Abstract

International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) is commonly used to distinguish various subgroups of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients with different prognosis and to make a therapeutic decision. However, the classic IPSS, defining lower-risk as low and intermediate-1 IPSS, seems to be insufficient to discriminate the prognostic groups of lower-risk MDS. Recently, IPSS was updated into the revised score (IPSS-R) to refine the IPSS by reassessing the major predictive features of MDS. The hypomethylating agents (HMA) are usually recommended for patients with lower-risk MDS who is not responsive to other therapies. However the role of HMA for the patients with lower-risk IPSS are still on debate. This study was conducted to find the rationale to treat HMA for the patients with lower-risk IPSS and to know whether IPSS-R further discriminate the prognosis of patients treated with HMA.
The data of 334 patients diagnosed with MDS lower-risk defined by IPSS after Jan 2006 were retrospectively reviewed. Lower-risk IPSS was revised into IPSS-R to know whether it could further discriminate the prognosis of this group of patients. The prognosis of lower-risk by IPSS and IPSS-R were analyzed in terms of overall survival (OS) and prognostic power was calculated with time-dependent Cox-hazard models. To define the role of HMA for patients with lower-risk IPSS, we categorized the lower risk patients into No-HMA group, early HMA group (HMA within 2 mo.), and late HMA group (HMA after 2 mo).
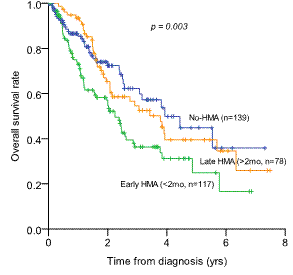
Out of 334 lower-risk patients (39 low and 295 intermediate-1), 195 patients (58.4%) were treated with HMA (azacitidine 163, decitabine 32). Median time to HMA treatment was 43 days (range 0-1778 days). 3yr-OS rate was not significantly different between HMA group (43.1¡¾4.2%) and non-HMA group (62.3¡¾5.9%) (p=0.099). Early HMA treatment (3yr-OS 36.4¡¾5.4%) didn't show survival benefits compared to late HMA group (54.6¡¾6.3%) or no-HMA group (62.3¡¾5.9%) (p=0.003). Plus, HMA response (CR/PR/HI) didn't guarantee OS benefits: 3yr-OS of 45.2¡¾7.4% in responders (CR/PR/HI, n=74) and 43.4¡¾5.0 in non-responders (SD/PD, n=121) (p=0.239).
Among 39 patients with IPSS low, 11 patients (28.2%) were revised into IPSS-R very low, 24 (61.5%) into low, 3 (7.7%) into intermediate, and 1 (2.6%) into high. Among 295 patients with IPSS intermediate-1, 4 patients (1.4%) were revised into IPSS-R very low, 84 (28.5%) into low, 133 (45.1%) into intermediate, 71 (24.1%) into high and 3 (1.0%) into very high. IPSS-R could further discriminate the IPSS lower-risk patients with regard to OS: 3yr-OS rates of 100% in very low, 64.5¡¾5.9% in low, 46.1¡¾5.5% in intermediate, 26.1¡¾6.6% in high, and 0% in very high (p<0.001).
The survival benefits of HMA for lower risk groups (very low and low) defined by IPSS-R (n=123) was not defined in the current study, where 3yr-OS was 83.8¡¾6.4% in no-HMA group (n=60) vs. 60.5¡¾7.1% in HMA group (n=63) (p=0.198).
The prognosis of the patients with lower-risk IPSS (low and intermediate-1) were successfully refined by IPSS-R. The IPSS intermediate-1 risk was heterogeneous group, which subdivided into very low to very high by IPSS-R. However, the beneficial effect of HMA for patients with lower-risk MDS, defined by IPSS (low and intermedite-1) and IPSS-R (very low and low), should be elucidated in the future studies.
Overall survival rate in patients with lower-risk IPSS (low and intermediate-1)
Overall survival rate in patients with lower-risk IPSS (low and intermediate-1)
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract