Abstract
LMO2, a germinal center marker and transcription factor with an important role in angiogenesis and erythropoiesis, was found to confer improved prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) when expressed in tissue microarray (TMA) samples (
Natkunam et al J Clin Oncol 2008,26:447
). Bcl-6, a transcriptional repressor controlling germinal center formation, has been associated with favorable outcomes in DLBCL patients treated with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) but was found to have no prognostic significance in DLBCL patients older than 60 treated with rituximab (R) + CHOP (Winter et al Blood 2006,107:4207
). Hans previously described an algorithm to subclassify DLBCL into germinal center B-cell like (GCB) and activated B-cell like (ABC) using immunohistochemical staining for CD10, bcl-6 and MUM1 with GCB exhibiting improved survival (Hans et al Blood 2004,103:275
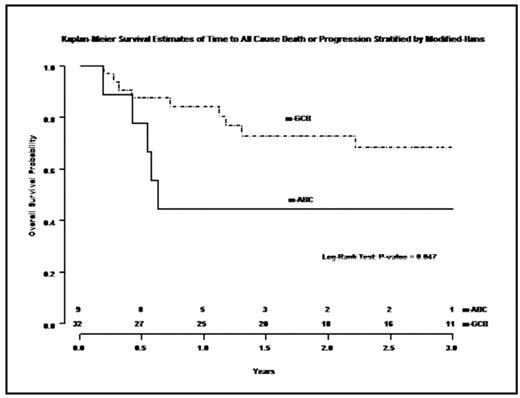
). The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of LMO2, CD10, bcl-6, bcl-2 and MUM1 expression in DLBCL patients treated with R-CHOP. We also applied the Hans classification to our cohort and incorporated LMO2 into the algorithm. Adults (>18 years) with DLBCL who were diagnosed and treated at the University of Virginia between 2000 and 2007 were retrospectively evaluated. Patients were selected based on adequate tissue, treatment with at least 3 cycles of R-CHOP and if a minimum of 6 months of follow-up data was available at the time of data analysis. Forty-one cases were included of which 26 were de novo DLBCL, 12 were DLBCL with concurrent follicular lymphoma (FL) and 3 cases were new diagnoses of DLBCL with a previous history of FL. H&E-stained sections from paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed blocks were used to define diagnostic areas, and 3 representative 1.0-mm cores were obtained from each case. TMA sections were then stained with antibodies to CD10, bcl-6, bcl-2, MUM1 and LMO2. Cases were assigned to GCB-like and ABC-like subgroups based on the Hans algorithm. The LMO2 stain was incorporated into the Hans algorithm to create modified-Hans (m-Hans) subgroups; the sample received an m-GCB designation if LMO2 positive but the normal Hans classification was applied if the sample was LMO2 negative. For 41 complete patient samples, a nonparametric Kaplan-Meier estimator was used to estimate overall survival (OS) probability for each group (m-GCB, m-ABC). A log-rank test demonstrated that there was a significant difference in OS probability between m-ABC and m-GCB groups (p = 0.047). Six month and 3 year survival for m-ABC and m-GCB were 71% and 88%, and 44% and 68% respectively. A semi-parametric Cox proportional hazard model was used to assess association between OS and each individual stain (CD10, bcl-2, bcl-6, MUM1 and LMO2), and a hazards ratio was used to quantify the effect of each stain. Bcl-6 and LMO2 expression were highly correlated, with bcl-6 expression significantly associated with OS (p=0.011). Patients without bcl-6 expression had more than four-fold risk than those expressing bcl-6 in OS (Hazard Ratio = 4.29, 95% CI: 1.4–13.1). Also, LMO2 expression showed a marginal association with OS (p=0.065). In conclusion, LMO2 incorporated into the Hans classification and bcl-6 expression are both significant predictors of OS in DLBCL patients treated with R-CHOP.Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author
2008, The American Society of Hematology
2008