Abstract
Abstract 1519
Receptor tyrosine kinases AXL and MER belong to the TYRO3 kinase family, first identified as a transforming gene in chronic myeloid leukemia and are found at high levels in various cancers, including hematopoietic malignancies like T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Aurora kinases play important roles in chromosome alignment and cytokinesis during mitosis and are also aberrantly expressed in ALL. We describe here characterization and pre-clinical testing of Huntsman Cancer Institute-2084 (HCI-2084), a small molecule inhibitor of AXL and MER kinases that also has activity against Aurora Kinases A and B, as a novel therapeutic for T-ALL treatment, a leukemia with poor prognosis.
Quantitative RT-PCR and Western Blot confirmed elevated levels of AXL/MER expression in Jurkat, a human T-ALL, cell line. Our compound, HCI-2084, was developed using a computational structure-based approach against AXL kinase. HCI-2084 activity against AXL/MER, in cell-based assays was evaluated utilizing ATPlite. To test activity against Aurora kinase, Jurkat cells were treated with various concentrations of HCI-2084 and VX 680, a known aurora kinase inhibitor, for 24 hours. Cell lysates were evaluated for phospho-AKT (Ser473), phospho-Aurora (Thr288) and phospho-Histone H3 (Ser10) using the Meso Scale Discovery platform (MSD). Cell cycle analysis was performed on Jurkat cells incubated in the absence (negative control) or presence of 100nM HCI-2084 or VX-680 for 24 hours, stained with propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry on FACS Calibur. Immunostaining was performed to evaluate the levels of phospho-Histone H3 (Ser10) and phospho-Aurora (Thr288) during mitosis in Jurkat cells incubated in the absence (negative control) or presence of 100nM HCI-2084 and VX-680 for 24 hours. In addition to the anti-phospho-Histone H3 and anti-phospho-Aurora antibodies, anti-alpha-tubulin and DAPI were used to determine the presence of mitotic chromosomes.
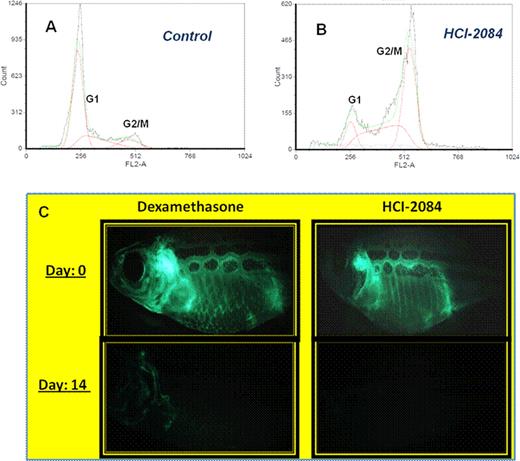
To examine HCI-2084 as a therapeutic agent for T-ALL treatment in vivo, we tested it using transgenic Zebrafish (Danio rerio) with T-ALL driven by human MYC (hMYC). Over-expression of endogenous D. rerio axl /mertk transcripts in T-ALL from hMYC fish were verified by qRT-PCR. Fish were treated with HCI-2084, Dexamethasone (a known T-ALL therapeutic; positive control), and DMSO vehicle (HCI-2084 is reconstituted in DMSO; negative control). Trials were conducted by housing fish with fluorescently-labeled T-ALL (GFP-tagged) in water containing the agent being tested, for 14 days with monitoring of disease response by fluorescent microscopy.
In in vitro studies, HCI-2084 showed potent activity in cell viability assays with an IC50 of 12 nM against AXL, 60 nM against MERTK and 15 nM against Aurora kinase. MSD assays demonstrated efficacy at 1 uM for reduction of phospho-AKT, phospho-Histone H3 and phospho-Aurora, as seen with VX 680. Cell cycle analyses performed on HCI-2084-treated Jurkat cells showed a significantly increased G2/M population and an accumulation of cells with ≥4N DNA, indicative of Aurora B inhibition and endo-reduplication (Figure A & B). Immunofluorescence analyzed using fluorescent microscopy demonstrated mitotic arrest with loss of phospho-Histone H3 and phospho-Aurora staining, demonstrating inhibition of Aurora kinase activity. HCI-2084 was also a potent therapeutic against Zebrafish T-ALL. Fish treated at 1uM HCI-2084 for 14 days, showed complete responses (CR), with efficacy comparable to our dexamethasone positive control (Figure C). Following treatment, fish remained disease-free for several days, and overall survival was prolonged significantly relative to untreated controls.
HCI-2084 shows dual action in vitro against Jurkat cells with potent cytotoxicity via AXL/MER kinase inhibition and anti-proliferative activity via Aurora kinase inhibition. In vivo, HCI-2084 demonstrates activity against a MYC-driven vertebrate model of T-ALL, prolongs survival, and is well tolerated. We conclude that HCI-2084 is a potent dual AXL/MER kinase and Aurora kinase inhibitor which should be explored further as a potential novel therapeutic in the treatment of human T-ALL.
Sharma:Millenium: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.