Abstract
Cardiac complications are the main cause of death in thalassemia major (TM) patients. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) plays a key role in their management, assessing myocardial iron overload (MIO), biventricular function, atrial dimensions, and myocardial fibrosis. We evaluated the predictive value of CMR parameters for cardiac complications, including heart failure (HF), arrhythmias and pulmonary hypertension (PH).
We followed prospectively 537 white TM patients enrolled in the MIOT network. Fifty patients were excluded from the analysis because a cardiac complication was present at the time of the first CMR. All prognostic variables associated with the outcome at the univariate Cox model were placed in the multivariate model and were ruled out if they did not significantly improve the adjustment.
At baseline the mean age was 29.5±9.0 years and 222 patients were males. The mean follow-up time was 58±18 months. After the first CMR only the 37.8% of the patients did not change the chelation regimen or the frequency/dosage.
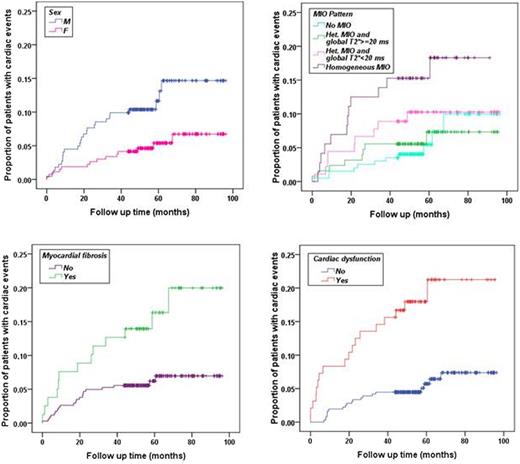
We detected few cardiac events thanks to a MR-guided, patient-specific adjustment of the chelation therapy. Severe and homogeneous MIO, myocardial fibrosis and ventricular dysfunction identify patients at high risk of heart failure. Heart T2* doesn’t have any power in predicting arrhythmias while male sex and atrial dilation are independent prognosticators. Male sex, severe and homogeneous MIO, myocardial fibrosis and ventricular dysfunction identify patients at high risk of cardiac complications globally considered.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.