Abstract
Background: Refining risk stratification of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) using molecular profiling, especially those with intermediate cytogentic risk, is becoming standard of care. However, current WHO and ELN classifications are focused on few markers, mainly FLT3, NPM1, and CEBPA. While these abnormalities are relatively common, not all patients with AML and intermediate or normal cytogenetics will have abnormalities in these genes leaving large percentage of patients without refined risk stratification. We demonstrate that using 8 different AML-related genes are adequate to provide one or more molecular markers to further risk stratify patients with de novo AML.
Method: Using direct sequencing we analyzed 211 samples referred from community practice with the diagnosis AML for molecular analysis. All samples were evaluated prospectively for mutations in FLT3, NPM1, IDH1, IDH2, CEBPA, WT1, RUNX1, and TP53 using direct sequencing. Fragment length analysis was used in addition to sequencing for FLT3 and NPM1. Available morphology, cytogenetics, and clinical data along with history were reviewed.
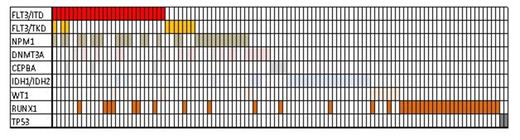
Results: Of the 211 samples tested 103 (49%) had at least one or more molecular abnormality adequate for refining the risk classification. The mutations detected in these 103 patients were as follows: 27 (26%) FLT-ITD, 10 (10%) FLT3-TKD, 30 (29%) NPM1, 7 (7%) CEBPA, 14 (14%) IDH1, 13 (13%) IDH2, 10 (10%) WT1, 38 (37%) RUNX1, and 2 (2%) TP53. There was significant overlap and most patients had more than one mutation as illustrated in the graph below. However, if the testing was restricted to FLT3, NPM1, CEBPA and DNMT3A, only 56 (54%) would have had refined risk classification and 46% of patients would have remained without subclassification. The most striking finding was that all the remaining patients, who had no molecular abnormality detected in any of these 8 genes, had either history of MDS evolved to AML, therapy-related AML, or cytogenetic abnormalities other than intermediate (multiplex cytogenetic abnormalities or core-binding factor abnormality).
Conclusion: Using FLT3, NPM1, CEBPA, and DNMT3A is inadequate for the molecular characterization of patients with AML. Patients with de novo AML and intermediate risk cytogenetics can be adequately prognostically subclassified and molecularly studied by testing only 8 genes. More importantly, this data confirms that the molecular biology driving de novo AML is significantly different from that driving MDS, AML with myelodysplasia-related changes, therapy-related AML, or AML with core binding factor or multiplex cytogenetics. Unlike de novo AML, these entities should be molecularly studied using MDS-specific driver genes. Furthermore, this data suggests that different therapeutic approaches should be developed for MDS and MDS-related AML.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.