Abstract
Abstract 5170
There are currently no approved, effective drug therapies for myelofibrosis (MF). Ruxolitinib (INC424), a potent and selective oral JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, has recently demonstrated rapid and durable reductions in splenomegaly and improved disease-related symptoms, role functioning, and quality of life in 2 phase 3 studies in patients with MF. Both studies met their primary endpoint of the proportion of patients with ≥35% reduction in spleen volume at 24 weeks (COMFORT-I) and at 48 weeks (COMFORT-II): 41.9% vs 0.7% (ruxolitinib vs placebo, P <.0001) and 28.5% vs 0% (ruxolitinib vs best available therapy, P <.0001), respectively. The most common grade ≥3 hematologic adverse events (AEs) were thrombocytopenia and anemia, which were manageable and rarely led to discontinuation (COMFORT-I: n=1 each; COMFORT-II: thrombocytopenia, n=1; anemia, n=0). Because of the limited available treatment options and medical need, ruxolitinib has been made available through an individual supply program (ISP) outside the United States.
Patients with PMF, PPV-MF or PET-MF who are determined by their physicians to be in need of treatment are considered for eligibility, irrespective of JAK2 mutation status. As in the COMFORT studies, the starting dose of ruxolitinib is determined on the basis of baseline platelet count and can be adjusted for efficacy and safety. Dose changes during treatment are registered, and AEs and serious AEs (SAEs) are monitored throughout the study.
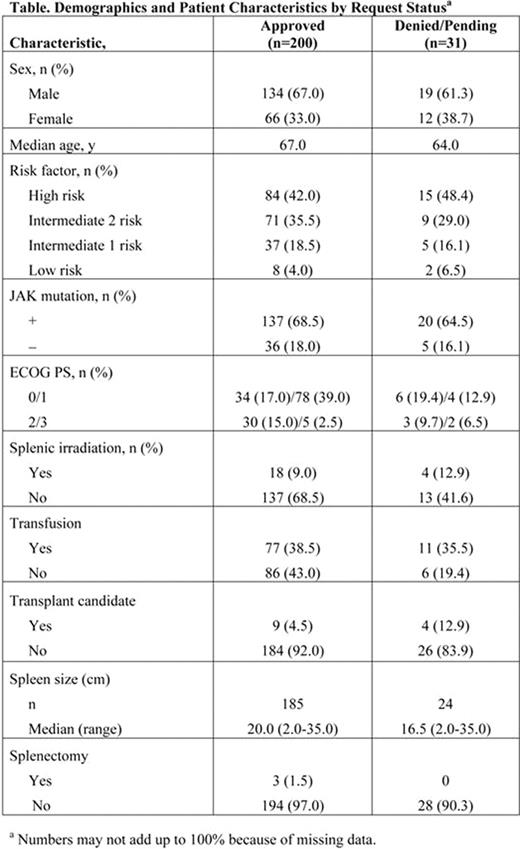
To date, 231 patients have been screened at more than 150 study sites in 28 countries, including Canada, Australia, and locations in Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia. The baseline characteristics for patients whose requests for access were approved/enrolled (n=200) and denied/pending (n=31) are shown below (Table).
The patient characteristics are generally similar to those expected in the overall MF patient population. To date, the proportion of patients with the JAK2V617F mutation enrolled in this ISP (68.5%) is higher than that for the general MF population (50–60%) and may reflect the tendency of physicians to include more JAK2V617F-positive patients in the ISP, even though ruxolitinib has demonstrated comparable efficacy in both patient types (Verstovsek S, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(12):1117–1127). Thrombocytopenia and herpes zoster were each reported as an AE in 1 patient, and no SAEs have been reported.
Ruxolitinib is currently the only drug to have completed phase 3 studies for the treatment of MF and has garnered a substantial number of requests for access through the individual supply program.
Barosi:Novartis: Consultancy. Cervantes:Bristol-Myers-Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Panagiotidis:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria. Perez:Novartis: Employment. Orlando-Harper:Novartis: Employment. Martin:Novartis Pharma AG: Employment. Willenbacher:Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sandoz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mundipharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AESCA: Honoraria, Research Funding. Ojeda:Novartis: Consultancy. Gisslinger:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Celgene Austria: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Aop-Orphan: Speakers Bureau. Knoops:Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.