Abstract
Introduction: Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is an aggressive and incurable disease caused by human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) that infects CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes, but most commonly the malignant cell present a CD4+ phenotype. However, clonal expansion and cell cycle abnormalities have been demonstrated in CD4+ and in CD8+ lymphocytes of HTLV-1 carriers.
Objectives: This study compared DNA content and G0/G1, G2/M and “S”-phases of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes among asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers, ATLL and health subjects.
Methods: Werestudied 38 HTLV-1 carriers, 20 ATLL and 35 health subjects pared by sex and age at the Hematology Department of the Faculty of Medicine, University of São Paulo. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated on Ficoll-Paque® and lymphocytes subtypes were obtained by positive selection in a magnetic column. Cell-cycle distribution and DNA index (DI) was assessed by flow cytometry after propidium iodide staining.
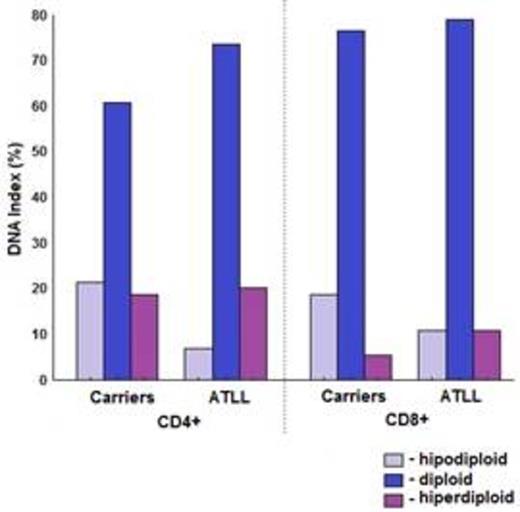
Results: In ATLL, themedian age was 53.5 years (24 to 72) and 50% were female, in HTLV-1 carriers was 55.5 years (33 to 80) with 63.2% of female and in control group was 50 years (24 to 80) with 54.3% of female. In the CD4+ lymphocyte a % of cells in G0/G1 (98.32%) in HTLV-1 carriers was higher than in control group (97.14%) (p=0.041) and in ATLL (97.25%) (p=0.023). S-phase was not statistically different in asymptomatic carriers (0.34%) and control group (0.63%) (p=0.073), but was higher in ATLL (1.80%) than in asymptomatic carriers (0.34%) (p<0.001) and in control group (0.63%) (p=0.02). G2/M-phase was not significantly different among all groups (p=0.960) (Table 1). The CD4+ lymphocytes were aneuploidy in 39.5% (18.4% DI > 1.05 and 21.5% < 0.95) of asymptomatic carriers and in 26.7% (20% > 1.05 and 6.7% < 0.95) of ATLL patients (p=0.557). All control groups were diploid.
Comparison of the cell cycle by flow cytometry of T lymphocytes CD4+
| . | CD4+ cells . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic carriers | ATLL | Control group | p-Value | |
| G0/G1 | ||||
| mean(dp) | 97.78 (2.182) | 95.69 (3.557) | 96.55 (2.964) | 0.035 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 97.03;98.32;99.64 | 91.40;97.25;98.32 | 95.01;97.14;98.64 | |
| G2/M | ||||
| mean(dp) | 1.55(1.848) | 1.91(2.798) | 2.03(2.902) | 0.96 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 0.00;0.88;2.67 | 0.12;0.99;1.99 | 0.00;0.56;2.97 | |
| S-phase | ||||
| mean(dp) | 0.68(1.207) | 2.80(3.372) | 1.43(1.780) | 0.003 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 0.00;0.34;0.65 | 0.65;1.80;3.51 | 0.04;0.63;2.55 | |
| . | CD4+ cells . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic carriers | ATLL | Control group | p-Value | |
| G0/G1 | ||||
| mean(dp) | 97.78 (2.182) | 95.69 (3.557) | 96.55 (2.964) | 0.035 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 97.03;98.32;99.64 | 91.40;97.25;98.32 | 95.01;97.14;98.64 | |
| G2/M | ||||
| mean(dp) | 1.55(1.848) | 1.91(2.798) | 2.03(2.902) | 0.96 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 0.00;0.88;2.67 | 0.12;0.99;1.99 | 0.00;0.56;2.97 | |
| S-phase | ||||
| mean(dp) | 0.68(1.207) | 2.80(3.372) | 1.43(1.780) | 0.003 |
| 1º; median;3ºq | 0.00;0.34;0.65 | 0.65;1.80;3.51 | 0.04;0.63;2.55 | |
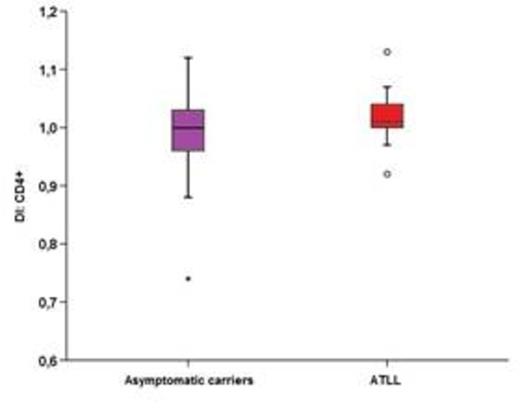
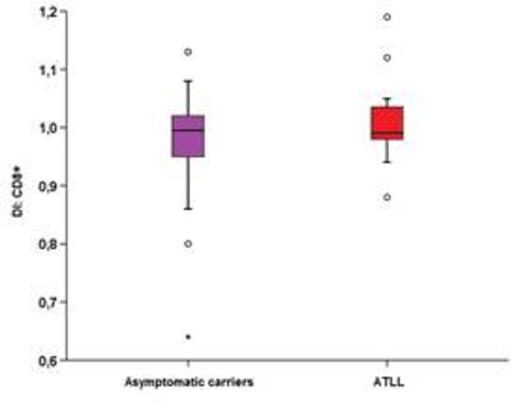
In CD8+ there was no found significantly difference in whole groups for G0/G1-phase (p=0.138) and G2/M-phase (p=0.374). ATLL presented higher S-phase (median 1.54%) than asymptomatic carriers (median 0.45%) (p=0.003) and control group. S-phase in asymptomatic carriers was not significantly different in comparison to control group (p=0.712). CD8+ were aneuploidy in 23.7% (5.3% DI > 1.05 and 18.4% < 0.95) of asymptomatic carriers and in 21% (10.5% > 1.05 and 10.5% < 0.95) of ATLL (p=0.603). In ATLL the median of DI was 1.01 (1.0; 1.05) in CD4+ and higher than in CD8+ median 0.99 (0.98; 1.0) (p=0.007). Aneuploidia was seen in 47.7% of ATLL, 26,7% (20% DI > 1.05 and 6,7% < 0.95) in CD4+ and 21,0% in CD8+ (10,5% > 1.05 and10,5% < 0.95) (p=0.625).
Dna index of CD4+ and CD8+. Aneuploidia was found in HTLV I carriers in both CD4+ and CD8+.
Dna index of CD4+ and CD8+. Aneuploidia was found in HTLV I carriers in both CD4+ and CD8+.
Comparison of DI between CD4+ and CD8+ of asymptomatic carriers and ATLL
Comparison of DI between CD4+ and CD8+ of asymptomatic carriers and ATLL
Conclusion:
We demonstrated for the first time “in vivo” that asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers display cell cycle arrest in G0/G1-phase in CD4+ lymphocytes and high rate of aneuploidia in both CD4+ and CD8+. ATLL showed high rate of hiperdiploidia in CD4+ and hipodiploidia in CD8+ and high rate of S-phase in CD4+. Genetic instability and proliferative disturbs are a hallmark not only in ATLL but also in HTLV-1 carriers and in both CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.