Abstract
Introduction: Circularly permuted TRAIL (CPT), a recombinant mutant of human Apo2L/TRAIL, is a promising anti-tumor candidate. In previous phase1/2 clinical trials of single-agent CPT in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM), transient elevations of serum AST and LDH were observed early after CPT treatment in most response patients, but not in the non-respondent. Positive correlations were found between increased AST/LDH on day 2 or 3 (24 or 48 hours) after CPT initial dosing and the clinical responses to CPT.
Objective: To determine whether transiently elevated AST/LDH is predictive of responses to CPT plus thalidomide in thalidomide-relapsed or refractory MM patient and the time course of AST or LDH elevation.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of a phase 2 study of CPT plus thalidomide. The changes of serum AST, LDH or ALT were analyzed before treatment and on days 2, 3 and 6 after initial dosing. Relationship was evaluated between ΔAST, ΔLDH, ΔALT (ratio of ASTD2, LDHD2 or ALTD2to baseline value) and the best clinical responses. Four MM cell lines (RPMI 8226, NCI-H929, MM.1S, MM.1R) sensitive to CPT were used to detect the concentrations of AST, ALT and LDH in the cytoplasm or the medium of CPT-treated cells, with the purpose of determining whether CPT-induced cell death could result in an elevation of AST or LDH.
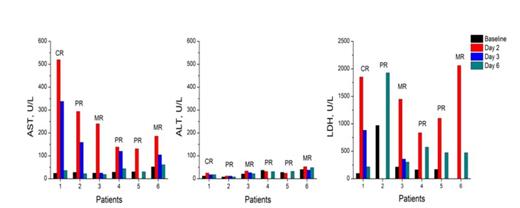
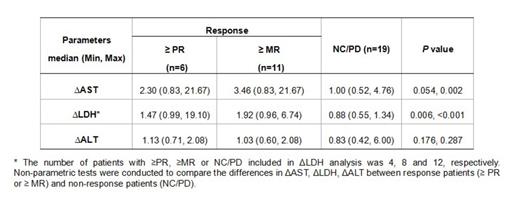
Results: Of 41 efficacy-evaluable patients, 9(22.0%) achieved a partial response (PR) or better and 14 (34.1%) achieved a minimal response (MR) or better. The serum ASTD2 and LDHD2 levels were dramatically increased from baseline in patients with ≥PR or ≥MR, but not in those with NC/PD. However, serum ALTD2 was comparable to baseline value either in response patients (≥PR or ≥MR) or in non-response ones (NC/PD). Consequently, the median ΔAST or ΔLDH of patients with ≥PR or ≥MR was significantly higher than that of patients with NC/PD (Table 1). The elevation of AST or LDH was transient with a peak on day 2 after treatment, then dramatically declined on day 3, and usually disappeared within one week (at most two weeks for LDH) (Figure 1), which was uniquely observed in the first treatment cycle. A univariate logistic-regression analysis showed that ΔASTwas predictive of achieving responses of ≥MR or not (P=0.04). Indeed, patients with higher level of ΔAST had higher probability of achieving responses of ≥MR (72.7% in patients with ΔAST>1.35 vs. 26.3% in patients with ΔAST≤1.35). In the cytoplasm of MM cell lines, abundant AST and LDH but only detectable level of ALT was observed. There was no significant change in the release rates of AST and LDH with CPT incubation for 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6 hours, even though the cell viabilities at 6h had already declined to about 10-20% of the control cells by ATP chemiluminescent assay. Remarkable increase in the release rates of AST and LDH occurred at 24h, with no evident change of ALT, which was consistent with what was observed in patients in the clinical study. It was suggested that the transient elevation of AST or LDH in RRMM patients was most likely resulted from CPT-induced myeloma cell death.
Conclusion: The early transient elevations of serum AST and LDH after CPT plus thalidomide treatment were positively correlated with the clinical responses to CPT plus thalidomide, and were possibly resulted from CPT-induced cell death. ΔAST on day2 could be a surrogate response biomarker for CPT treatment in RRMM patients.
Representative time course of AST, ALT or LDH changes before and after CPT plus thalidomide treatment in response patients
Representative time course of AST, ALT or LDH changes before and after CPT plus thalidomide treatment in response patients
Differences in ΔAST, ΔALT and ΔLDH between response patients (≥PR or ≥MR) and non-response patients (NC/PD)
Differences in ΔAST, ΔALT and ΔLDH between response patients (≥PR or ≥MR) and non-response patients (NC/PD)
Wei:Beijing Sunbio Biotech Co., Ltd.: Employment. Yang:Beijing Sunbio Biotech Co., Ltd.: Employment. Zheng:Beijing Sunbio Biotech Co., Ltd.: Employment. Pang:Beijing Sunbio Biotech Co., Ltd.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.