Abstract
Abstract 1434
The prognostic significance of minimal residual detection (MRD) in both leukemia and lymphoma has been demonstrated in multiple cohorts. We will present a novel clinical assay, ClonoSIGHT, which leverages the advances in throughput and cost of DNA sequencing for T and B cell enumeration based on the deep sequencing of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor rearrangements. This standardized clinical assay can be used for routine clinical monitoring of MRD in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). The LymphoSIGHT platform for the universal amplification of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH@) variable (V), diversity, and joining gene segments from genomic DNA in diagnostic and follow-up DNA samples has been presented previously. In this study, we demonstrate the technical performance of this technology as a clinical laboratory test.
Primer sets for the amplification of variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) gene segments from genomic DNA for IgH@ have been demonstrated. These primer sets have been augmented by the development of universal primers capable of amplifying the full range of immune cell receptor rearrangements (D-J rearrangements for IgH@, and V-J rearrangements for IgK@, TCRB@,TCRG@, and TCRD@). Using these universal primer sets, we amplify rearrangements from genomic DNA in diagnostic and follow-up DNA samples from ALL and MCL patients. In order to make the platform compatible with routine clinical use, these amplicons are sequenced using a fast turnaround time platform (MiSeq from Illumina) to obtain multiple reads per sample enabling a 7 day time to result. Malignant clonotypes are automatically determined using diagnostic material (bone marrow or peripheral blood) and quantitated in follow up samples using standardized algorithms. In order to make these measurements clinically actionable, methods for determining the absolute number of malignant cells were developed and tested using artificially constructed samples. Sensitive methods for directly confirming the lack of sample to sample contamination were developed, which are critical to the integrity of a high sensitivity test.
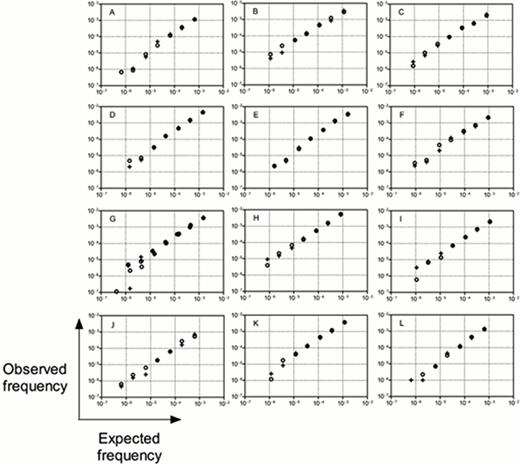
The absolute quantitation of the IgH V-J assay has been demonstrated using dilution experiments from 12 ALL patients carrying 13 leukemic IgH clonotypes. The assay unequivocally detected leukemic signatures in all dilutions with expected concentration of at least one leukemic cell in 1 million leukocytes (a sensitivity of 10−6) (Figure 1). High precision was illustrated by low random error (4.1% to 7.6% average relative standard deviation at clonotype frequencies at or above 3×10−5). For each clonotype, the assay showed high r2 values with a range of 0.977 and 0.996 (mean 0.988, median 0.991) between each of the expected and measured clonotype frequencies. The slopes ranged from 0.878 to 1.14 (mean 1.00, median 0.977), illustrating the quantitative nature of the assay over at least 3 orders of magnitude. In an analysis of all clonotypes together, we measured an r2 value of 0.94 and a slope of 1.01 between the expected and measured clonotype frequencies. The ability to identify malignant clonotypes in multiple receptors has been demonstrated in ALL and MCL clinical samples. The ability to detect multiple clonotypes within a calibrating receptor has also been demonstrated in these clinical samples; data will be presented. We will also describe the laboratory workflow and quality system that has been developed, as well as standardized algorithmic approaches to measure contamination in every sample and sequencing run, to ensure high fidelity of the data.
In order for a novel MRD assay to be clinically useful, it must exhibit superior performance compared with existing platforms and be capable of reproducibly measuring absolute MRD levels across multiple receptors in a rapid turnaround fashion with high data integrity and without any cross contamination of samples. The ClonoSIGHT assay has demonstrated these qualities and can thus be considered for clinical use. Regulatory infrastructure, laboratory process controls, quality systems, and standardized documentation associated with CLIA-approved laboratories have been developed. Validation results will be presented.
Willis:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Asbury:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Carlton:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Fang:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Klinger:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Moorhead:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Pothuraju:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Weng:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Zheng:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding. Faham:Sequenta, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.