Abstract
Follicular lymphoma (FL), the most frequent form of indolent NHL (iNHL), accounts for 20% to 30% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL). Median survival is 8–15 years (yrs) for patients (pts) with advanced disease. Approximately 2/3 of pts relapse or become refractory to 1st line treatment. Progression-free survival (PFS) for pts with RRFL is usually less than 2 yrs. This SLR examined current literature on RRFL, comparing the efficacy of treatments by meta-analysis where possible.
PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase were systematically searched for studies on the efficacy and safety of treatments for RRFL published from 1997 to August 2, 2012. In addition, conference abstracts, reference lists of included articles, recent reviews, and the Clinicaltrials.gov database were searched for otherwise unpublished comparative studies. Main efficacy outcomes were objective response rate (ORR), complete response, partial response, duration of response, PFS, and overall survival (OS). Safety endpoints were grade 3/4 toxicities and treatment withdrawals for toxicity. Studies were selected if they reported on RRFL after ≥ 1 standard treatment in pts ineligible for stem cell transplant and if they were specific to or reported FL outcomes separately. We used the Bucher method for conducting adjusted indirect comparisons.
3,308 publications of potential interest were identified; 280 provided relevant data for iNHL; 29 reported on 23 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in iNHL; 10 were specific to FL and 5 included FL findings in a mixed histology population. OS and PFS were infrequently reported. Criteria for relapsed or refractory disease were often not defined, with only 8 studies providing varying definitions. The most commonly evaluated therapy in patients with FL was rituximab (R) either alone or with bortezomib (B) or lenalidomide (L). ORR, reported in 5 studies, ranged from 49% to 93%. Median PFS in 5 studies ranged from 10 to 25 months but was >50 months for R-CHOP followed by R maintenance. Median OS was not reported, but OS at 1-, 2-, or 3-yrs was reported in several studies. Efficacy results are shown in Table 1.
Grade 3/4 toxicities included hematological events (anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia) in 8%-77% of pts. Frequent non-hematological events (≥ 5% pts) included fatigue, diarrhea, and infection.
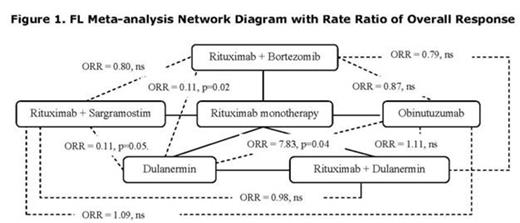
Overlapping treatments were identified in 4 FL trials in which R was identified as a common comparator allowing indirect comparisons via meta-analysis. The ratios of ORR for R + B, R + S, and O were all clinically and significantly higher than for D (Figure 1). No other comparisons were significantly different.
This SLR found that while rituximab contributes substantially to the efficacy of treatment in pts with RRFL, a need for more effective treatments remains. The relatively small number of RCTs, few overlapping treatment arms, and variability in endpoints studied make it difficult to formally compare available therapies or treatments under developments for RRFL. Significant variability in RCT features (infrequent reporting of OS/PFS, limited information on prior treatments/responses or definition of relapse/refractory) are further challenges to meaningful comparisons. Additional well designed RCTs are needed to fully understand the impact of more recently developed therapies.
This research was supported by funding from Sanofi.
Police:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Trask:Sanofi: Employment. Colosia:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Olivares:Sanofi: Employment. Khan:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Abbe:Sanofi: Employment. Njue:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Wang:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Kaye:RTI Health Solutions: Employment. Ruiz-Soto:Sanofi: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.