Abstract
Aim
To identify the causes and consequences of omission and/or reduction of methotrexate (MTX) doses in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis used during allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT).
Method
We conducted a retrospective medical record review of 125 alloHCTs performed between the years 2011 and 2013 at our hospital where MTX (15, 10, 10, 10 mg/m2 intravenously on day [D] +1, D+3, D+6, D+11 respectively) is used with cyclosporine as GVHD prophylaxis. The association of MTX dose omission with overall survival (OS), non-relapse mortality (NRM) and acute GVHD, measured from a landmark of D+12, was evaluated with univariate and multivariate analysis.
Results
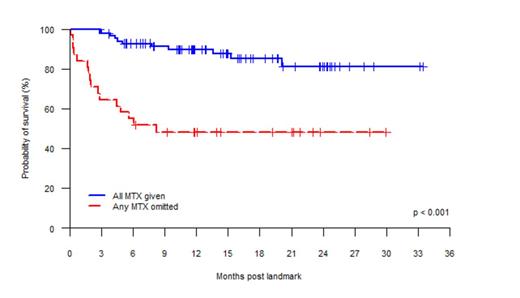
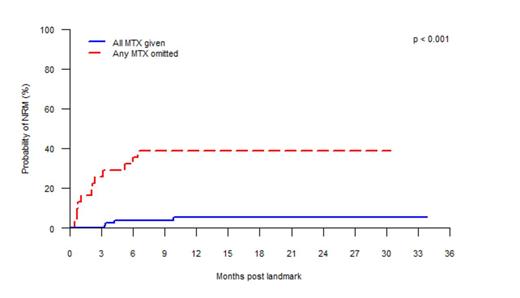
116 patients (median age 48, range 17-67, 59% male) were eligible for analysis. Commonest indications for alloHCT were acute leukemia (47%) and chronic lymphoproliferative disorders (28%). Conditioning was myeloablative in 54%, donors were siblings in 53%, and grafts were peripheral blood in 87%. 85 patients (73%) received all four full doses of MTX. 22 patients had a dose omission at D+11, and two at both D+6 and D+11. 43 patients were given folinic acid rescue. Documented reasons for MTX alteration were mucositis (n = 22; World Health Organisation mucositis grade 4 in 16 patients, grade 3 in 4 patients and grade 2 in 2 patients), fluid overload (n = 10), liver impairment (n = 8, median bilirubin 83 micromol/L, range 19-204 micromol/L, normal < 21 micromol/L), renal impairment (n = 8, median creatinine 138 micromol/L, range 67-276 micromol/L, normal 45-90 micromol/L) and sepsis (1). MTX omission was associated with poorer OS (48% vs 90%; hazard ratio [HR] for mortality 5.4, 95% CI 2.5-11.7, P < 0.001, Figure 1) and higher NRM (39% vs 5%, HR 10.2, 95% CI 3.4-30.8, P < 0.001, Figure 2) at 12 months post landmark. A pattern of ongoing NRM was observed beyond day 100. Strikingly, those patients who received all four full doses of MTX had NRM of 0% at 100 days post landmark. There was no difference in rates of grade 2-4 (24% vs 22%, P = .950) or grade 3-4 (9% vs 11%, P = .662) acute GVHD, or relapse (20% vs 17%, P = .514), at day 100 post landmark.
Conclusion
MTX dose reduction has no significant impact on GVHD development, suggesting that MTX omissions or other adjustments of GVHD prophylaxis did not lead to enhanced T cell activation. However, it seems that the need to reduce MTX indicates an increased risk of NRM, likely reflecting ongoing organ dysfunction. Older patients or those with pre-transplant co-morbidities may be better served by strategies that lower the likelihood of organ toxicity, including reduced intensity conditioning and lower initial doses of MTX.
Overall survival according to whether or not any methotrexate (MTX) was omitted.
Overall survival according to whether or not any methotrexate (MTX) was omitted.
Non-relapse mortality according to whether or not any methotrexate (MTX) was omitted.
Non-relapse mortality according to whether or not any methotrexate (MTX) was omitted.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract