Abstract
This report is a retrospective analysis of patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP-21. The aim of the study was to determine the impact of peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte count (ALC), Ki67 proliferation index and immunohistochemical expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-6 at diagnosis on complete response rate and survival.
The study group consisted of 161 patients with stage II-IV who were treated with six cycles of R-CHOP-21 between January 2004 and December 2013. With International Prognostic Index (IPI), 29% patients were low, 29% low-intermediate, 25% high-intermediate and 17% high risk. Bcl-2 and Bcl-6 expression was detected with immunohistochemical staining on paraffin sections in 83% and 77% of patients, respectively. Bcl-2 expression with high Ki67 proliferation index, greater than 80%, was found in 15% of patients. BcL-6 expression with Ki67 index of 80% or lower was detected in 52% of patients. Median ALC at diagnosis was 1.4 G/L (0.1-4.2). ALC below 1.0 G/L was revealed in 27% patients.
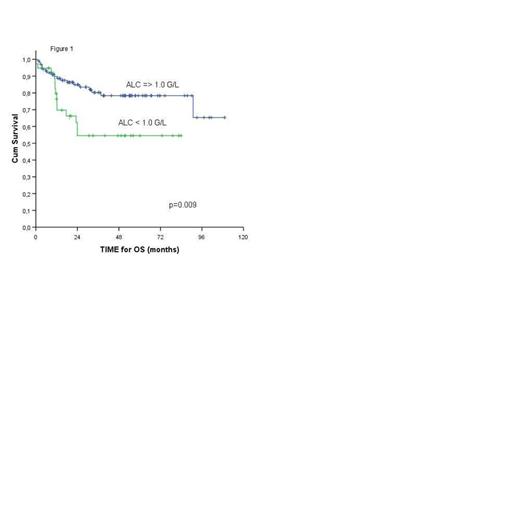
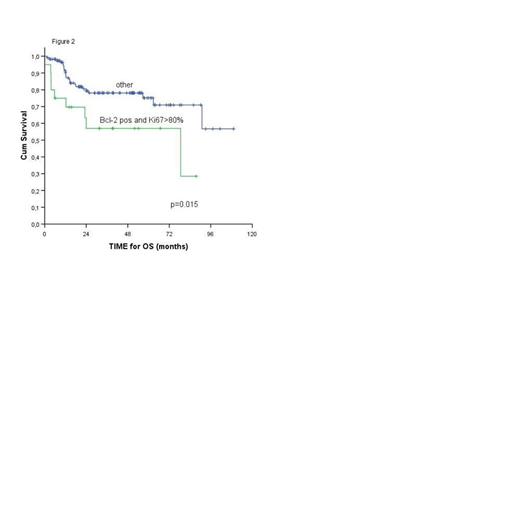
Results: The complete response rate to R-CHOP was 69%. In univariate logistic regression for complete response to immunochemotherapy, the variables that were correlated with lower response rate were IPI > 2 (p=0.016) and ALC < 1.0 G/L (p=0.014). In multivariate logistic regression, ALC < 1.0 G/L remained the only independent variable associated with failure to achieve complete response (OR 2.6; 95%CI 1.2-5.9; p=0.03). After the median follow-up time of 37 months (6-109), the 5-year progression free and overall survival (OS) estimated with Kaplan-Meier method were 67% (95% CI 56-76) and 66% (95% CI 55-75), respectively. In univariate analysis IPI (log-rank test, p=0.001), ALC (log-rank test, p=0.009) (fig.1), Bcl-2 expression with high Ki67 index (log-rank test, p=0.015) (fig.2) and Bcl-6 expression with low Ki67 index (log-rank test, p=0.05) were statistically significant for OS. In the multivariate analysis with Cox model, ALC at diagnosis (HR 2.9; 95%CI 1.1-7.3; p=0.024) and Bcl-2 expression with high Ki67 index (HR 2.8; 95%CI 1.1-7.5; p=0.039) remained significant for OS. IPI higher than 2 tended to impact negatively OS (HR 2.4; 95%CI 0.9-6.3; p=0.067).
In conclusion, our results indicate that low ALC at diagnosis is independent predictor of poor response to R-CHOP for patients with DLBCL. In addition, low ALC and Bcl-2 expression with high Ki67 index adversely influence patient survival in the rituximab era.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.