Abstract
Background. Patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) have a high risk of portal thrombosis. This problem leads to the disability of the patient without prompt treatment, or with resistance to conducted therapy.
The aim of this publication is to present own experience with antithrombin III, which subsequently will form the basis for the development of new treatment approaches for acute and subacute portal thrombosis resistant to therapy with anticoagulants (heparin, low molecular weight heparins (LMWH)) in patients with MPN.
Material and methods. At the outpatient department of National Hematology Research Center (Moscow) were observed 5 patients with MPN (3 patients with primary mielofibrosis, 2 essential thrombocythemia). Course of the disease was complicated by acute and subacute thrombosis of the portal system, resistant to treatment by anticoagulants. Antithrombin III was used for treatment of these patients in the outpatient department first time. Antithrombin III was administered regardless of the level of endogenous antithrombin III in combination with LMWH in therapeutic or prophylactic doses. The drug was used at a dose of 1,000 IU by intravenous bolus injections of 3-5 in 3 days (total dose rate of 3000-5000 IU).
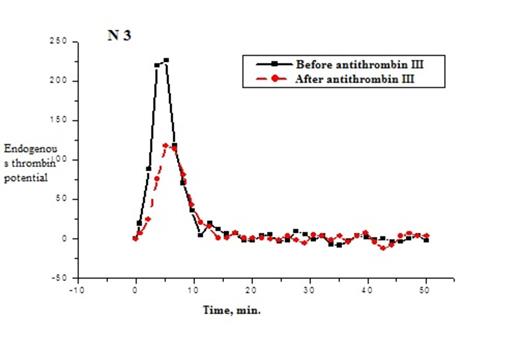
Results. Treatment was performed on an outpatient basis, the side effects were not observed. In all 5 cases, use of the antithrombin III in combination with LMWH observed positive clinical effect as a quick relief of pain, and early recanalization of the thrombosed vessels (from 3 weeks to 1.5-2 months) (Table 1). In all cases it was normalization of increase of endogenous antithrombin to normal values; it was observed positive changes in other parameters: the value of D-dimers, fibrinogene, XII-dependent fibrinolysis (Figure 1).
Conclusion. Antithrombin III therapy is indicated for the management of acute and subacute portal thrombosis in patients with MPN who are resistant to treatment with anticoagulants (heparin and LMWH). The advantage of the therapy is the possibility of therapy on an outpatient basis without the risk of side, including hemorrhagic complications.
Dynamics of clinical parameters in therapy with Antithrombin III.
| Patient . | Diagnosis. Clinical features. . | Localisation of thrombosis . | Preliminary treatment. Duration of the preliminary treatment . | Treatment with antithrombin III, 1000 IU. . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of injections . | Total dosage . | The efficiency. Duration of treatment . | ||||
| 1. L.T | PMF, JAK-2 - 31%. Thrombocytosis, leukocytosis. | The portal and superior mesenteric vein (complete occlusion). | Heparin, clopidogrel, aspirin. 2 weeks. | 3 | 3000 IU | Pain relief after the first injection. Complete recanalization of the portal and superior mesenteric veins in 3 weeks |
| 2. D.T. | PMF, JAK-2 - 83%. Ðistory of bleeding from the duodenal ulcer. | Occlusive thrombosis of the portal and splenic veins. | The patient received long-term antiplatelet therapy. | 5 | 5000 IU | Partial recanalization of the portal vein, complete recanalization of the splenic vein in 8 days. Complete recanalization of the portal vein in 4 weeks. |
| 3.V.T. | ET, Varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach grade 2-3. History of gastric bleeding. Splenectomy with secondary thrombocytosis. | Occlusive thrombosis of the main part and the left branch of the portal vein. | Heparin, LMWH, aspirin, clopidogrel. 1.5 months. | 5 | 5000 IU | Recanalization of the left branch of the portal vein in 10 days, partial recanalization of the portal vein in 1.5 months. |
| 4.Ts.I. | PMF, JAK-2 - 25%. History of radiation therapy of the spleen. | Thrombosis of the main part and the left branch of the portal vein, splenic vein. | Heparin, LMWH - 5 months with partial recanalization of the portal vein, the persistent pain. | 5 | 50000 IU | Pain was stopped in 2 weeks, recanalization of the left branch of the portal vein, the appearance of the blood flow in the hepatic portal vein in1 month. |
| 5. I.R. | ET, JAK-2 – 34%. Genetic thrombophilia - prothrombin gene mutation G20210A (het). Pregnancy 22-23 weeks | Hepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrom). Ascites, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. | Heparin LMWH - 2 months with reduction of ascites, no changes of thrombosis. | 3 | 3000 IU | Absence of pain and ascites, partial recanalization veins of the liver, a significant decrease liver and spleen size, a significant improvement in coagulation in 2 months. |
| Patient . | Diagnosis. Clinical features. . | Localisation of thrombosis . | Preliminary treatment. Duration of the preliminary treatment . | Treatment with antithrombin III, 1000 IU. . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of injections . | Total dosage . | The efficiency. Duration of treatment . | ||||
| 1. L.T | PMF, JAK-2 - 31%. Thrombocytosis, leukocytosis. | The portal and superior mesenteric vein (complete occlusion). | Heparin, clopidogrel, aspirin. 2 weeks. | 3 | 3000 IU | Pain relief after the first injection. Complete recanalization of the portal and superior mesenteric veins in 3 weeks |
| 2. D.T. | PMF, JAK-2 - 83%. Ðistory of bleeding from the duodenal ulcer. | Occlusive thrombosis of the portal and splenic veins. | The patient received long-term antiplatelet therapy. | 5 | 5000 IU | Partial recanalization of the portal vein, complete recanalization of the splenic vein in 8 days. Complete recanalization of the portal vein in 4 weeks. |
| 3.V.T. | ET, Varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach grade 2-3. History of gastric bleeding. Splenectomy with secondary thrombocytosis. | Occlusive thrombosis of the main part and the left branch of the portal vein. | Heparin, LMWH, aspirin, clopidogrel. 1.5 months. | 5 | 5000 IU | Recanalization of the left branch of the portal vein in 10 days, partial recanalization of the portal vein in 1.5 months. |
| 4.Ts.I. | PMF, JAK-2 - 25%. History of radiation therapy of the spleen. | Thrombosis of the main part and the left branch of the portal vein, splenic vein. | Heparin, LMWH - 5 months with partial recanalization of the portal vein, the persistent pain. | 5 | 50000 IU | Pain was stopped in 2 weeks, recanalization of the left branch of the portal vein, the appearance of the blood flow in the hepatic portal vein in1 month. |
| 5. I.R. | ET, JAK-2 – 34%. Genetic thrombophilia - prothrombin gene mutation G20210A (het). Pregnancy 22-23 weeks | Hepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrom). Ascites, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. | Heparin LMWH - 2 months with reduction of ascites, no changes of thrombosis. | 3 | 3000 IU | Absence of pain and ascites, partial recanalization veins of the liver, a significant decrease liver and spleen size, a significant improvement in coagulation in 2 months. |
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.