion to laminin was also increased for patients on HU (HU: 9.3 ± 5.9; no HU: .3 ± .3, p=.2), although this increase was not significant, given the variability in adhesion seen among patients and the small number of subjects. Nevertheless, the increase in adhesion corresponded to the increase in BCAM/LU expression. In contrast, adhesion to endothelial cells was decreased, although not significantly, in patients on HU (HU: 38.1 ± 38; no HU: 127.2 ± 122.5, p=.6). Our findings thus confirm earlier published data showing that HU increases the expression of BCAM/LU measured by flow cytometry and further shows that this increased expression is associated with increased adhesion to laminin but not to endothelial cells. Potential mechanisms by which HU affects adhesion molecule expression and activity merit further investigation, as does the physiologic role of these alterations. Comparison of results from patient-matched pre-treatment and post-treatment samples should also help define the effects of HU.
Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.