Abstract
Abstract 2703
Poster Board II-679
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an incurable disease with a highly variable course. Improvements in therapy have been impeded by the lack of a universal prognostic model, making risk stratification and comparisons across clinical trials difficult. The International Prognostic Index (IPI) and Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) have been applied but show limitations in MCL, especially in distinguishing low and intermediate-risk patients (pts).
The MIPI (Mantle Cell International Prognostic Index) was developed to overcome these limitations, and is based on WBC, age, and LDH (analyzed as continuous variables) and ECOG performance status.1 However, the MIPI has yet to be independently validated, and failed to predict outcome of MCL pts treated with Hyper-CVAD.2 To examine the prognostic capacity of the MIPI, we reviewed outcomes of pts diagnosed with MCL from 1998–2008 at the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute (CCTCI).
Cases of MCL diagnosed at CCTCI were identified from our pathology database, yielding 85 unique pts. These subjects were retrospectively analyzed with approval of our Institutional Review Board. A total of 48 pts with advanced stage disease who underwent immediate treatment (within 90 days of diagnosis), and for whom adequate data for assignment of both MIPI and IPI existed, were the subject of review. Survival was identified from medical records and confirmed using a public social security database. Outcomes were compared using log-rank analysis of Kaplan-Meier survival analyses, and MIPI was calculated in accordance with the initial publication.1
Pt characteristics at diagnosis were: median age 62 (range 39–85), 73% male, 75% ECOG performance status of 0-1, 96% stage IV disease, 52% elevated LDH, and 40% had extranodal involvement other than bone marrow (23% with GI involvement). Six pts had the blastoid variant of MCL. IPI scores at diagnosis were as follows: low (17%)/ low-intermediate (31%)/ high-int (25%)/ high (27%). MIPI scores at diagnosis were: low (33%) / int (25%)/ high(42%).
Initial treatment included an anthracycline in 71% and rituximab in 60%. HyperCVAD was given 33%, and 23% underwent upfront (CR1/PR1) autologous transplantation.
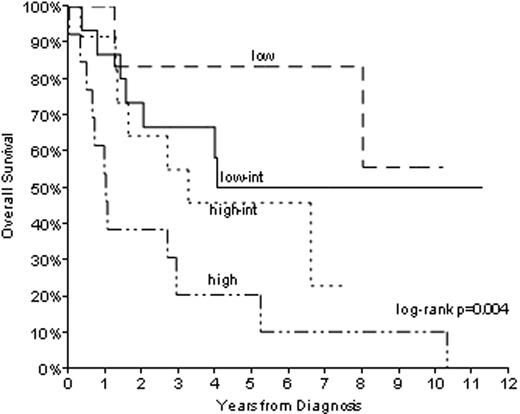
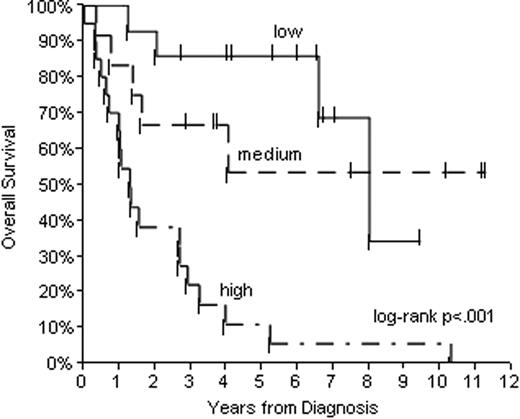
Median follow-up of survivors is 5.7 years. Median OS and RFS for all pts is 3.9 and 2.5 years, respectively. The IPI distinguished low and high-risk groups, but low-int and high-int groups were closely approximated (Figure 1). On the other hand, the MIPI distinguished 3 separate groups (Figure 2), including a high risk group with a 5-year survival of 11%. The MIPI maintained its prognostic capacity even in HyperCVAD-treated pts (log rank p=.01 for low/int/high MIPI among 16 pts, figure not shown.) The use of regimens including rituximab was not associated with improved OS (log rank p=0.21, comparing rituximab at any time vs none, figure not shown).
Based on long-term follow-up of 48 pts diagnosed with MCL at CCTCI from 1998–2008, we verified the accuracy and ease of application of the MIPI for determining prognosis in MCL. On further analysis, rituximab did not impact OS of MCL pts. Clinical trials in MCL should employ the MIPI as a risk-stratification tool, and novel approaches are urgently needed for pts in the high-risk group.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.