Abstract
Background. Patients with multiple myeloma are at risk of thromboembolism. However, studies investigating the relationship between multiple myeloma and ischemic stroke are limited. Therefore, we conducted a nationwide population-based study to investigate the risk of stroke among patients with multiple myeloma and the association between myeloma-related therapy and development of stroke.
Material and methods. We recruited patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma aged 20 years or older without antecedent cerebrovascular events from Taiwan's National Health Insurance database between January 1, 2004 and December 31, 2011. Hazard ratios (HRs) of stroke risk for patients with multiple myeloma compared with an age-, sex-, and comorbidity-matched cohort were calculated by Cox proportional regression analysis. Additionally, therapeutic agents were put into Cox models as time-dependent covariates to avoid immortal time bias.
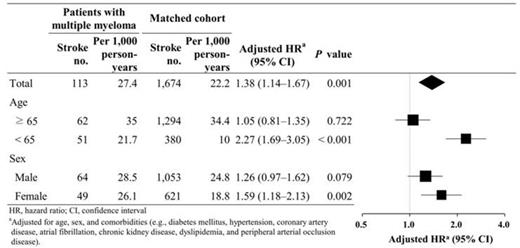
Results. This study consisted of 2,296 patients with multiple myeloma and 22,960 matched individuals, with a median age of 65 years (interquartile range 55-73). One hundred thirteen cerebrovascular events developed among 2,296 patients with multiple myeloma, with a follow-up of 4,119.2 person-years. The stroke incidence was 1.23 times higher in the multiple myeloma cohort than in the matched cohort (27.4 vs. 22.2 per 1,000 person-years), with an age-, sex-, and comorbidity-adjusted HR of 1.38 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.14-1.67; P < 0.001). The multivariable Cox proportional hazard models showed bortezomib treatment as an independent risk factor determining the subsequent stroke in patients with multiple myeloma (adjusted HR 2.01; 95% CI 1.22-3.28; P = 0.006). This effect was not seen with steroids, thalidomide, or other chemotherapy agents.
Conclusion. Our study reveals an increased risk of stroke among patients with multiple myeloma compared with the matched cohort. Bortezomib treatment is associated with a higher risk of stroke in patients with multiple myeloma.
Incidence of stroke occurrence in patients with multiple myeloma and the matched cohort
Incidence of stroke occurrence in patients with multiple myeloma and the matched cohort
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.