Abstract
Introduction
Early bone marrow (BM) evaluation (during aplasia or at “day 14” (D14)) in patients with AML undergoing conventional induction therapy has been adopted from clinical practice in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). While it has been shown that early persistence of AML correlates with decreased complete remission (CR) rates and overall survival (OS), unlike in ALL, there are no data to indicate that early initiation of re-induction therapy based on these findings will positively influence outcome. In fact, early re-induction, especially in older patients, may increase morbidity and mortality from prolonged cytopenias, infectious complications, and longer hospital stays. Moreover, it can be challenging to determine the nature of scattered blasts identified in a hypocellular BM at D14, as they may represent normal recovering marrow elements or malignant blasts. Even if malignant, the chemosensitivityof these cells will only be fully determined by later assessment of the BM at the time of expected count recovery (“day 28”). For these reasons, early re-induction therapy may not be advisable. In this retrospective study, we sought to evaluate the validity of D14 BM assessments as post-therapy prognostication to guide treatment decisions in AML.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective institutional study (2006-2014) of AML patients undergoing routine induction chemotherapy where diagnostic, interim (around D14) and recovery (D21-42) BM evaluations were available for review. Clinical information and pathology data were retrieved from our institutional database. Responses at D14 were categorized morphologically into three categories: optimal response (OR, blasts ≤5%), indeterminate response (IR, blasts 6-19%), and residual leukemia (RL, blasts ≥20% or a relative decrease in blast count from baseline of <20%). Published response criteria were used to define responses at marrow recovery. Suboptimal response (SOR) at D14 was defined as either IR or RL during the assessment period. Mann-Whitney's U test was used to compare non-normally distributed variables. The Fisher's exact test was employed to assess for associations between response to treatment at D14 and likelihood of recovering in CR. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of a D14 BM to predict CR were calculated for patients that were observed without re-induction.
Results
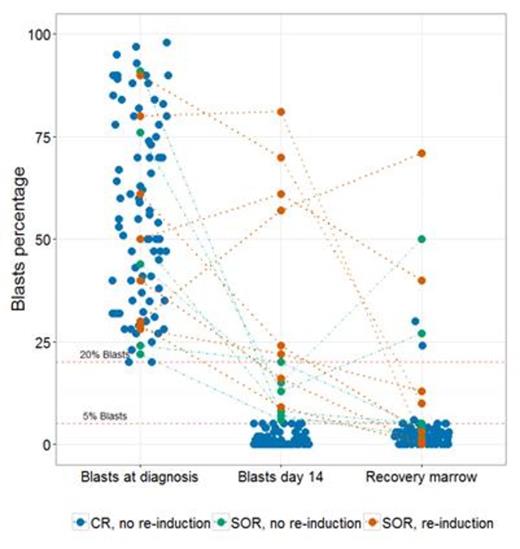
Evaluable patients (n=98) had a mean age of 51 years (20-73), and 45% were male. The median BM blast percentages at diagnosis, D14 and recovery were respectively 54.5%, 0% and 2.5% (Figure 1). There was a significantly greater absolute decrease in blast percentage from diagnosis to D14 in patients who recovered in CR compared to those who did not achieve CR (median: 53.5% vs 23.0%, P = 0.001). In patients that got early re-induction therapy for SOR at D14, the relative differential in baseline and D14 BM blasts was significantly lower compared to patients with D14 SOR who did not get re-induction therapy (median: 21.8% vs 77.8%, P=0.004) Ninety patients did not receive early re-induction therapy. Of these, 86 (95.6%) achieved CR and 4 patients (4.4%) recovered counts with residual leukemia. Fourteen (14.3%) patients were classified as SOR at D14. Of these, 6 (6.7%) did not receive re-induction therapy and 4 of these 6 patients (67%) achieved a CR. Eight patients received early re-induction therapy based on SOR at D14 (IR = 2, RL = 6); of these, 4 patients (50%) achieved CR at count recovery. Achieving an OR at D14 was predictive of achieving CR at recovery (sensitivity = 95.3%, PPV = 97.6%). However, not achieving an OR at D14 had low specificity (50%) and NPV (33.3%) for achieving CR (P = 0.021).
Conclusions
Our results indicate that a SOR at the D14 BM evaluation does not uniformly identify patients with primary induction failure (low NPV) and should not be used to dictate the timing of re-induction therapy. We confirmed the PPV of achieving an OR at D14 as previously reported, but we argue that no additional prognostic data is provided by an OR at D14, beyond what can already be predicted by pre-treatment variables (e.g., age and chromosomal abnormalities). We suggest that the D14 BM should be omitted from the routine evaluation of AML patients during induction therapy outside the context of a clinical trial.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.