Abstract
Abstract 256
Several recent reports indicated low response rates (20–30%) and poor outcome with standard anthracycline and cytarabine (3+7) induction regimen for sAML arising from MDS after azanucleosides failure (Bello et al. Cancer 2011 Apr 117) (Jabbour et al, Cancer 2010 August 15,116) (Prebt et al, JCO 2011 July) (Lin et al, ASH 2010 #2913). CLAG-M is an effective regimen in treating relapsed/refractory AML including relapsed/refractory sAML. The CR rate for CLAG-M was reported as high as 58% (Wrzesien-Kus, Robak et al. Eur J Haematol 2008 Feb). We compared the efficacy of CLAG-M to standard 3+7 as induction strategy in sAML after azanucleosides failure.
This was a retrospective case-control study. Data were obtained from the Moffitt Cancer Center (MCC) electronic records. Patients (18 years of age and older) with sAML who received primary induction therapy with the CLAG-M regimen (Cladribine 5 mg/m2/d intravenous (IV) over 2 hours(hrs) days (d) 1–5, Cytarabine (Ara-C) 2 g/m2/day IV over 4 hrs starting 2 hrs after cladribine d1-5, Mitoxantrone (Novantrone)10mg/m2/d IV d1-3, Filgrastim (Neupogen) 300 mcg subcutaneous d0-5), were compared to matched controls (sAML, prior azanucleoside failure) who received standard 3+7 regimen ((Ara-C) 100 mg/m2/d civi d1-7 and Idarubicin 12 mg/m2/d iv d1-3) or (Cytarabine (Ara-C) 100 mg/m2/d civi d1-7 and Daunorubicin 45–60 mg/m2/d iv d1-3)). Baseline characteristics collected included age, gender, race, ECOG performance status, prior treatments, MDS IPSS score, leukocyte count and myeloblast percentage at induction, karyotype risk group, and duration between original MDS diagnosis and sAML. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), and secondary endpoints included response rates defined by standard AML response criteria and feasibility of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo SCT).
Descriptive statistical analyses were utilized. Chi square analysis and t- test were utilized to compare categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate OS and log rank test was used to compare the 2 groups. All data were analyzed using SPSS version 19.0 statistical software.
Twenty five patients who received CLAG-M were compared to a control of 24 patients treated with 3+7 for sAML arising from MDS after azanucleosides failure treated at MCC. The baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups with no statistically significant differences noted except that more patients had an ECOG PS 1 in 3+7 group (table-1).
Baseline Patient Characteristics
| Variable . | . | CLAG-M . | 3+7 . | P-Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Age > 60 years | 18 (72%) | 19 (79.2%) | 0.56 |
| Gender | Male | 19 (76%) | 17 (70.8%) | 0.70 |
| Race | Caucasian | 23 (92%) | 20 (87%) | 0.48 |
| ECOG PS | 0 | 19 (76%) | 9 (40.9%) | 0.032 |
| 1 | 6 (24%) | 11 (50%) | 0.32 | |
| 2 | 0 | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| missing | 0 | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| Karyotype | Intermediate | 11 (44%) | 14 (58.3%) | |
| Poor | 14 (56%) | 10 (41.7%) | 0.95 | |
| WBC (k/μL) | mean | 8.4 | 8.2 | |
| Myleoblasts % | mean | 35 | 44 | 0.07 |
| Prior MDS IPSS | Int-2 | 1 (4%) | 1 (4.3%) | 0.95 |
| High | 24 (96%) | 22 (95.7%) | 0.08 | |
| missing | 0 | 1 | ||
| Hypomethylating Agent Use | Yes | 22 (88%) | 24 (100%) | |
| Duration between MDS and AML (mo) | mean | 17 | 13 | 0.44 |
| Variable . | . | CLAG-M . | 3+7 . | P-Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Age > 60 years | 18 (72%) | 19 (79.2%) | 0.56 |
| Gender | Male | 19 (76%) | 17 (70.8%) | 0.70 |
| Race | Caucasian | 23 (92%) | 20 (87%) | 0.48 |
| ECOG PS | 0 | 19 (76%) | 9 (40.9%) | 0.032 |
| 1 | 6 (24%) | 11 (50%) | 0.32 | |
| 2 | 0 | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| missing | 0 | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| Karyotype | Intermediate | 11 (44%) | 14 (58.3%) | |
| Poor | 14 (56%) | 10 (41.7%) | 0.95 | |
| WBC (k/μL) | mean | 8.4 | 8.2 | |
| Myleoblasts % | mean | 35 | 44 | 0.07 |
| Prior MDS IPSS | Int-2 | 1 (4%) | 1 (4.3%) | 0.95 |
| High | 24 (96%) | 22 (95.7%) | 0.08 | |
| missing | 0 | 1 | ||
| Hypomethylating Agent Use | Yes | 22 (88%) | 24 (100%) | |
| Duration between MDS and AML (mo) | mean | 17 | 13 | 0.44 |
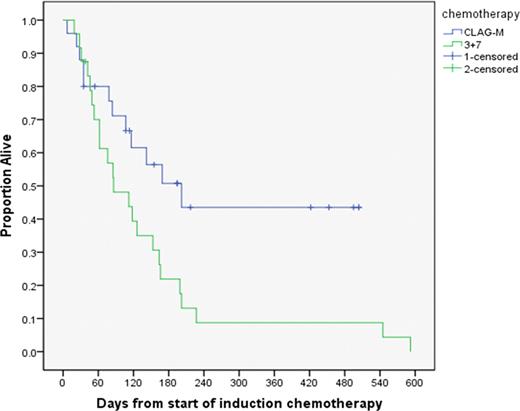
The CLAG-M cohort had a trend towards higher overall response rate (CR/CRi) 56% (N=14) compared to 29% (N=7) standard 3+7 (p=0.058). The median OS was 202 days (95%CI 97–307) versus 86 days (95%CI 30–142) (p=0.025) respectively in CLAG-M and 3+7 (Figure-1). The one year OS was 45% in CLAG-M group compared to 9% in 3+7 group.
Seven patients (28%) in the CLAG-M cohort versus 1 patient (4.2%) in the 3+7group received allo SCT (p= 0.024). The median OS was not reached for patients who proceeded to allo SCT in the CLAG-M cohort compared to 112 days for patients who did receive allo SCT in the 3+7 cohort (p=0.007). The mean duration of hospitalization was 33 days with CLAG-M compared to 41 days with 3+7 (p=0.08).
CLAG-M as an induction regimen for sAML from MDS after azanucleosides failure was associated with better OS compared to standard 3+7 therapy. There was a trend towards higher response rates with the CLAG-M regimen which allowed more patients to proceed to allo SCT. These results need to be confirmed in a randomized prospective clinical trial.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.