Abstract
Abstract 973
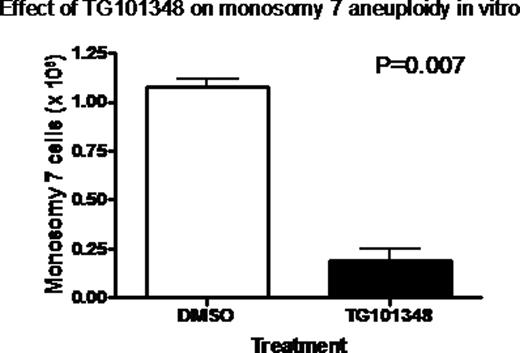
The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are bone marrow disorders characterized by cytopenias and a variable risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Monosomy 7 is the second most common cytogenetic abnormality in MDS, and the most frequent karyotypic aberration occurring in aplastic anemia patients following immunosuppressive therapy. Monosomy 7 MDS carries a particularly poor prognosis, with patients manifesting severe cytopenias and a high propensity to develop treatment-refractory AML. There are currently no targeted therapies for this disorder. We previously reported that monosomy 7 bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNCs) express high levels of a differentiation-defective granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor isoform (IV), an alternative splice variant that exhibits constitutive signaling through the JAK-2 and STAT-1 pathway, while levels of STAT-3 and -5 are unchanged (Sloand et al, PNAS, 2006, 103:14483). As a result, the cell's ability to differentiate is limited, while its ability to proliferate remains intact. Here we examine the effects of the highly selective JAK2 inhibitor TG101348 on monosomy 7 aneuploidy in BMMNCs, as well as the activity of this compound on CD34+ stem cells and CD13+ myeloid cells in culture, and on the JAK-2 signaling apparatus. Incubation of BMMNCs with TG101348 for 5 days significantly decreased absolute numbers of monosomy 7 aneuploid cells in a concentration dependent manner versus vehicle- treated controls (0.187 × 106 vs 1.08 × 106, P=0.007), while diploid cell numbers remained stable (0.338 × 106 vs 0.213 × 106, P=0.50). Flow cytometry experiments demonstrated that incubation with increasing concentrations of TG101348 decreased the absolute number of CD34+CD13- stem cells, and increased numbers of more differentiated CD34-CD13+ myeloid cells, with median CD34+/CD13+ ratios of 6.547 and 2.216 for cells treated with vehicle and 100 nM TG101348, respectively. By immunoblot, STAT-1 protein expression in monosomy 7 BMMNCs treated with 1uM TG101348 was decreased relative to vehicle- treated controls, while there was no difference in STAT-3 and STAT-5 levels. Thus TG101348 decreases monosomy 7 MDS blasts in vitro through inhibition of JAK-2/STAT-1 signaling, a finding that warrants further study of this agent in clinical trials for patients with monosomy 7 MDS and AML.
Disclosures:
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2010 by The American Society of Hematology
2010