Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is a potentially curative option for patients with hematological malignancies. However, its success is limited by life-threatening graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). Strategies to control GvHD are often associated with suppression of the immune system leading to the impairment of the beneficial graft versus tumor (GvT) effect. The ideal approach to prevent and treat GvHD would limit alloantigen-specific reactivity while preserving immunity against malignant cells and pathogens. This study extends our previous findings on the beneficial effect of the inhibition of JAK signaling on acute GvHD (aGvHD) (Carniti et al, ASH2012), evaluating whether INCB18424 (Ruxolitinb) treatment preserved the GvT effect in a mouse model of aGvHD.
A major histocompatibility complex (MHC) mismatched HSCT mouse model was set up. Lethally irradiated BALB/c mice received spleen (SC) and bone marrow (BM) cells from donors C57BL/6 (B6) mice, and were treated with INCB18424 for 14 days at the dose of 90mg/kg/day (INC90), 45mg/kg/day (INC45) or 22.5mg/kg/day (INC22.5). Syngeneic transplants (B6-B6) and BALB/c recipients treated with B6 BM cells only were also used. To determine the GvT activity, allo-HSCT recipients were co-injected with either a B-cell lymphoma cell line (A20) or a myeloid leukemia cell line (RMB-1) and treated or not with INCB18424 at the dose of 45mg/kg/day. Mice were monitored for overall survival (OS) and weight loss. GvHD was histologically scored in tissues harvested on day 14, 30 and 60 and cytokine production by ELISA. Immune reconstitution and tumor cells were monitored by flow cytometry.
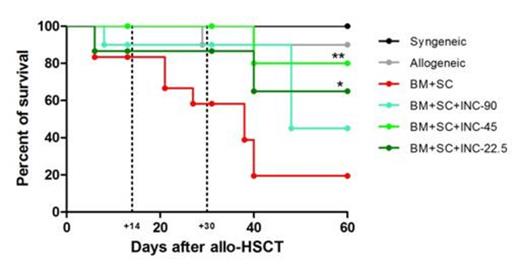
INCB18424 treatment caused significantly less GvHD when compared to untreated animals, as determined by survival (INC45, p<0.005; INC22.5 p<0.05; INC90 ns), weight loss, and histopathology of GvHD target organs (INC90 and INC45, p<0.0005; INC22.5 p<0.005) The INC90 cohort displayed a lower OS probably due to drug toxicity as indicated by centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy and vacuolar degeneration. Plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and Il-12) were significantly reduced in all treated animals when compared with controls. Daily administration of INCB18424 post allo-HSCT, did not alter hematologic parameters and did not impair immune reconstitution but shifted the CD4+ Treg to CD8+ effector cell ratio because of a relative decrease in the latter population and a relative increase in Treg in GvHD treated mice. A reduction in the Th17/Treg ratio was also observed. When allo-HSCT recipients were challenged with tumor cells, the GvT activity in INCB18424 treated mice was intact in the absence of GvHD, resulting in significantly improved survival compared to untreated animals (A20, p<0.0001; RMB1, p<0.001) and reduced presence of tumor cells.
The inhibition of Jak/STAT signaling using the sensitive and specific inhibitor of Jak1/Jak2, INCB18424 at the dose of 45mg/kg/day, conferred effective protection from lethal acute GvHD in a MHC mismatched HSCT mouse mode. Mice retain the ability to mount aggressive graft-versus-tumor (GvT) effects and to generate complete donor T-cell reconstitution. Taken together, these data suggest that INCB018424, recently approved for the treatment of Myelofibrosis, might also be tested for GVHD prophylaxis and treatment in clinical trials.
INCB18424 administration prevents aGvHD while preserving a robust GvT activity. A) Effect of INCB18424 on survival. Irradiated BALB/c mice received BM+SC cells from donors C57BL/6 (B6) and were treated or not with INCB18424 for 14 days at the three different doses of (INC90, INC45,INC22.5). Mice receiving B6 BM cells only (allogeneic) and syngeneic transplants were included. Data represent the pool of 2 independent experiments. N=15 each group, N=10 in control groups. B) GvHD score. Tissue sections of skin, liver, and intestine were graded by a veterinary pathologist on day 14 after allo-HSCT. C) Effect of INCB18424 on the survival of allo-HSCT recipients challenged with tumor cells. Allo-HSCT recipients were co-injected A20 (BM+SC+A20) or a RMBI (BM+SC+RMB-1) cells and treated or not with INCB18424 45mg/kg/day (BM+SC+A20+INC45; BM+SC+RMB1+INC45). Control mice did not receive SC (BM-A20; BM-RMB1). Data represent the pool of 2 independent experiments. N=10 each group.
INCB18424 administration prevents aGvHD while preserving a robust GvT activity. A) Effect of INCB18424 on survival. Irradiated BALB/c mice received BM+SC cells from donors C57BL/6 (B6) and were treated or not with INCB18424 for 14 days at the three different doses of (INC90, INC45,INC22.5). Mice receiving B6 BM cells only (allogeneic) and syngeneic transplants were included. Data represent the pool of 2 independent experiments. N=15 each group, N=10 in control groups. B) GvHD score. Tissue sections of skin, liver, and intestine were graded by a veterinary pathologist on day 14 after allo-HSCT. C) Effect of INCB18424 on the survival of allo-HSCT recipients challenged with tumor cells. Allo-HSCT recipients were co-injected A20 (BM+SC+A20) or a RMBI (BM+SC+RMB-1) cells and treated or not with INCB18424 45mg/kg/day (BM+SC+A20+INC45; BM+SC+RMB1+INC45). Control mice did not receive SC (BM-A20; BM-RMB1). Data represent the pool of 2 independent experiments. N=10 each group.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.