Abstract
Introduction: Data on clinical response and predictors of response outside clinical trials are limited. Previous SIMPLICITY data include cytogenic response (CyR) and molecular response (MR) monitoringpatterns in patients (pts) with CP-CML differing from NCCN/ELN guideline recommendations, as well as the clinical predictors of these patterns.
Methods: SIMPLICITY (NCT01244750) is an ongoing observational study of CP-CML pts in routine clinical practice receiving first-line (1L) imatinib (IM), dasatinib (DAS) or nilotinib (NIL) in the US and Europe (Eu). Clinical response following start of 1L tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy was assessed by CyR (karyotype or FISH) and MR (PCR on the international scale). Descriptive statistics are presented and p values were calculated using a chi-square test. A proportional odds model was used to reveal factors associated with a better category of clinical response among those evaluated for ‘optimal’, ‘warning’ or ‘failure’ response, as defined by ELN 2013 guidelines.
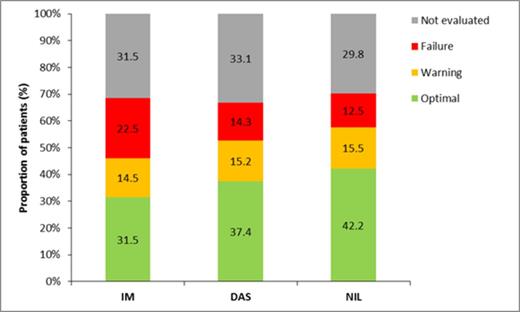
Results: 1083 pts (US: 66%; Eu: 33%) were enrolled prospectively through 1Apr2014, receiving IM (n=415), DAS (n=343) or NIL (n=325). Pts were older (median age [interquartile range] for SIMPLICITY population overall, 57 [46, 67] years) than those enrolled in pivotal Phase 3 studies (IRIS, ENEST, DASISION). Other pt characteristics, including comorbidities, were similar across cohorts, except IM pts were slightly older. 1050, 985 and 862 pts were followed for up to 3, 6 and 12 months (mths), respectively.Limited response data for patients followed for up to 3 mths hinder analysis (13% tested for CyR, 19% tested for MR, and 26% tested for CyR or MR). 31% and 45% of pts were tested for CyR, and 56% and 72% of tested pts achieved complete CyR (CCyR), in the first 6 and 12 mths from the start of 1L TKI. The proportion of pts achieving CCyR differed according to 1L TKI: of those tested by 6 mths, 50%, 58% and 65% of pts on 1L IM, DAS and NIL achieved CCyR; this proportion increased by 12 mths (IM: 63%, DAS: 79%, NIL: 81%). These percentages were considerably lower when calculated using the set of patients followed through the period, but not necessarily tested within the period. Mean (±SD) time from start of 1L TKI to best response was 3.5 (± 1.4) and 5.4 (± 2.8) mths for the 0–6 mths and 0–12 mths cohorts, respectively. In each timeframe, there was no meaningful difference in mean time to best response between TKI cohorts. By 6 and 12 mths from start of 1L TKI, 46% and 64% of pts were tested for MR; of these, 34% and 57% achieved major MR (MMR) and 12% and 27% achieved MR4.5 by 6 and 12 mths. By 6 mths, MMR was achieved by 28%, 31% and 46% for IM, DAS and NIL cohorts, and 6%, 14% and 18% achieved MR4.5. By 12 mths from start of 1L TKI, 51%, 59% and 65% of IM, DAS and NIL cohorts achieved MMR, and 20%, 33% and 30% achieved MR4.5. Mean (± SD) time from start of 1L TKI to best MR was 4.0 (± 1.3) and 7.3 (± 3.0) mths for the 0–6 mths and 0–12 mth cohorts. In each timeframe, there was no meaningful difference in mean time to best response between TKI cohorts. The proportion of pts with ‘optimal’, ‘warning’ and ‘failure’ responses, according to 2013 ELN guidelines, varied over time and by 1L TKI (see figure). In the first 12 months of 1L TKI, ‘optimal’ response was achieved by more DAS- and NIL-treated pts compared with IM-treated pts (IM: 46%, DAS: 56%, NIL: 60%). The proportion of pts with a ‘warning’ response by 12 months was equivalent between TKI cohorts (IM: 21%, DAS: 23%, NIL: 22%). However, more pts receiving 1L IM experienced ‘failure’ compared with those receiving DAS and NIL (IM: 33%, DAS: 21%, NIL: 18%). Of candidate predictors, gender and use of NIL or DAS as 1L TKI were associated with a better category of clinical response (‘optimal’, ‘warning’ or ‘failure’) by 12 mths; women (odds ratio [OR]=1.77) and pts on DAS and NIL had a better category of clinical response by 12 mths compared with IM (OR=2.03). In sensitivity analyses, both DAS and NIL were associated with a better category of clinical response than IM (OR=1.85 and OR=2.17 for DAS and NIL, respectively, compared with IM).
Conclusion: In SIMPLICITY, the proportions of CCyR and MR increased over time. Compared with DAS- and NIL-treated pts, a lower proportion of IM-treated pts achieved CCyR and MR (MR4/5 and MMR), and a higher proportion experienced ELN 2013-defined ‘failure’ by 12 mths. Factors associated with a better category of clinical response included female gender second-generation TKI as 1L therapy.
Mauro:Ariad: Consultancy; Novartis Oncology: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy. Gambacorti-Passerini:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding. Goldberg:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis Oncology : Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Cortes:Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Teva: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Khoury:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria; Teva: Honoraria. Michallet:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding. Paquette:Ariad : Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy. Simonsson:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding. Turner:ICON Clinical Research: Employment. Mohamed:BMS: Employment. Subar:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Zyczynski:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.