Abstract
Abstract 4699
We have evaluated the possibility to use the new BD Cytometric Bead Array to detect the presence of the BCR-ABL fusion protein2 in peripheral blood samples with a routine blood hematology analyser, the Abbott Cell-Dyn Sapphire, for a quick identification of those positive samples, both at diagnosis and at follow up to detect the MRD. This pilot study was carried out on 5 samples with different level of BCR-ABL fusion protein2 plus 2 control samples positive and negative respectively: results were compared with those obtained with the BD FACScanto and the standard FISH analysis reference method.
Flow cytometry allows for the discrimination of particles on the basis of attributes such as size and fluorescence. BD Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) systems provide a way of coupling a soluble analyte or set of analytes with beads of known size and fluorescence, making it possible to detect analytes through flow cytometry.1 The BD” BCR-ABL Protein Kit uses this technology to detect BCR-ABL fusion proteins2 in human blood research samples.
Cell-Dyn Sapphire is a routine automated hematology analyzer for full blood count. Moreover the system employs immuno-fluorescence analysis technology, similar to that used on a dedicated fluorescence flow cytometer, for analysis of MAb applications.
BD FacScant is a routine dedicated flow cytometer using 6 fluorescence channels.
FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridation) is a cytogenetic technique using fluorescent probes that bind to only those part of the chromosome with which they show a high degree of sequence similarity in interphase nuclei and on metaphase chromosome.
FISH detects and localizes the presence, the absence or the translocation of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. In this patients' category, LSI bcr/abl dual fusion DNA probe hybridises to chromosome 22q11.2 (breakpoint cluster region SpectrumGreen) and to chromosome 9q34 (abl oncogene SpectrumOrange). In interphase nuclei of normal cells, the probe signals generally appear as two distinct signals of each colour. In the pathological cells with bcr/abl translocation, individual orange and green signals from the normal 9 and 22 chromosome and two orange/green fusion signals (one each from the derivative 9 and 22 chromosomes) is observed. We have analysed 200 nuclei in fluorescence microscopy for each sample.
Statistical analyses were performed using the MedCalc program comparing the median fluorescence values obtained by the 2 cytometers and with the standard diagnostic procedure.
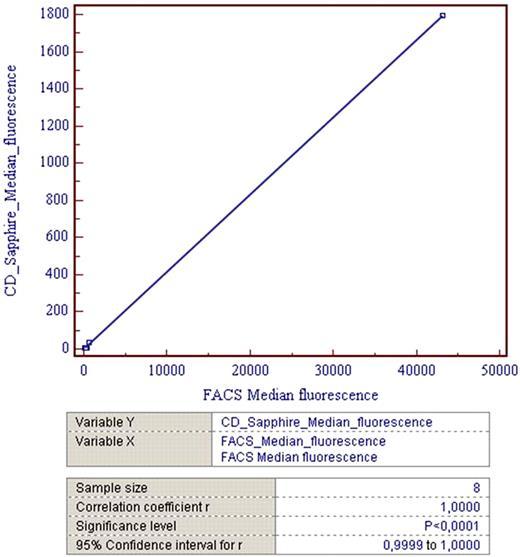
Correlation of median fluorescence data between the BD FACScanto and the CD Sapphire is excellent with a Correlation coefficient r = 1,0000 and a Significance level P<0,0001 (Fig 1).
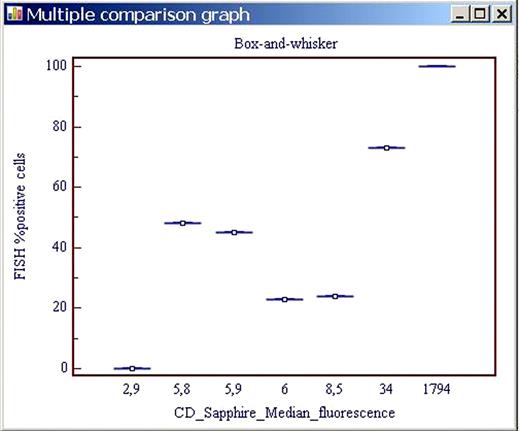
The Box –and –whisker Multiple comparison graph of the CD method versus the FISH reference one is represented in Figure 2.
The results of our pilot study demonstrate the robustness of this new diagnostic tool in detecting the presence of the BCR-ABL fusion protein2 in the routine Laboratory of Hematology. The main limit to use this tool is now represented by the high cost of the BD Cytometric Bead Array.
Correlation of median fluorescence data between the BD FACScanto and the CD Sapphire
Correlation of median fluorescence data between the BD FACScanto and the CD Sapphire
Box –and –whisker Multiple comparison graph of the CD method versus the FISH reference one.
Box –and –whisker Multiple comparison graph of the CD method versus the FISH reference one.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.