Abstract

Cancer and its treatment are recognized risk factors for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) filters are utilized to provide mechanical thromboprophylaxis to prevent pulmonary embolism (PE) or to avoid bleeding from systemic anticoagulation in high risk patients.
This study was performed at a stand-alone, Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited comprehensive cancer center. Hospital database was searched for all patients discharged with IVC filter insertion. Additionally, the radiology database was queried for cancer patients undergoing IVC filter placement.
A total of 107 cancer patients; 59 (55.1%) males and 48 (44.9%) females who had their IVC filter inserted and followed up at our institution were included. The mean age (±SD) of the whole group was 50.8 (± 14.2) years. All patients had active cancer; the most common primary sites were gastrointestinal 32 (29.9%), brain 16 (15.0%) lung 13 (12.1%) and gynecological tumors 11 (10.3%). Majority of the patients had advanced-stage disease; out of 86 patients with identifiable TNM stage (Tumor, Node, Metastasis), 81 (94.2%) patients had locally-advanced stage III or metastatic stage IV disease, whereas only 5 (5.8%) had stages I or II disease.
During the 6 weeks prior to IVC filter placement, 74 (69.2%) patients were on active anticancer therapy with 45 (42.1%) were on chemotherapy and 7 (6.5%) were on radiotherapy. Nineteen (17.8%) of the patients had surgical intervention for their cancer while only 3 (2.8%) were on hormonal therapy. The remaining 33 (30.8%) patients were on hospice and palliative care service with 18 (16.8%) were already placed “DNR” (Don't Resuscitate). Prior to IVC filter insertion, a diagnosis of DVT was made on 76 (71.0%) patients while 14 (13.1%) had PE; the other 17 (15.9%) had both DVT and PE.
Contraindication to anticoagulation was the main indication for IVC filter placement reported in 85 (79.4%), while 18 (16.8%) had their filter inserted because of failure of anticoagulation (had DVT and/or PE while on therapeutic doses of anticoagulation). Other indications included large, free-floating iliocaval thrombus and poor compliance with anticoagulation.
Filters were placed utilizing the jugular approach in 86 (80.3%) while 18 (16.8%) had their filter placed through a femoral approach. Complications following IVC filter placement occurred in 14 (13.1%); majority were recurrent DVT in 10 (9.3%), PE in 3 (2.8%) and filter thrombosis in one patient.
Following IVC filter insertion, 42 (39.3%) were also anticoagulated; majority (86%) with LMWH (enoxaparin or tinzaparin). Twenty (47.6%) of these anticoagulated patients were considered, at the time of IVC filter insertion, as having a contraindication to anticoagulation.
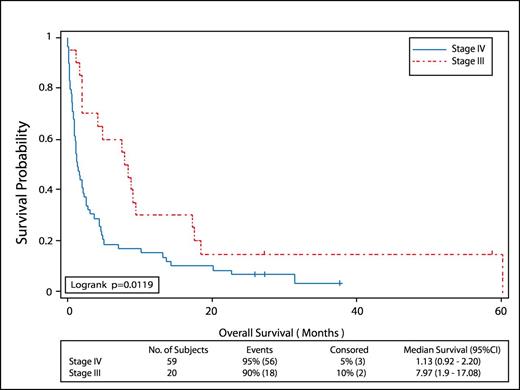
Survival data following IVC filter insertion was available for 100 patients. The median survival for the whole group was 2.39 months (range: 0.03-60.2). The median survival for patients with stage III and IV disease were 7.97 (1.90-17.08) and 1.31 months (0.92-2.20), respectively; p=0.0119; (Figure) Few patients had stage I and II disease (two had stage I while three others had stage II disease) and thus were excluded from survival analysis.
Among the 59 patients with stage IV disease for whom survival data was available, 23 (39.0%) survived less than a month, while 40 (67.8%) survived less than three months. Survivals of patients with stage III disease were better with only one out of 20 patients (5.0%) survived less than a month, while 14 (70.0%) survived more than three months.
Cancer patients with advanced-stage disease may gain little benefit from IVC filter insertion, so disease stage and life expectancy should be taken in consideration prior to filter placement.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract