Abstract
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation is the therapeutic option for a variety of malignant and non-malignant haematological diseases. Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) is a common post transplant complication. In 40% of these patients, GvHD is steroid refractory and associated with a mortality of around 60%. Basiliximab is a chimeric murine –human antibody also selective for interleukin -2 receptor (IL-2R) with a half life of 7 days. It is routinely used as part of the induction therapy in renal transplant recipients to prevent acute rejection following successful phase III studies. Phase 2 studies have demonstrated its superior efficacy in treating patients with steroid refractory GvHD (1). We administered Basiliximab in 14 patients with steroid refractory GvHD with a median age of 41 (range 20-69). M: F 7:7. All patients but one 13/14 received PBSC from unrelated donors and 6/13 had mismatched unrelated donors. Overall response was in the order of 12/14 (85%). One patient could not be assessed. 7/14 (50%) achieved a complete response to treatment. We aimed to study the in vivo T- and B-cell changes following Basiliximab administration as this would be an ideal platform to monitor the alterations in the regulatory T and B-cell compartment.
PBMCs were obtained from all donors after informed consent, Immucan (Nr 11-116) approved by our local ethics committee, prior to and after weekly administration of Basiliximab 40mg for 4 weeks. Control samples were obtained from patients with steroid responsive acute GvHD.
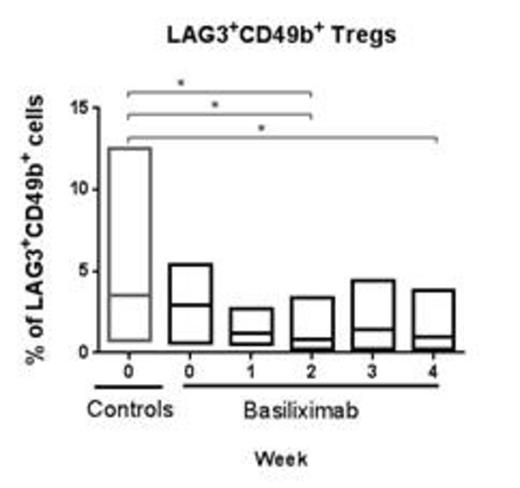
The total number of CD3+ as well as CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells remained constant during treatment and no change was observed on comparison with the controls. Gagliani et al (2) demonstrated that regulatory type 1 T-cells can be identified by the co-expression of CD49b and Lag3. No difference was observed between the % CD49d+, Lag3+ T-cells in the control cohort and the treatment cohort prior to therapy, ie day 0. The % CD49d+, Lag3+ T-cells decreased during the treatment period (statistically significant) in comparison to the control cohort. Despite the use of the CD25-antibody, a small population of CD25+, CD127+ cells could be detected and this population correlated to the % CD49d+, Lag3+ T-cells.
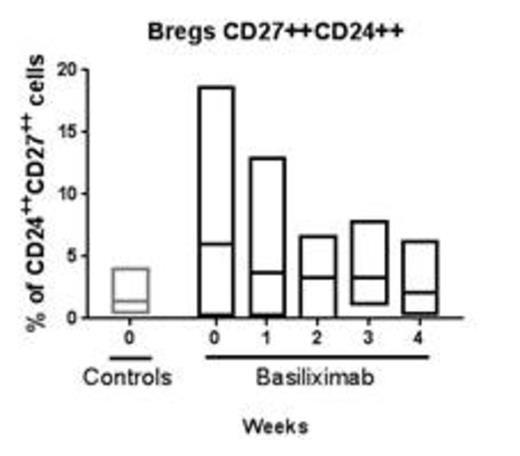
The % CD19+, CD20+ B-cells were similar prior to treatment in the treatment group and control. Following the first administration a rise was observed followed by a decline over the next 3 weeks. No changes were seen in the activated (CD20+, CD86+) and anergic B-cell subsets (CD20+, CD21-) during the observation period. The % of CD24high, CD27+ regulatory B-cells were found to be twice that seen in the controls. With treatment a decrease was seen in this population. The CD24high, CD38high transitional B-cells were also found to be higher than that seen in the controls. No change was observed in this subset with treatment.
This is the first attempt to study the in-vivo changes induced by a CD25 antibody in patients with steroid refractory GvHD. We conclude that this antibody not only depletes the alloreactive CD25+ T and B-cell population but also alters the regulatory T and B-cell subsets in comparison to patients with steroid responsive GvHD. Our clinical data supports the efficacy of this drug in patients with steroid refractory GvHD. Contrary to the current knowledge that regulatory T-cells are required for GvHD suppression our data suggests that Basiliximab facilitates regulatory T-cell depletion. The reduction of the regulatory T-cell subset observed in patients responding to anti CD25 treatment suggests a complex regulation and potential dichotomous role of these cells in acute GvHD.
Schmidt-Hieber M, Fietz T, Knauf W, Uharek L, Hopfenmuller W, Thiel E, et al. Efficacy of the interleukin-2 receptor antagonist basiliximab in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2005 Aug;130(4):568-74.
Gagliani N, Magnani CF, Huber S, Gianolini ME, Pala M, Licona-Limon P, et al.Coexpression of CD49b and LAG-3 identifies human and mouse T regulatory type 1 cells. Nat Med. 2013 Jun;19(6):739-46
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.