Abstract
Abstract 4939
Single or tandem Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation (ASCT) has been considered standard approach in adult (<65y) Multiple Myeloma (MM) patients (pts), however post ASCT disease progression occurs in the majority of cases suggesting that post ASCT maintenance treatment might be useful. The role of Bortezomib in the post-ASCT context is still not well defined. In December 2007 this single center study was activated in the aims to assess the impact of Bortezomib maintenance a) on time to progression (TTP), b) the possible toxicity related to a prolonged administration of the agent.
Between October 2002 and July 2008, at Hematology Unit of S. Giovanni Hospital, 24 pts (median age 59.5y, min 38-max 67y) with newly diagnosed intermediate/advanced MM underwent single (8), or tandem (16) ASCT, respectively. Of these, 13 pts autotransplanted (8 single and 5 tandem) between 2002 and 2007, who did not receive any treatment post-ASCT, were considered as historic control group, while the remaining 11 autotransplanted from December 2007 to September 2008, received Bortezomib as maintenance treatment. Maintenance schedule consisted of Bortezomib as single agent given at dosage 1.5 mg (total dose) every 15 days until progression. Response was evaluated according to the International Myeloma Working Group uniform response criteria, while minimal residual disease (MRD) was assessed every 3 months on bone marrow (BM) samples by 6-colour BDFACS CANTO II. Abnormal plasma cells (APC) were identified using an Ab panel against the following markers: CD38, CD138, CD19, CD20, CD45, CD56, CD117, CD28, CD200. The condition was optimized in order to obtain a sensitivity level ' 1×10-3 (<0.01). Moreover, the presence of peripheral neuropathy (PN) was monitored before maintenance start, then every 3 mo by neurophysiologic tests including motor and sensory conducting studies.
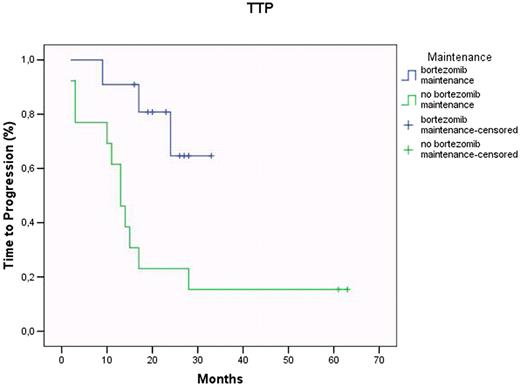
In the Bortezomib group, post -2nd ASCT, 5 pts achieved complete (CR) or a very good partial response (VGPR), 4 partial response (PR), and 2 maintained stable disease (SD), respectively; the overall response rate was 82%, with 45% CR+VGPR. Maintenance was started in a median time of 3.8 mo (min 1.7 - max 13.7 mo). As of July 2009, after a median maintenance length of 16.2 mo (min 4.1 - max 19 mo), all 11 pts are alive. As disease status, of the 4 pts in PR after 2nd ASCT, 1 achieved stringent CR (sCR), 1 CR and 2 progressed, respectively. The 5 pts who were previously in CR/VGPR maintained the same type of response, with no detectable MRD (< 0.01), except 1 pt who shifted to PR. Finally, of the 2 pts in SD, 1 persisted in SD after 10 months from the beginning of the Bortezomib maintenance, while the other one progressed. Thus, to date, of the 11 pts entered in the study, 55% are sCR+CR+VGPR, with an overall response rate of 63%. It is noteworthy that the 3 pts who relapsed (at 3, 4, 16 mo from maintenance start) had chromosome 13 deletion at diagnosis. Considering that not all pts underwent 2nd ASCT, TTP was evaluated from 1st ASCT. In the Bortezomib group (median follow-up 26 mo; range: 15 – 33 mo), median TTP has not yet been reached, whereas in the control group (median follow-up 34 mo; range: 14 – 62 mo), median TTP was 13 mo (log-rank P<0.01) (Fig 1). Finally, none of the pts in the Bortezomib group experienced grade 3 or 4 haematologic toxicity and/or PN requiring dose reduction or discontinuation of the drug.
The preliminary results of this single center study, even though limited to a small cohort of pts, suggest that Bortezomib as single agent in post-ASCT maintenance may improve the quality of previously achieved response and prolong TTP. However, these preliminary results need to be confirmed by a longer follow-up and a randomized multicenter study.
Time to progression according to post ASCT maintenance regimens (bortezomib vs no bortezomib)
Time to progression according to post ASCT maintenance regimens (bortezomib vs no bortezomib)
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.