Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) of the liver occurs after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) as a result of the toxic damage on sinusoidal and hepatic cells caused by the conditioning regimen. Diagnosis of VOD is usually based on clinical criteria. Intensity of preparative regimen, pre-existing liver disease, busulfan (Bu) as part of the conditioning, etc. have been proposed as significant risk factors with myeloablative conditioning (MAC). In the present study, we examined the incidence and the risk factors for VOD after allogeneic-HSCT using a reduced intensity conditioning regimen (RIC).
From April 1996 until November 2012, 271 consecutive patients with various hematological malignancies underwent allo-HSCT in our department with the same RIC regimen. The RIC regimen consisted of fludarabine 30 mg/m2/day x 6, oral Bu 4 mg/kg/day or i.v. Bu 3.2 mg/kg/day x 2, and ATG. Oral Bu was given to 138 patients, while 133 patients were treated with the intravenous formulation.
Diagnosis of VOD was confirmed using the Seattle criteria. Clinical characteristics of patients are shown in Table 1.
Patient's characteristics
| . | Patients without VOD . | Patients with VOD . | Statistics . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | No=247 patients | No=24 patients | |
| Age, median (range) | 44 years (15-71) | 40 years (16-66) | p=n.s |
| Sex, male/female | 162/85 | 15/9 | p=n.s |
| Years of transplant | |||
| Before 1/2004 | 161 | 18 | |
| After 1/2004 | 86 | 6 | p=n.s |
| Disease | AML (77 patients) | AML (8 patients) | p=n.s |
| ALL (22 patients) | ALL (3 patients) | ||
| MDS (22 patients) | MDS (6 patients) | ||
| CML (34 patients) | CML (1 patient) | ||
| PIM (4 patients) | PIM (1 patient) | ||
| NHL (60 patients) | NHL (3 patients) | ||
| CLL (4 patients) | CLL (1 patient) | ||
| HD (10 patients) | HD (0 patients) | ||
| MM (15 patients) | MM (0 patients) | ||
| Disease risk pre-transplant Standard/high | 113/134 | 10/14 | p=n.s |
| Previous Auto-SCT | 39/271 | 3/24 | p=n.s |
| Donor | Matched-sibling=155 | Matched-sibling=18 | p=n.s |
| Mismatched-related=7 | Mismatched-related=1 | ||
| Matched-unrelated=76 | Matched-unrelated=3 | ||
| Mismatched-unrelated=9 | Mismatched-unrelated=2 | ||
| Busulfan per-os/intravenous | 121/126 | 17/7 | p=0.053 |
| Pre-existing liver disease | 4/247 | 0/24 | p=n.s |
| . | Patients without VOD . | Patients with VOD . | Statistics . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | No=247 patients | No=24 patients | |
| Age, median (range) | 44 years (15-71) | 40 years (16-66) | p=n.s |
| Sex, male/female | 162/85 | 15/9 | p=n.s |
| Years of transplant | |||
| Before 1/2004 | 161 | 18 | |
| After 1/2004 | 86 | 6 | p=n.s |
| Disease | AML (77 patients) | AML (8 patients) | p=n.s |
| ALL (22 patients) | ALL (3 patients) | ||
| MDS (22 patients) | MDS (6 patients) | ||
| CML (34 patients) | CML (1 patient) | ||
| PIM (4 patients) | PIM (1 patient) | ||
| NHL (60 patients) | NHL (3 patients) | ||
| CLL (4 patients) | CLL (1 patient) | ||
| HD (10 patients) | HD (0 patients) | ||
| MM (15 patients) | MM (0 patients) | ||
| Disease risk pre-transplant Standard/high | 113/134 | 10/14 | p=n.s |
| Previous Auto-SCT | 39/271 | 3/24 | p=n.s |
| Donor | Matched-sibling=155 | Matched-sibling=18 | p=n.s |
| Mismatched-related=7 | Mismatched-related=1 | ||
| Matched-unrelated=76 | Matched-unrelated=3 | ||
| Mismatched-unrelated=9 | Mismatched-unrelated=2 | ||
| Busulfan per-os/intravenous | 121/126 | 17/7 | p=0.053 |
| Pre-existing liver disease | 4/247 | 0/24 | p=n.s |
Cumulative incidence was calculated using a competitive risk model. In multivariate analysis the following variables were entered: age, sex, disease risk status, year of transplant, donor status, previous myeloablative conditioning, pre-existing liver disease, and route of Bu administration.
Incidence of VOD and outcome: VOD was developed in 24 out of 271 patients. The cumulative incidence of VOD in the whole cohort of patients was 8.5% (95% CI, 5.8 - 12.6%). VOD onset occurred in a median of 3 days post graft infusion (range, 0 -24 days). Moderate and severe VOD was observed in 20 and 4 patients respectively.
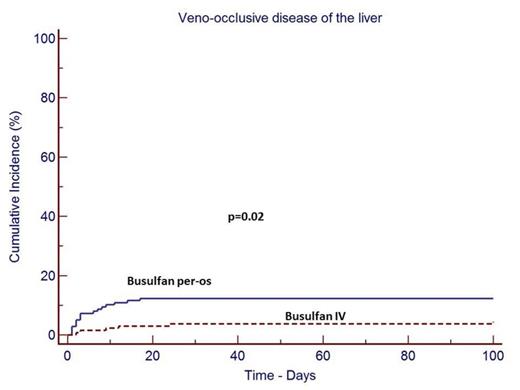
Risk factors for VOD: Using a univariate and multivariate analysis the only variable associated with VOD incidence was the route of Bu administration. The cumulative incidence of VOD was 11.7% (95% CI, 7.3 - 18.5%), and 5.3% (95% CI, 2.5 - 10.8%) in the groups of patients who received Bu per-os and intravenously respectively (p=0.02). (Figure 1). Severe VOD was observed in only 4 patients and none of the variables tested in multivariate analysis was significantly associated with the incidence of severe VOD.
Outcome of patients with VOD: VOD resolved in most of the patients (20/24) in a median of 21 days (range, 8-82 days). The cumulative incidence of VOD resolution was 83%. All 4 patients with severe VOD died before day 100 and before VOD resolution. The overall cumulative incidence of VOD-related mortality was 1.8%. In multivariate analysis, none of the variables tested was significantly associated with VOD-related mortality.
As compared with the reported incidence of VOD with MAC, RIC with low dose Bu is associated with reduced incidence of VOD, VOD severity and mortality. In our study, we observed that Bu administered intravenously was associated with significantly reduced incidence of VOD in comparison with Bu administered per-os.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.