Abstract
Abstract 3287
Durable responses with lenalidomide monotherapy have been reported in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. In relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), higher responses were observed in the activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtype than in the germinal centre B-cell (GCB)-like subtype (Czuczman, et al. British Journal of Haematology, 2011, 154, 477–481). Herein, the molecular mechanisms involved in the differential efficacy of lenalidomide in DLBCL subtypes were investigated.
A panel of DLBCL cell lines, with 5 of ABC-subtype and 11 of non-ABC subtype, was collected and cell of origin subtype was confirmed based on literature, molecular and genetic analysis. The direct antiproliferative effect of lenalidomide on DLBCL cells was assessed using the 3H-thymidine incorporation assay and apoptosis analysis. The molecular mechanisms involved in the antiproliferative efficacy of lenalidomide in DLBCL subtypes were investigated by western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and qRT-PCR analysis of key signaling events during B-cell receptor (BCR)-dependent NF-κB activation. The critical roles of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), and cereblon (CRBN) in lenalidomide efficacy were established by knock-in or knock-down of these proteins in sensitive ABC cells. Finally, a mouse xenograft model was used to confirm the antitumor effect of lenalidomide and the relevance of the molecular mechanism involved.
Using DLBCL cell lines, lenalidomide treatment was found to preferentially suppress proliferation of ABC-DLBCL cells in vitro at a concentration range of 0.01–100 μM (the median plasma concentration at Cmax for patients receiving 25 mg lenalidomide is 2.2 μM) and delay tumor growth in a human tumor xenograft model of OCI-Ly10 cells (lenalidomide 3–30 mg/kg, p.o. qdX28), with minimal effect on non-ABC-DLBCL cells.
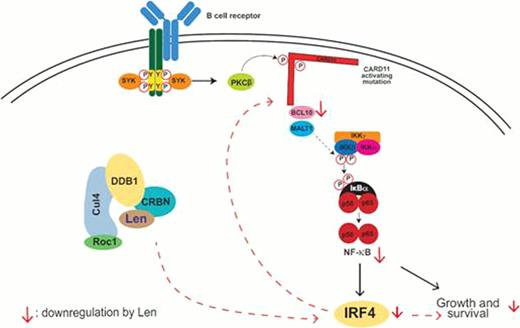
This tumoricidal effect of lenalidomide was associated with downregulation of IRF4, a survival factor in ABC-DLBCL cells. Treatment with lenalidomide for 1–3 days, similar to the inhibitors of PKCb and MALT1 (LY-333,531 and z-VRPR-fmk, respectively), was found to significantly (p<0.05) downregulate IRF4 protein levels in sensitive cell lines such as OCI-Ly10 and U2932. IRF4 inhibition by lenalidomide reduced CARD11-BCL-10-MALT1 complex activity of ABC-DLBCL cells (as measured by BCL-10 cleavage) and resulted in downregulation of B-cell receptor (BCR)-dependent NF-κB activity. An NF-κB-driven luciferase assay revealed that lenalidomide (1 μM) inhibited transcriptional activity of NF-κB up to 56% in the sensitive ABC-DLBCL cell lines OCI-Ly10 (p <0.05) and U2932 (p <0.01) after 2-day drug treatment. Lenalidomide also significantly (p <0.05) inhibited DNA binding by Rel A/p65, p50 and c-rel/p70 in 4 lines of ABC cells. While IRF4-specific siRNA mimicked the effects of lenalidomide reducing NF-κB activation, IRF4 overexpression conferred cell resistance to lenalidomide, indicating the crucial role of IRF4 inhibition in lenalidomide efficacy in ABC DLBCL.
Furthermore, knockdown of CRBN in OCI-Ly10 (p <0.05) and U2932 (p <0.01) conferred resistance to lenalidomide as demonstrated by the abrogation of the inhibitory effects of lenalidomide on IRF4 expression, BCL-10 cleavage, NF-κB activity, and proliferation of these cells, whereas the activity of inhibitors to PKC β and IKKα/β (LY-333,531 and CC-415501, respectively) remained unaffected. These data indicate that antitumor effects of lenalidomide on ABC-DLBCL cells require the presence of cereblon.
These data may provide a mechanism for the preferential efficacy of lenalidomide in ABC-DLBCL observed in clinical studies. These findings suggest that lenalidomide has direct antitumor activity against DLBCL cells, preferentially ABC-DLBCL cells, by blocking IRF4 expression and the BCR-NF-κB signaling pathway in a cereblon-dependent manner (also see Figure below).
Molecular mechanisms of differential efficacy of lenalidomide on subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Molecular mechanisms of differential efficacy of lenalidomide on subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Zhang:Celgene Corp: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kosek:Celgene Corp: Employment, Equity Ownership. Wang:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Heise:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Schafer:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Chopra:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.