Abstract
Abstract 3463
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is common in survivors of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (SCT). However, evolution over time of kidney dysfunction and its association with post-SCT acute kidney injury (AKI) are unclear.
A retrospective cohort study was performed in 86 myeloablative allogenic SCT patients who received SCT between 1990 and 1999 and lived without relapse for 10 years or more. CKD was defined as a sustained decrease in estimated GFR less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 at least for a period more than 3 months. Post-SCT AKI was classified into three stages according to the acute kidney injury network (AKIN) criteria within 100 days after SCT. Incidence of new-onset CKD was studied by 1-year interval along the course of follow-up. Cumulative CKD incidence was evaluated by the Kaplan-Meier analysis. The factors associated with CKD at the time of 10 years after SCT were examined using Cox regression analysis.
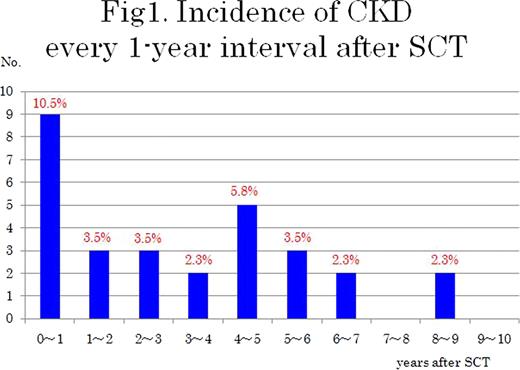
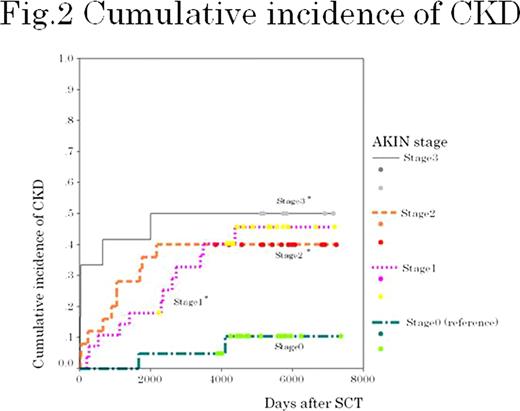
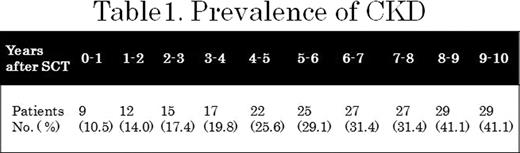
The incident of new CKD was the highest (10.5%) at the first year after SCT and then remained almost constant (2.3 to 3.5%) (Figure 1 ). The prevalence of CKD increased along the follow-up time (Table 1 ). The cumulative incidence of CKD increased according to increasing AKI stages with significant difference between stages ≥1 and no AKI (Figure 2 ). Cox regression showed that each AKIN stage was a significant predictor of CKD: stage 3: hazard ratio (HR) 12.7, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.42–97.6; stage 2: HR 7.75, 95% CI 1.83–53.6; and stage 1: HR 4.36, 95% CI 1.06–29.5. Other predictors included total body irradiation (TBI) (HR, 4.00; 95% CI, 1.63–10.5) and age on SCT (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03–1.13).
CKD accumulated among long-term survivors receiving myeloablative allogenic SCT. Post-SCT AKI, regardless of the AKIN stages, is the most significant risk of CKD in such SCT population.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.