Abstract
Abstract 4840
The causes of drug resistance in acute leukemias (AL) have been studied very intensively and the key research was done on Bcl-2 family proteins. Last studies have showed that high level Bcl-2 expression in acute leukemia is really associated with drug resistance andpoor prognosis [Haematologica 2007, U. Testa]. It was demonstrated that lower Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (<0,3) was associated with FAB M0-M1 classes (p=.00001), poor-risk cytogenetics and poor prognosis [Blood 2003, G. Poeta]. But there were no studies on the dynamic evaluation of Bcl2 and Bax expression on CD34+ cells during chemotherapy. Renin-angiotensin system and angiotensin concertin enzyme (ACE) influence on leukogenesis is extensively investigated. It was reported that ACE expression on blast cells is high [Leuk Lymphoma 2006, S. Aksu]. Recent publications indicate that primitive hematopoietic precursors have different characteristics regarding ACE: CD34+ACE+cells transplanted into NOD/SCID mice contribute 10-fold higher numbers of multilineage blood cells than their CD34+ACE- counterparts and contain a significantly higher incidence of SCID-repopulating cells than the unfractionated CD34+ population [Blood 2008, V. Jokubaitis]. But it's still unknown how CD34+ACE+ cells in AL behave on and after chemotherapy.
We have studied the dynamics of Bcl-2 and Bax expression by flow cytometry in CD34+ cells of peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) in pts with AL. PB and BM samples were collected before treatment, on days +8, +36, only PB - on day + 21. Bcl-2 and Bax were detected on CD34+ cells by flow cytometry using specific monoclonal antibodies: CD34 (8G12, BD), Bcl-2 (100, BD), Bax (2D2, Santa Cruz). ACE (9B9, BD) expression was also evaluated. We calculated 10 000 cells in each sample.
10 pts were included in the study: 4 AML, 6 ALL. The control group comprised 4 healthy donors. At time of diagnosis CD34+ cells number in BM was 38,7%± 9,75, in PB - 38,3%± 8,14 in AL pts, not differing much in AML and ALL, and indicating blast cells population. CD34+ cells numbers in BM and PB of healthy donors were 1,35% and 0,23%, respectively. After induction therapy and WBC recovery (days +36-38) CD34+ cells number in AL pts decreased dramatically in BM to 3,83%±1,51 (p=0,001) and in PB to 0,98%± 0,29 (p=0,0001), indicating the efficacy of chemotherapy. The dynamics of Bcl-2, Bax and ACE expression on CD34+ cells of BM and PB in AL pts are presented in fig.1-6
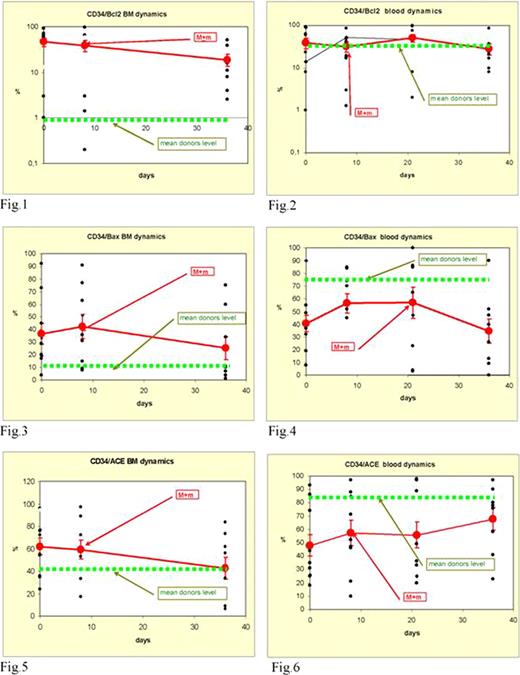
As seen in the fig.1,2 CD34/Bcl-2 expression in BM is significantly higher (p=0,04) and in PB is similar in AL pts at the diagnosis comparing with donors. It's also worth to note that BM and PB CD34+ cells in donors had different expression characteristics of Bcl-2 demonstrating much higher level of antiapoptotic marker in PB cells. On the contrast CD34+ AL cells in BM and PB had similar characteristics regarding CD34/Bcl-2 expression. This expression level decreased substantially in BM at day +36 comparing with day 0 (p=0,04), but it never reached the donors level remaining extremely high and supposing the persistence of antiapoptotic activity in CD34+ cells in AL pts. It did not change at all during chemotherapy in PB cells, being identical to donors characteristics.
The fig.2,3 demonstrate that, CD34/Bax expression in BM is almost 3-times higher (p=0,14) and in PB is twice lower (p=0,02) in AL pts in comparison with donors. It's interesting that CD34/Bax expression in leukemic BM and PB cells looks very similar, when in donors we had very low expression in BM and high - in PB. This fact demonstrates the heterogeneity of donor CD34+cells in BM and PB and points that leukemia CD34+cells in BM and PB are rather similar in Bax expression. Chemotherapy caused the significant augmentation of CD34/Bax expression in PB on day +8 (p=0,01) and near significant on day +21 (p= 0,09) showing the increased level of “dieing” cells in PB after cytostatic influence.
The fig. 5,6 show that CD34/ACE coexpression in BM cells of AL pts and donors did not differ much at any time of evaluation. But CD34/ACE expression in PB cells of AL pts was much lower (p=0,02) than in donors and substantially increased at day +36 almost reaching the donor level.
We may conclude that Bcl-2, Bax, ACE expression on CD34+ cells in AL pts and donors significantly differs, the dynamics of expression in AL while chemotherapy shows critical changes in CD34/Bcl-2 expression in BM, CD34/Bax and CD34/ACE in PB.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.