Abstract
Abstract 5040
Clinical Experience with Azacitidine In Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) in Spain
Pablo González Navarro 1*, Regina García Delgado 2*, Alicia Bailén Garcia 3*, Juan Antonio Muñoz Muñoz 4*
1MD, PhD. Hospital San Cecilio, 18014 Granada, Spain, Teléfono: 958023600 tatumgonzale@hotmail.com; 2Hospital Virgen De La Victoria, Málaga, Spain; 3Hospital Carlos Haya, Málaga, Spain; 4MD, PhD. Hospital Universitario Puerta del Mar, Cádiz, Spain
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells often occurring in elderly patients. In the new WHO classification, CMML has been reclassified as a myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease. CMML has been subdivided in two subclasses: CMML-1:<5% blasts in peripheral blood and 5–9% blasts in bone marrow, and CMML-2: <10% blasts in peripheral blood and 10–19% blasts in bone marrow (Greco et al. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis.2011).
Azacitidine (AZA) is an hypomethylating agent approved in Europe for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, with an intermediate to high risk of progressing to AML or death; chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) and AML that has developed from a myelodysplastic syndrome (prescribing information EMEA 2011). Until its approval in May 2009, AZA was used in Spain under compassionate use in clinical trials.
AZA produce a direct decrease of DNA methyltransferase activity, reverting aberrant DNA methylation and increasing the expression of silenced genes, leading to celular differentiation and/or apoptosis (Greco et al. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2011).
We report the results of a retrospective, longitudinal, multicenter Spanish study of 27 patients to assess the effectiveness of AZA to treat CMML. We present results of: Response, Overall Response, Overall Survival and Progression Free Survival.
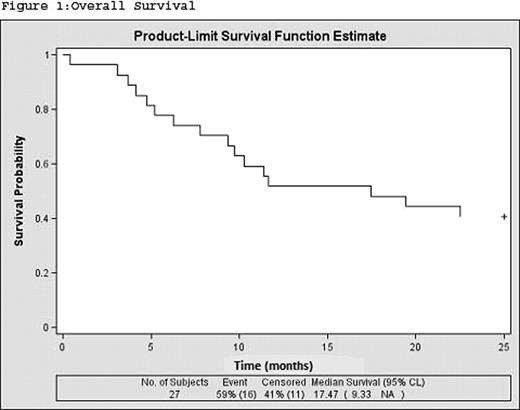
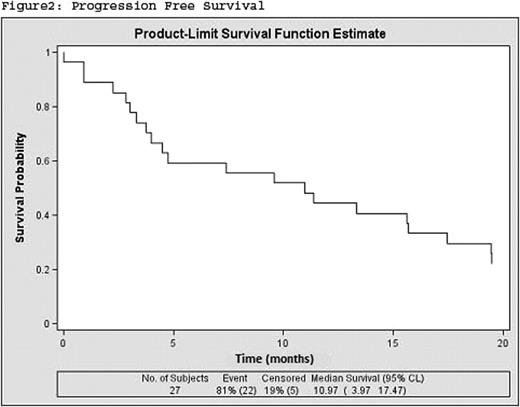
Eighteen of the patients (69.23%) had Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) type 1 and nine (30.77%) CMML type 2. Median age at diagnosis was 69 years. Male/female ratio: 19/8. ECOG performance status score 1–2 was 78%, twenty patients (74%) received an initial dose of 75 mg/m2 of AZA, whereas three patients (11%) received 50mg/ m2. The mean number of cycles received was 8.32, 95%IC (5.91; 10.73). Overall response to treatment was 53% (CR+PR+HI+mCR): 14.81% complete response, 7.4% partial response, 3,7% Medular complete response and 29,62% Hematological Improvement. In addition, 18,51% had stable disease. Thirty-six percent of patients were alive at the end of treatment with AZA. Median Overall Survival and Progression Free Survival were 17.47 months (95%CI 9.33, upper limit not reached) and 10.97 (95%IC 3.97, 17.47) respectively (Figure 1, 2).
Our results show that AZA is an active drug in the treatment of patients with CMML, with similar response rates in the published literature. More data from this study and further investigation with different clinical trials are needed to confirm these outcomes as well as safety and effectiveness of this treatment.
García Delgado:Celgene and Novartis: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.