Abstract
Background: Renal impairment is a common feature of multiple myeloma (MM) seen in over a quarter of newly diagnosed patients (pts). Studies have confirmed the presence of renal impairment (RI) as a strong predictor of inferior survival in MM. Some studies have also indicated that reversibility of RI is associated with improved survival. However, it is not clear if normalization of renal function improves the outcome to that expected for MM pts without RI at diagnosis.
Methods: We evaluated 1,135 consecutive pts with newly diagnosed MM seen at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester between December 2002 and January 2011. Renal function was assessed by the estimated creatinine clearance (CrCl) which was calculated by the modified MDRD formula. We examined these pts for improvement in renal function based on their CrCl at diagnosis and their highest CrCl during their disease course. RI was defined as having a CrCl of < 60. Pts were categorized based on their renal function at diagnosis and response to therapy: Group 1- CrCl >60 at diagnosis, Group 2- CrCl <60 at diagnosis but improved to >60 after therapy and Group 3- CrCl <60 at diagnosis and remained <60 after therapy. The degree of restoration of renal function was evaluated according to the IMWG criteria. Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method and differences assessed using the log rank test.
Results: The median age at diagnosis was 65 years (range; 22 - 93) and 682 (60%) were male. The median follow up for the entire group from diagnosis was 73 mos (95% CI; 69 - 77). At diagnosis, 123 (11%) pts had a CrCl < 30, 322 (28%) had a CrCl of 30-59 and 690 (61%) had a CrCl >60. Most pts (N=754, 67%) received novel agent induction (NAI) therapy. The median PCLI was 0.7 (range: 0 – 22) and 91 (21%) pts had high-risk cytogenetics by FISH. The median OS for the pts with CrCl at diagnosis of < 30, 30-59 and >60 were 41 mos, 60 mos and not reached respectively (P < 0.001).
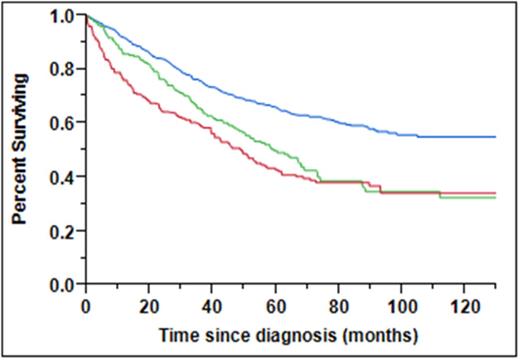
Of the 445 patients with RI, the median absolute creatinine and CrCl at diagnosis were 1.6 mg/dL (range: 1 – 11) and 44 (range: 4 – 59) respectively. Among pts with RI, any improvement in CrCl was seen in 295 (66%) with median time to highest CrCl of 5 months and 228 (51%) had complete reversal of their RI. The median OS for pts with RI at diagnosis receiving and not receiving NAI therapy was not reached (NR) vs. 46 mos (P < 0.001). The median OS for Groups 1, 2 and 3 were NR, 60 and 49 mos respectively (Figure 1 , P < 0.001). At a 6 month landmark analysis, the median OS for Groups 1, 2 and 3 were NR, 67 and 62 mos respectively (P < 0.001). The complete renal response and no renal response rates for pts with RI at diagnosis receiving and not receiving NAI induction therapy was (57% vs. 44%, P=0.004) and (29% vs. 39%, P=0.04) respectively. In a univariable analysis, presence of RI at diagnosis, no NAI therapy, older age, ISS stage 3, high-risk FISH, elevated PCLI, diagnosis prior to 2007 and increased LDH were found to predict for worse OS; however only older age (P<0.001), high-risk FISH (P=0.037) and lack of NAI therapy (P=0.023) retained their negative prognostic significance in a multivariable analysis.
Conclusion: MM pts with RI treated with novel agent induction therapy demonstrate improved responses in their renal function and OS. The results also demonstrate improved outcome for pts with improvement in renal function, but it remains inferior to pts with normal renal function at diagnosis. These results have implications for early treatment strategies for pts at risk of developing renal insufficiency.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.